Why ASRT CE Approval Matters for Your Educational Programs
ASRT CE approval is the process by which the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT) reviews and authorizes continuing education activities for radiologic technologists. This approval ensures that courses meet the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) standards and qualify as Category A or A+ credit toward the mandatory 24 CE credits required every biennium.
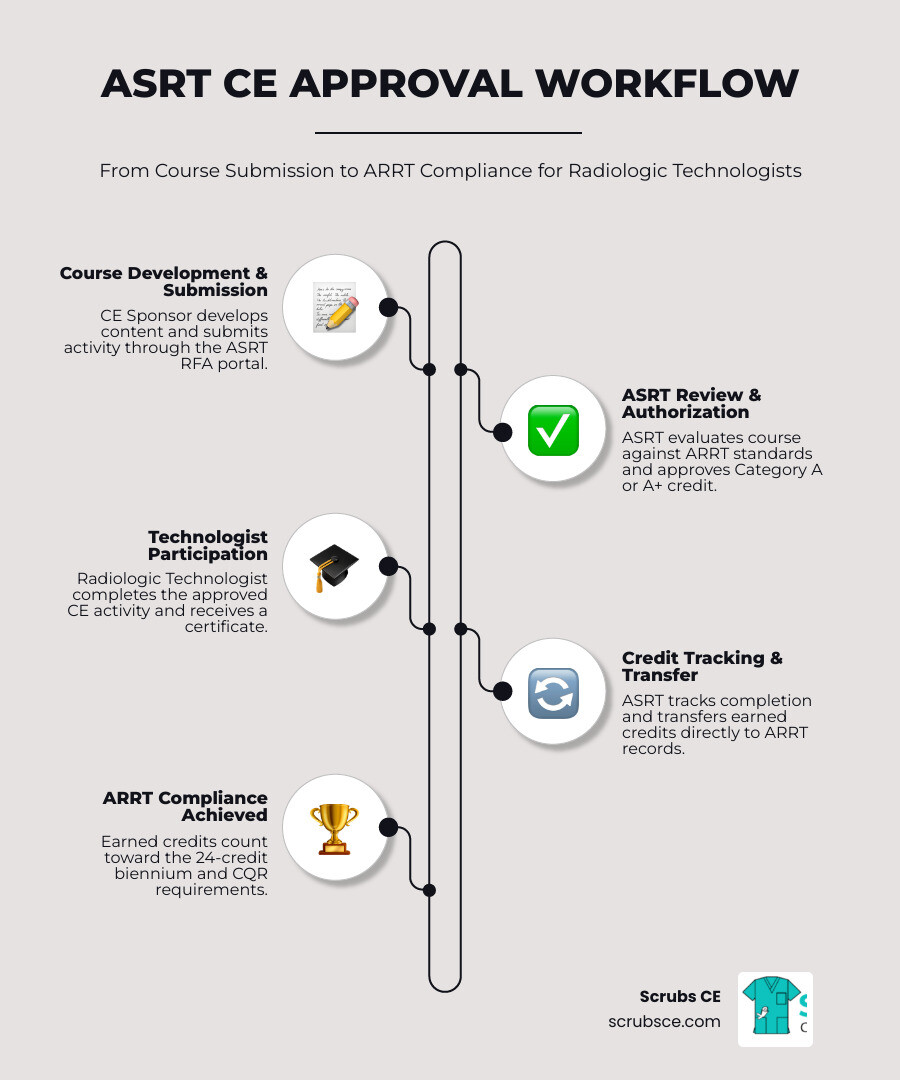
Quick Overview: The ASRT CE Approval Process
- Prepare Your Materials – Gather objectives, speaker credentials, content, and post-tests
- Submit Through the RFA Portal – Use ASRT’s electronic system to request approval
- Await Review – ASRT evaluates your activity against ARRT standards
- Receive Approval – Get your reference number and credit designation (Category A or A+)
- Issue Certificates – Provide participants with documentation containing required elements
If you’re a CE sponsor looking to serve radiologic technologists, understanding the ASRT approval process is essential. Without it, your courses won’t qualify for the credits R.T.s need to maintain their ARRT certification.
The ASRT is a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM) by the ARRT. This means activities approved by the ASRT automatically meet ARRT’s standards and can be counted toward the 24 CE credits technologists must earn every two years. The ASRT also tracks and transfers these credits directly to the ARRT, making life easier for both sponsors and technologists.
But getting ASRT approval isn’t automatic. The process has specific requirements for different activity formats—whether you’re offering live lectures, online courses, webinars, or hands-on training. Your content must meet depth and scope standards, your post-tests must follow specific guidelines, and your certificates must include mandatory information.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know about ASRT CE approval. You’ll learn what materials to prepare, how to submit your request, what happens after approval, and the specific requirements for different types of educational activities.
