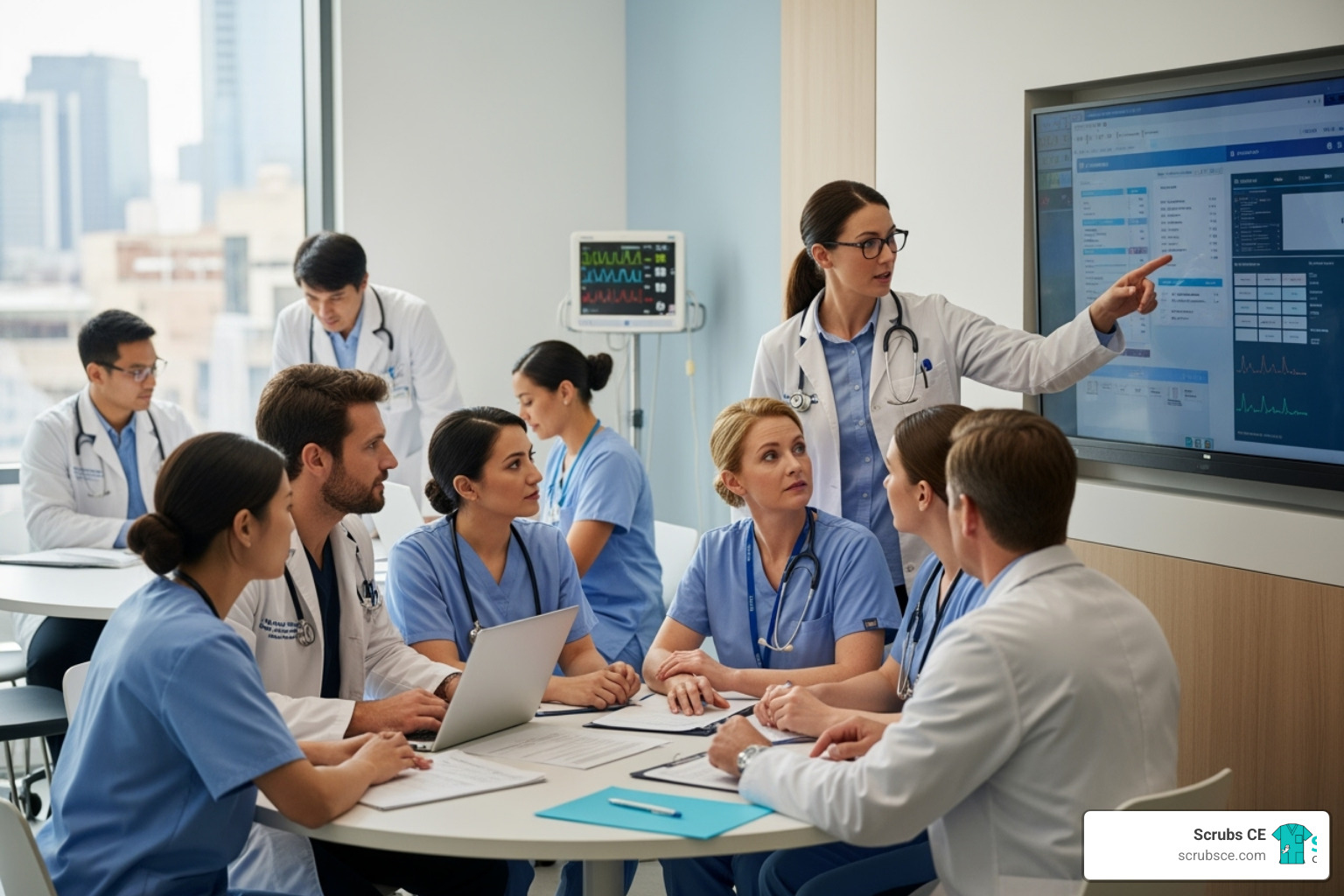