I’m Zita Ewert, and I’ve spent years helping CE providers steer the ASRT CE approval process to deliver quality education to imaging professionals. My experience guiding sponsors through approval requirements has shown me which steps cause the most confusion and how to streamline the process for faster approval.
Understanding the ASRT CE Approval Landscape
The landscape of continuing education for Radiology professionals can seem complex, but at its heart is the crucial role of the ASRT. As a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM), the ASRT acts as a gold standard for approving CE activities. This means that when an activity receives ASRT CE approval, it’s automatically recognized by the ARRT as meeting their rigorous standards for Category A or A+ credit. This recognition is vital for radiologic technologists who need to earn 24 CE credits every two years to maintain their certification, a period known as a biennium. It’s also integral to the ARRT’s Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR) process, ensuring professionals stay current with evolving practices. For a more in-depth look at these requirements, check out our ASRT CE Requirements Complete Guide.
Why ASRT Approval is Crucial for CE Sponsors
For any organization or individual offering continuing education to radiologic technologists, ASRT CE approval is not just a badge of honor; it’s a necessity. Here’s why:
- Importance of Approval: Without ASRT approval, your courses will not count towards the mandatory CE credits required by the ARRT. This severely limits your market reach, as technologists primarily seek out approved activities.
- Credibility and Market Access: ASRT approval lends instant credibility to your educational programs. Technologists trust ASRT-approved courses to be high-quality, relevant, and compliant with professional standards. This trust opens doors to a wider audience of dedicated professionals.
- Technologist Trust: R.T.s rely on ASRT to vet CE activities. When they see that coveted approval, they know the course content is robust and directly applicable to their practice, ensuring they meet their ARRT’s 24-credit biennium requirement with confidence.
- Supporting the CQR Process: The ARRT’s Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR) are designed to ensure technologists maintain competence throughout their careers. Many ASRT-approved activities can directly fulfill the CE prescriptions identified through the CQR process. Understanding this connection is key for sponsors. For more details on CQR, refer to our guide: What You Need to Know About ARRT’s Structured Education Solutions and Requirements.
Key Roles in the CE Ecosystem: Approvers, Trackers, and Transferors
To truly understand ASRT CE approval, it’s helpful to differentiate between the various roles within the continuing education ecosystem:
- CE Approver Definition: A CE Approver, like the ASRT, reviews CE activities and determines if they meet ARRT requirements, assigning a credit value (e.g., Category A or A+). Organizations seeking to become ARRT CE Approvers must be national in scope, not-for-profit, and Radiology/medical imaging-based.
- CE Tracker Definition: A CE Tracker verifies the completion of CE activities and maintains records of the credits technologists earn. The ASRT acts as a full-service record keeper for its members.
- CE Transferor Definition: A CE Transferor electronically submits technologists’ completed CE records to the ARRT. The ASRT efficiently transfers credits for its members to the ARRT and other regulatory bodies, often automatically if member profiles are up-to-date.
The ASRT proudly serves as a CE Approver, CE Tracker, and CE Transferor, streamlining the entire process for its members. This integrated approach makes meeting CE requirements significantly easier for radiologic technologists. You can find a comprehensive list of ARRT-recognized CE partners and their roles on the ARRT website.
Category A vs. Category A+ Credit Explained
Understanding the distinction between Category A and Category A+ credit is fundamental for both CE sponsors and technologists:
- Category A Requirements: This is the standard credit type for most radiologic technologists. Category A activities are those evaluated and approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM), such as the ASRT. All 24 credits required by the ARRT for biennial renewal must be Category A or A+ credit. These activities have broad applicability, covering general topics relevant to the practice of Radiology.
- Category A+ Criteria: Category A+ credit is a specialized designation primarily for Registered Radiologist Assistants (R.R.A.s). To qualify for Category A+ status, CE materials must be directly related to one or more clinical activities outlined in the R.R.A. role delineation. While specifically custom for R.R.A.s, any R.T. can complete Category A+ activities to satisfy their required CE credits each biennium.
When submitting an activity for ASRT CE approval, sponsors will indicate whether the content is designed for Category A or Category A+ credit, ensuring appropriate evaluation and designation.
The Step-by-Step Guide to Gaining ASRT CE Approval
Navigating the ASRT CE approval process can seem daunting, but we’re here to break it down. This section provides a clear roadmap for sponsors seeking approval, ensuring your educational programs are recognized and valued by radiologic technologists.
Step 1: Preparing Your Submission Materials
Thorough preparation is key to a smooth approval process. Before you even touch the submission portal, ensure you have all necessary documentation and content ready:
- Actionable Learning Objectives: These are critical. Each activity must have clearly defined, measurable learning objectives that describe what the participant will be able to do after completing the activity. For example, “After completing this activity, the participant will be able to display proper collimation techniques when performing a pediatric abdomen exam.” These objectives should align with the ARRT task inventories where applicable, especially for psychomotor components.
- Speaker Information: For live lectures or presentations, you must provide the full name, credentials, email address, and place of employment for each speaker.
- Detailed Program Agenda: If your lecture or activity is longer than two hours, a detailed agenda or schedule is mandatory. This must include start and end times for each segment, breaks, meals (if applicable), and dedicated time for interactive exercises or Q&A.
- Course Content: Depending on the format, this could be the full text of a self-learning module, a detailed outline of a live lecture, a video script, or access to the recorded presentation. All images, charts, diagrams, tables, and text must be legible and correctly labeled. Ensure all acronyms are spelled out on first use or provide a glossary.
- Post-Test and Answer Key: For self-learning activities, a comprehensive post-test is required. This must include all test bank questions and answers, along with an answer key that indicates where the answers can be found within the course content. We’ll dig deeper into post-test requirements later.
- Supporting Documentation: Any reprinted material must have permission from the original source. For academic courses, you’ll need the course syllabus and official transcript showing a grade of ‘C’ or better.
For a comprehensive understanding of what the ARRT expects, we strongly recommend reviewing the ARRT Education Requirements.
Step 2: Navigating the Electronic Submission Process
Once your materials are carefully prepared, it’s time to submit your request for ASRT CE approval. The ASRT uses an efficient electronic process:
- ASRT’s RFA Portal: All submissions are made through the ASRT’s Request for Approval (RFA) portal. This online system is designed to streamline the application process.
- Creating a Sponsor Account: If you’re a new sponsor, you’ll need to create an account first. Existing customers can simply log in.
- Submitting New Activities: The portal guides you through inputting all the information gathered in Step 1. You’ll specify the activity type (live lecture, self-learning, etc.) and whether you’re seeking Category A or A+ credit.
- Renewing Previously Approved Activities: If you have an activity that was previously approved, the portal allows you to access and renew it, often requiring updates to content or speaker information.
- Fees: Effective August 1, 2024, ASRT has updated its pricing structure for self-learning CE approval, introducing new tiers for 16- and 24-credit activities. It’s important to check the current fee schedule on the ASRT website.
For those also working with ARRT directly, you might find their CE Sponsor Suite useful for managing various aspects of CE.
Step 3: Post-Approval Responsibilities and Certificate Requirements
Congratulations! Your activity has received ASRT CE approval. Now, your responsibility shifts to properly documenting participant completion and adhering to certificate requirements.
- Mandatory Certificate Elements: A CE certificate is a crucial document for technologists. It must contain the following information for each activity:
- Sponsor’s name
- Participant’s full name and ASRT ID number or ARRT ID Number
- Title for each activity attended (individual lecture titles, not just overall conference details)
- Credit amount earned for each activity (e.g., 1.0 Category A)
- Reference number for each activity
- The date the activity was attended or completed
- Signature of the instructor or authorized representative of the sponsor
- Name of the group or organization that awarded the approval (e.g., ASRT)
- Credit Category A or A+ designation
- Course expiration date
- Attendance Verification Methods: For live activities, robust attendance verification is non-negotiable. We’ll explore specific methods in the next section, but generally, this involves sign-in sheets for groups or login/logout data for individuals.
- Documentation Retention: Sponsors must maintain attendance documentation for five years.
- Certificate Integrity: Certificates must be issued only after successful completion. They should be designed so that participants cannot alter them. Altered certificates (e.g., with white-out) are not accepted by ASRT for tracking. If changes are needed, the sponsor must issue a new certificate.
Specific Guidelines for Different CE Activity Formats
This section breaks down the unique requirements for various types of educational activities to ensure your program meets ASRT standards. It’s not a one-size-fits-all process; each format has its nuances for ASRT CE approval.
Live Lectures, Webinars, and Web Conferencing
Live educational experiences remain a popular way for technologists to earn credits. Here’s what you need to know for ASRT CE approval:
- Credit Calculation (Contact Hour): CE credit is primarily based on contact hours. One CE credit typically equals 50-60 minutes of instruction. The ASRT has precise calculations:
- 15-29 minutes = 0.25 credit
- 30-49 minutes = 0.5 credit
- 50-62 minutes = 1.0 credit
- And so on, rounding down total minutes not equally divisible by 50 to the nearest quarter credit. Activities less than 15 minutes are not awarded credit.