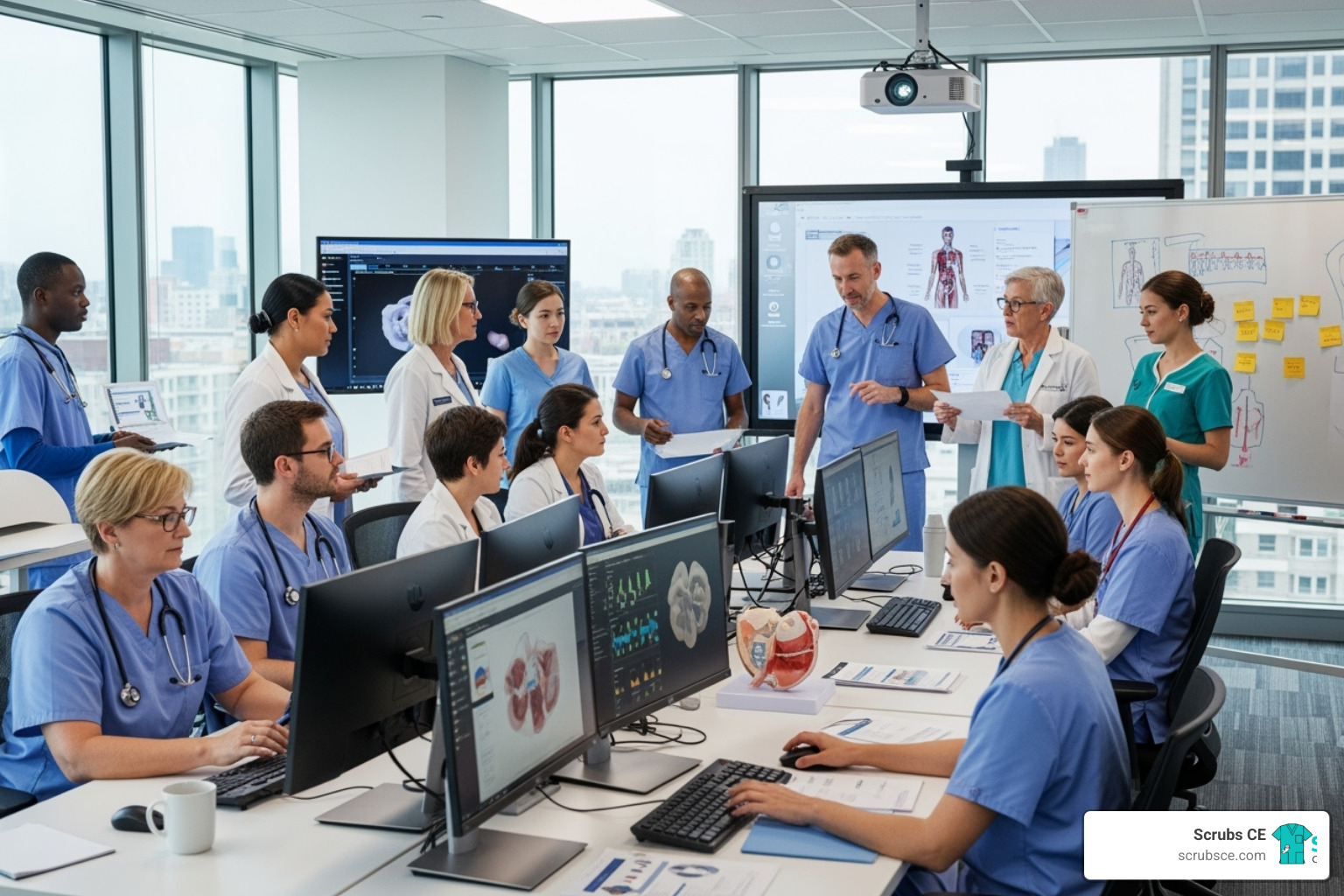
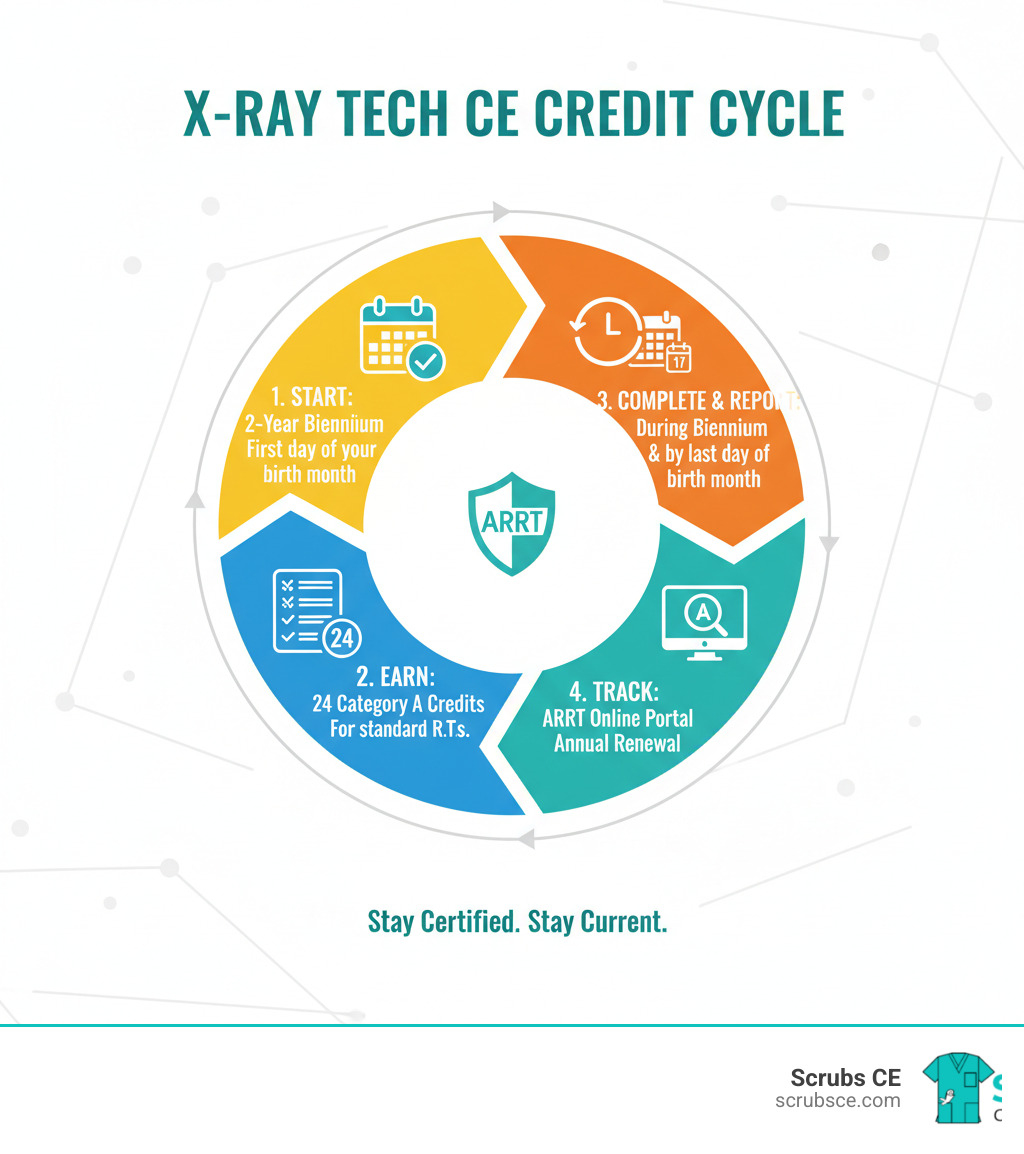
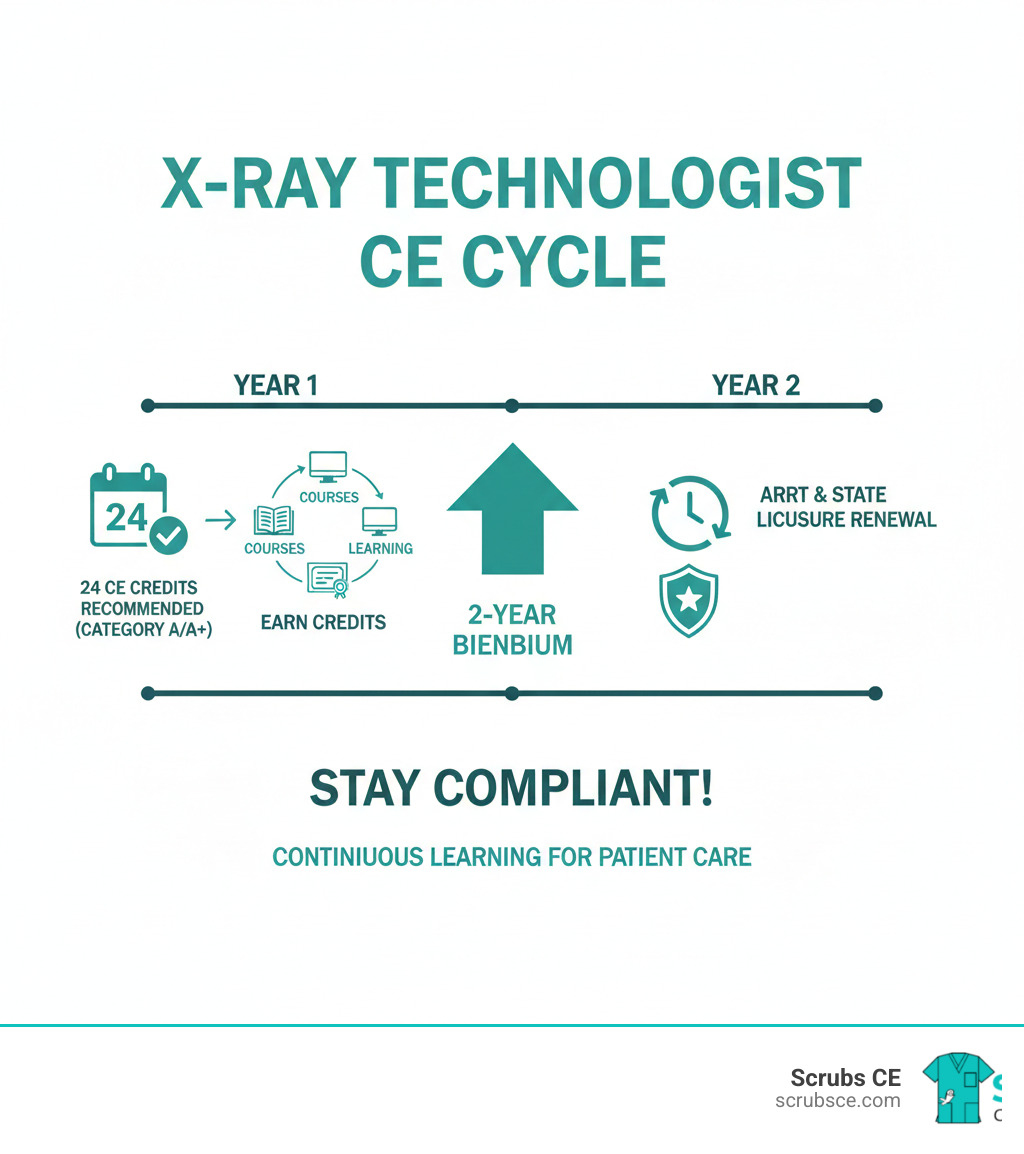