- Attendance Monitoring: Verifying attendance is paramount.
- Group Viewing: For groups watching a webinar together, a sign-in sheet is required, along with a designated site monitor to confirm participation.
- Individual Viewing: For individuals, attendees must register, and the coordinator records login/logout data. Additionally, one of the following is needed: a post-broadcast quiz, a survey, engagement data (e.g., polling responses), or visual monitoring.
- Lectures by Student Technologists: These are not typically approved for CE credit.
- Lectures During Meals: The ASRT discourages scheduling educational sessions during meals. Time for meals should be completed before or after CE activities.
- Backup Lectures: These can be submitted for approval, provided they meet all other criteria.
- Handling Panel Discussions and Q&A Sessions: Time spent in moderated panel discussions and structured Q&A sessions, where educational content is exchanged, can count toward credit. However, unstructured, informal discussions generally do not.
For more information on various CE options, explore our Radiologic Technologist CE Complete Guide.
Self-Learning Activities (Online Courses and Directed Readings)
Self-learning activities, including online courses and Directed Readings, offer flexibility and are a cornerstone of modern CE. Here’s what’s required for their ASRT CE approval:
- Post-Test Guidelines: A robust post-test is mandatory to assess learning.
- Passing Score: Participants must achieve a minimum passing score of 75%.
- Attempts: A maximum of three attempts is allowed.
- Question Quantity: The number of questions required depends on the credit amount. For text-based self-learning, it’s generally 8 post-test questions per credit. For video/audio, it varies, for example, 0.25 credit requires 2 questions, 0.5 credit requires 4 questions, and 3 credits require 24 questions.
- Question Quality: All test bank questions and answers must be provided, along with an answer key indicating where answers are located in the content. Questions should be distinct from interactive questions embedded in the content. At least 60% of questions should be multiple-choice.
- Interactive Testing Requirements: Self-learning activities must incorporate interactive elements. For video/audio content, a maximum of two interactive activities per 15 minutes of viewing time is recommended. These interactive questions should offer remediation for incorrect responses.
- Credit Calculation for Text-Based vs. Video/Audio:
- Text-Based: Credit is determined by word count. For example, 1,600 words typically earn 0.25 credit, and 49,300 words can earn 10.0 credits. This calculation excludes things like table of contents, references, and appendices.
- Video/Audio: Credit is determined by viewing/listening time. For instance, 12-17 minutes yield 0.25 credit, while 150-162 minutes can yield 4.25 credits.
- Textbook/E-book Chapter Activities: As of August 31, 2022, ASRT no longer reviews or renews textbooks, textbook chapters, eBooks, or any published text-based materials for CE approval.
For a comprehensive guide to online CE, check out our Continuing Education Credits Online Guide.
Hands-On Training, Simulations, and Equipment Training
Hands-on and practical training activities are invaluable for skill development. Here’s how they are evaluated for ASRT CE approval:
- Psychomotor Component Guidelines: Activities with a “hands-on” or psychomotor component are approved when they align with ARRT task inventories and have clear, actionable learning objectives. These components must be directly supervised or evaluated.
- Credit Caps for On-Site Training (‘F’ Designation): For on-site (facility) applications training, the ARRT caps credit at 8 CE credits per biennium. These activities are designated with an ‘F’ in their reference number. This cap, effective January 1, 2011, applies to training conducted at the technologist’s primary facility.
- Corporate Training (‘C’ Designation): Online, webinar, and corporate facility training (not at the technologist’s primary facility) are not affected by the 8 CE credit cap. These are designated with a ‘C’ in their reference number.
- Eligible Components: Credit is awarded for lecture portions, instructor-led demonstrations, and actual hands-on practice. It is not awarded for time spent reviewing manuals or performing patient scanning (which is considered clinical practice).
- Tumor Boards/Case Reviews: These can be approved as one-time presentations, provided an outline, case descriptions, and moderator/presenter credentials are submitted. Patient identifying information must be strictly avoided.
For more insights into various CE formats, including practical training, see our Rad Tech CE FAQ Guide.
Frequently Asked Questions about the ASRT Approval Process
We know that navigating the intricacies of ASRT CE approval can lead to many questions. Here, we address some of the most common inquiries CE sponsors have about getting their continuing education activities approved by the ASRT.
What topics are not approved for ASRT CE approval?
Not all educational content is eligible for ASRT CE approval. The ASRT maintains strict guidelines to ensure relevance and professional development for radiologic technologists. Topics generally deemed ineligible include:
- Content Not Aligning with ASRT’s Mission: Activities that do not improve the knowledge and skills underlying the professional performance of radiologic technologists.