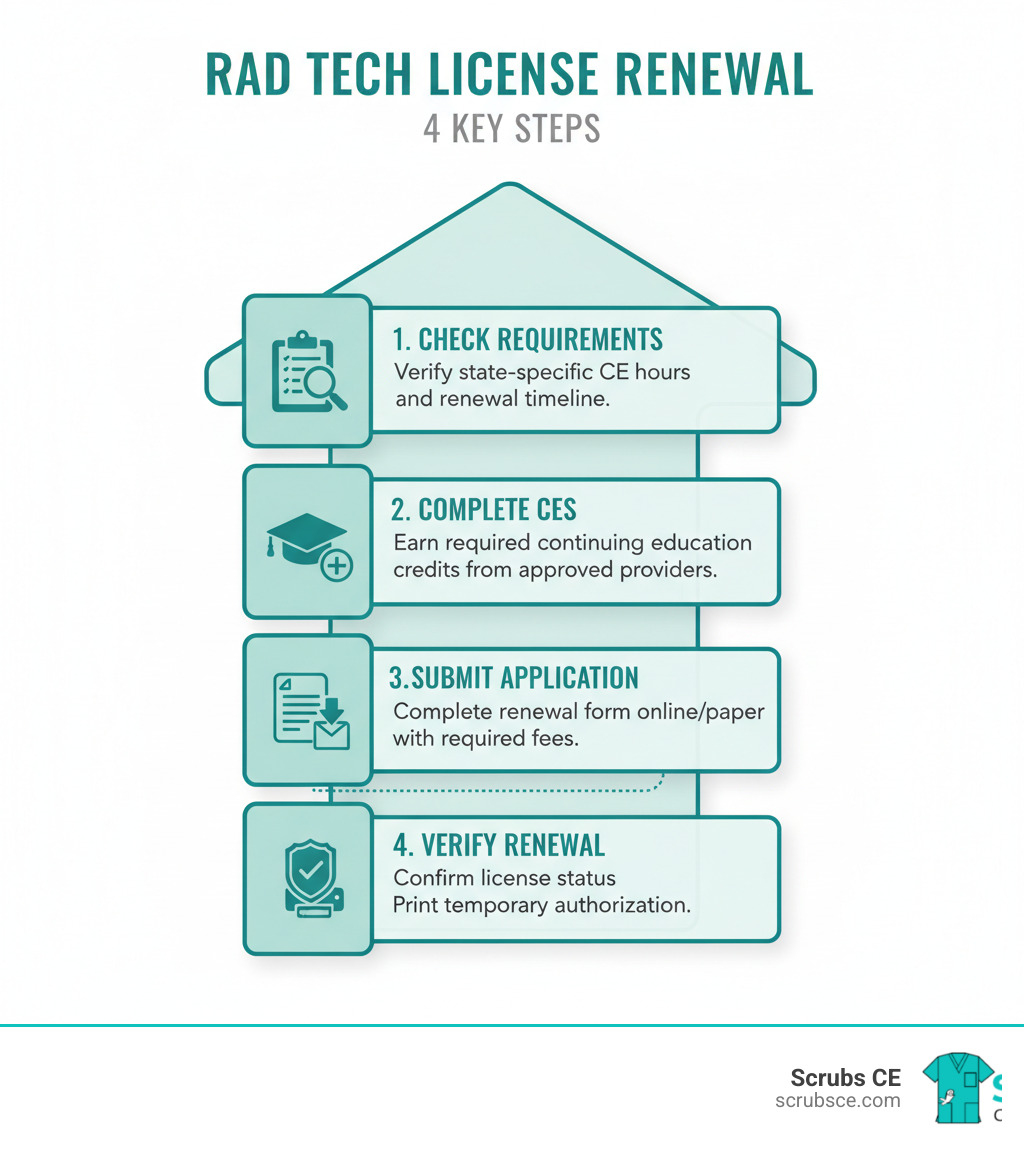
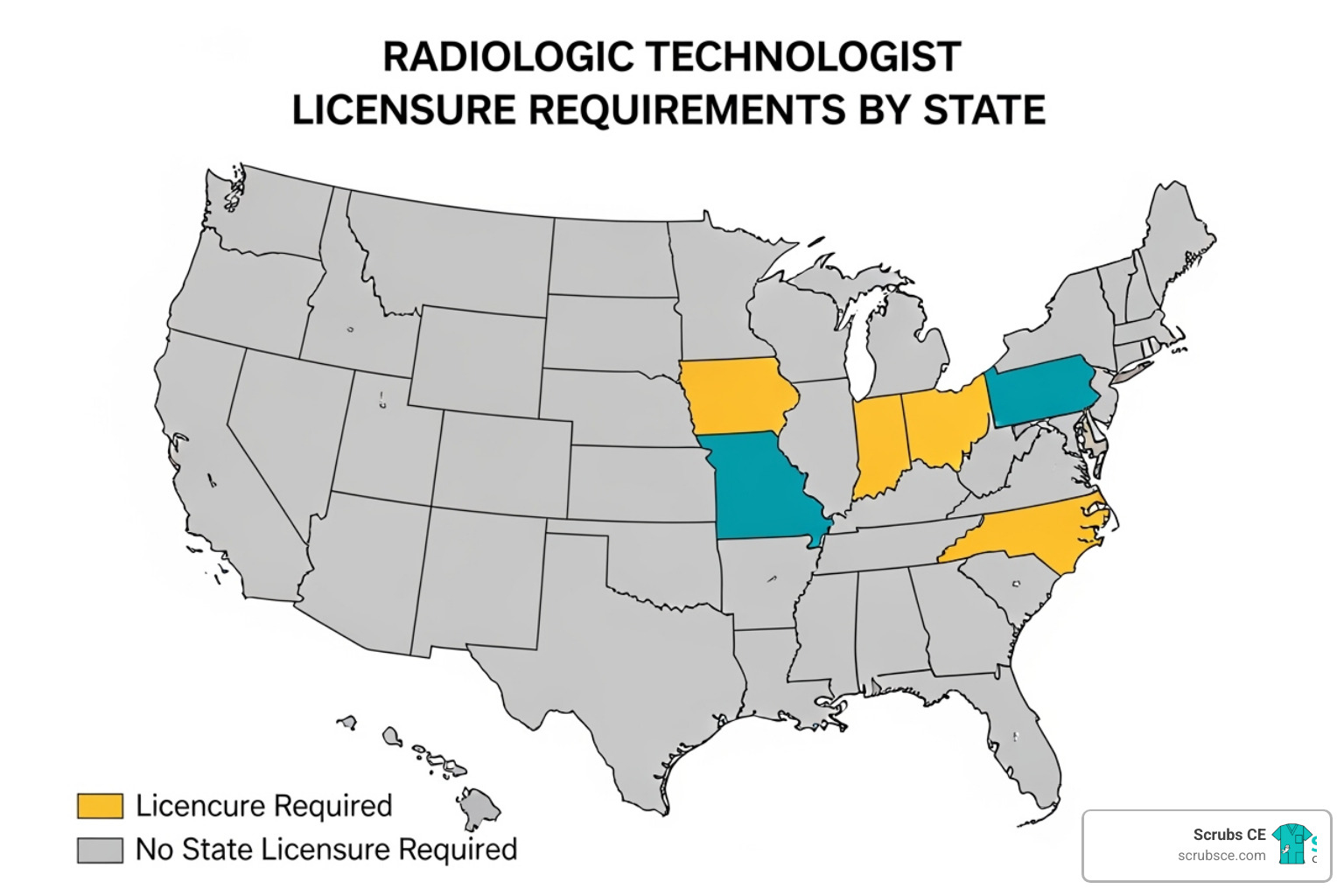
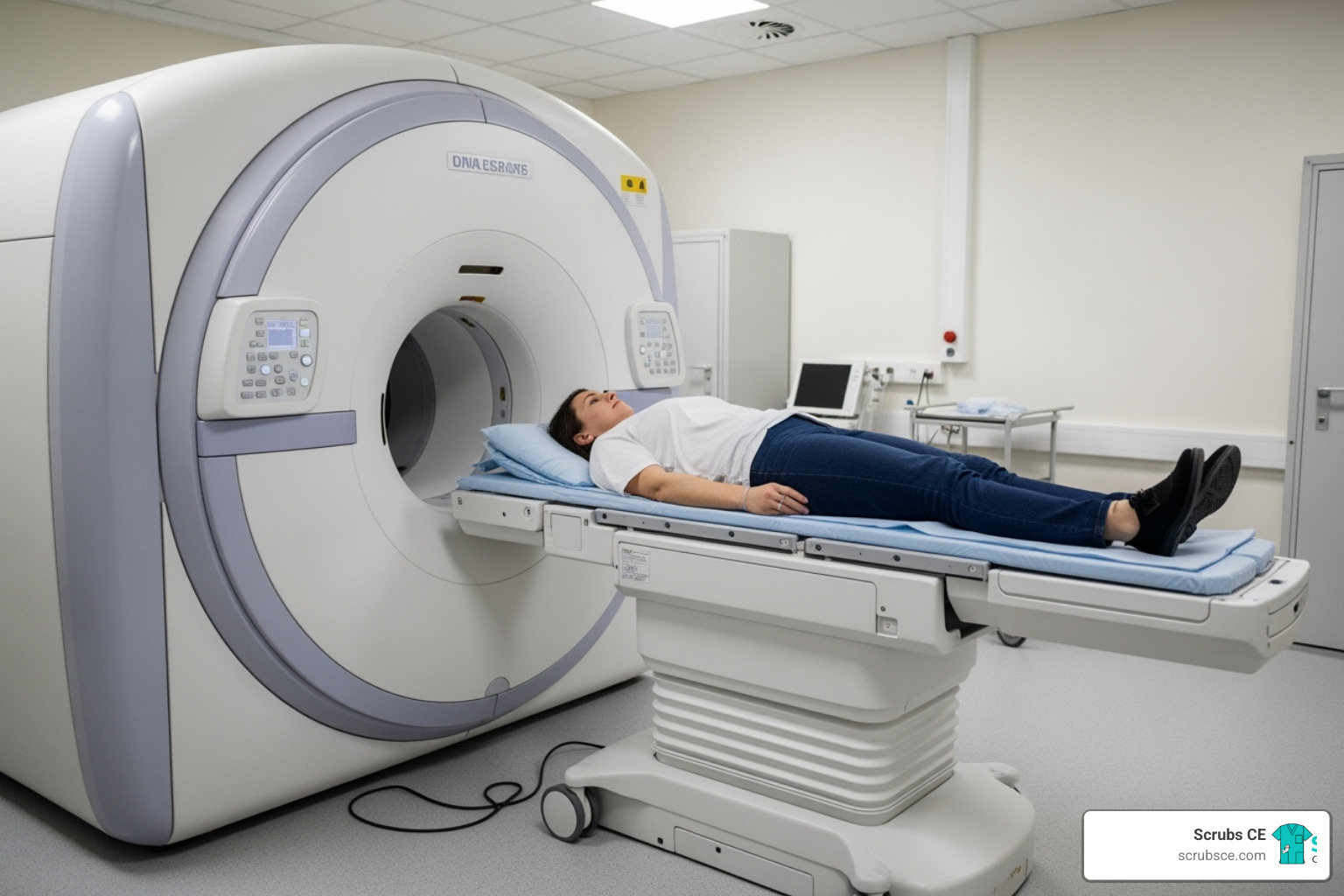