- General CE Requirements: Topics considered basic job responsibilities, like basic CPR (BLS) completed after January 1, 2007 (though ACLS and PALS can earn up to 6 CE credits per biennium).
- Personal Finance: Courses on wealth management, investment strategies, or personal budgeting.
- General Computer Programming: While medical informatics is approved, generic coding or software development unrelated to medical imaging is not.
- Topics Lacking Sufficient Depth or Scope: Activities that are too brief, superficial, or do not provide substantial educational value.
- Non-Radiologic Sciences: Subjects like digital photography (unrelated to medical imaging), airport security, art, general explorations in movement, drumming, yoga, Tai Chi, massage, and therapeutic touch.
- Routine Operational Activities: Department meetings, chart rounds, journal clubs, poster sessions, tours, viewing exhibits, or employer-specific policy courses are not approved.
How does ASRT handle state-specific CE requirements?
The ASRT understands that many states have their own licensing requirements in addition to ARRT certification. While ASRT CE approval is widely recognized, some states have unique stipulations:
- California Requirements (X-ray Application Focus): The California Department of Health Services radiologic technology regulations require CE credits to be earned in “subjects related to the application of x-ray to the human body.” This means that while ASRT-approved activities are generally accepted, subjects in MRI and ultrasound are typically not accepted for California CE credit, as they are not related to x-ray application. Sponsors should be aware of this distinction if targeting a California audience.
- Florida Credit Transfer Process: The ASRT facilitates automatic credit transfer to the Florida Department of Health for members with a Florida state license or address. This transfer occurs on the 10th of each month, with credits typically reflected on the FLDOH website by the 15th. The Florida Department of Health does not accept the transfer of 0.25 or 0.75 credit CE activities. For more, visit the Florida Department of Health – Bureau of Radiation Control website.
- Texas “Direct” vs. “Indirect” Credit Designation: For Texas licensure CE requirements, some ASRT CE certificates may include “DIRECT” or “INDIRECT” in activity titles. This distinction indicates whether the course is directly related to the use of ionizing radiation. Sponsors should be aware of these designations if their activities are relevant to Texas licensees.
The ASRT also tracks and transfers credits to other certification bodies like the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS), Medical Dosimetrist Certification Board (MDCB), and Nuclear Medicine Technology Certification Board (NMTCB) for members whose profiles are up-to-date with the necessary identification numbers.
What happens if my ASRT CE approval request is denied?
While we strive for successful submissions, sometimes an ASRT CE approval request may be denied or withdrawn. Understanding the common reasons can help you avoid them:
- Common Reasons for Denial:
- Outdated Content: Information that is no longer current or relevant to modern practice.
- Factual Errors: Inaccuracies in the educational material.
- Non-compliance with Format Guidelines: Failure to meet specific requirements for post-tests, learning objectives, agenda details, or attendance verification.
- Lack of Depth or Scope: The activity does not provide sufficient educational value to improve professional knowledge and skills.
- Ineligible Topic: The content falls outside the approved subject areas for radiologic technologists.
- The Appeals Process: If your request is denied, the ASRT typically provides feedback explaining the reasons. You may have the opportunity to revise and resubmit your activity based on this feedback. It’s crucial to carefully review the feedback and make the necessary adjustments to align with ASRT standards. ASRT’s goal is to ensure quality education, so they often work with sponsors to help them meet approval criteria.
Conclusion: Lift Your CE Program with ASRT Approval
Gaining ASRT CE approval is more than just a procedural step; it’s a strategic move that significantly improves the value and reach of your continuing education programs. ASRT approval signifies quality and relevance, making your CE activities highly valuable to radiologic technologists across the nation. It assures them that your courses meet the rigorous standards set by the ARRT and contribute directly to their professional compliance.
By adhering to the ASRT’s comprehensive guidelines for submission, content, and certificate issuance, you streamline the process for R.T.s to meet their ARRT, CQR, and state licensure requirements. This not only builds trust and credibility for your organization but also plays a vital role in fostering a well-educated and competent workforce in medical imaging and Radiation Therapy.
At Scrubs CE, we understand the importance of seamless and high-quality continuing education. That’s why we carefully ensure our courses meet these stringent standards, offering convenient, affordable online options that are fully ASRT-approved. We provide high-quality, self-paced courses with instant certificates to help professionals meet licensure requirements and advance their careers.
Explore our extensive catalog of Radiology Continuing Education for the ARRT Biennium and empower radiologic technologists with the education they need to excel.



Recent Comments