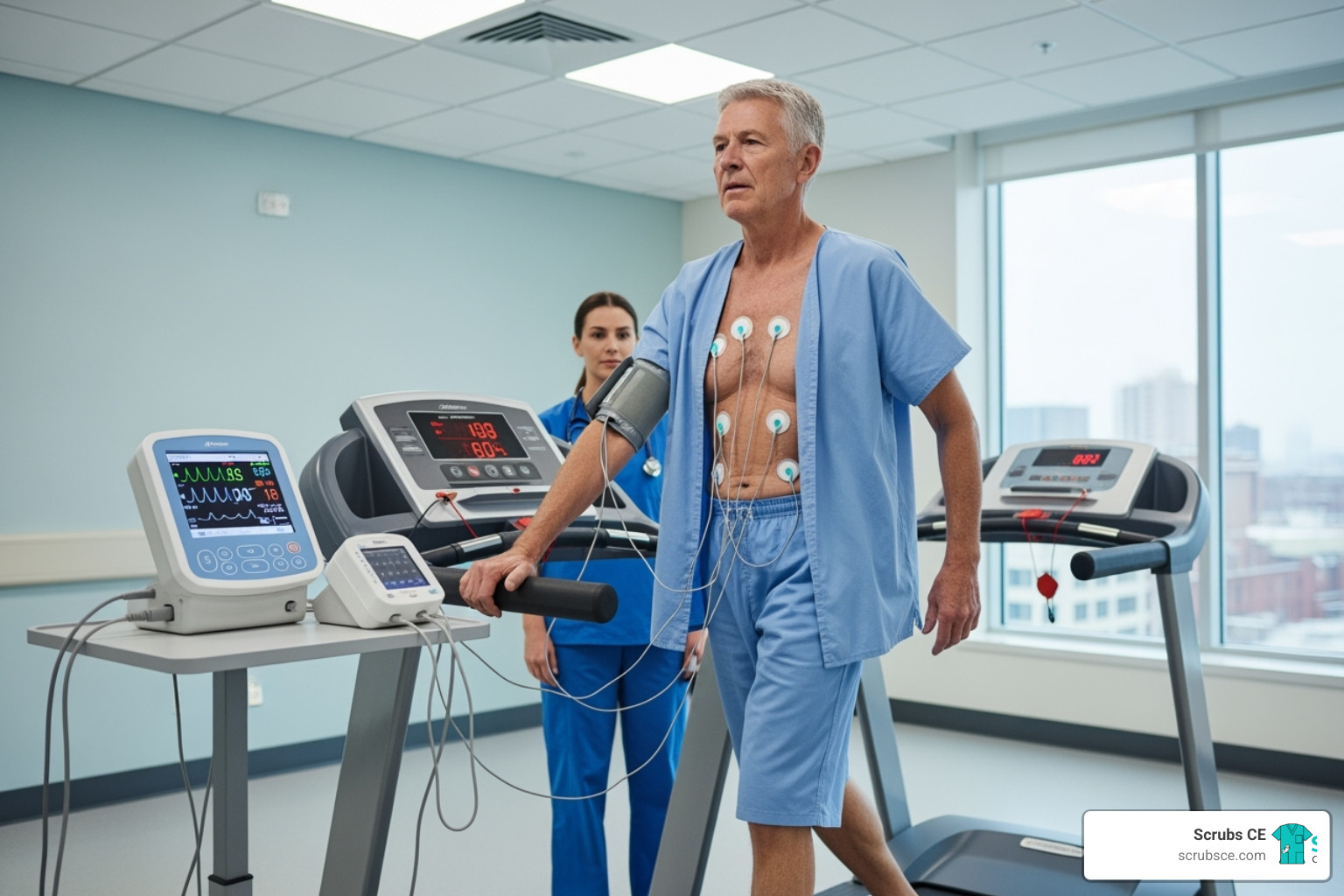
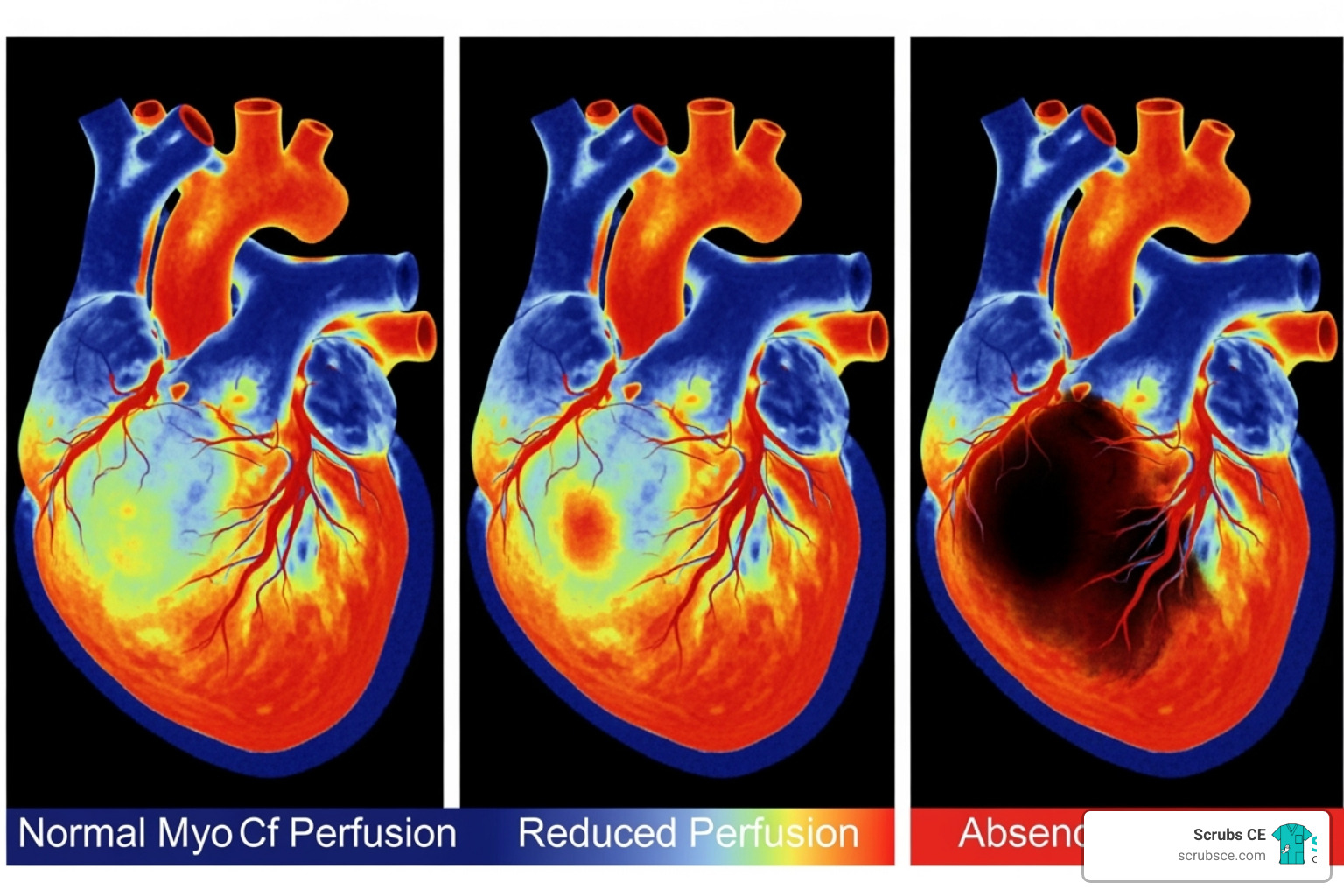
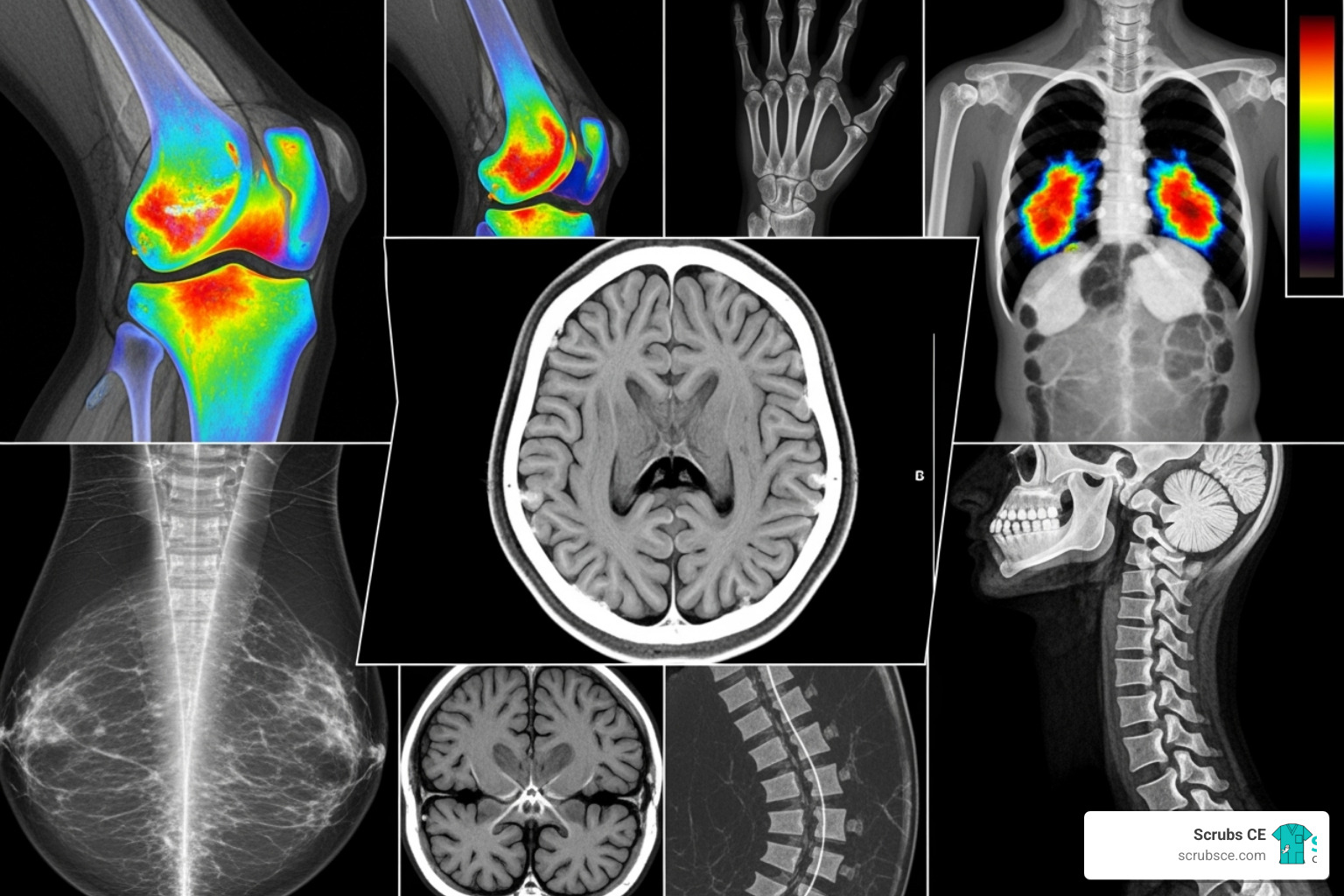
Elevate Your Skills: Mastering Mammography Through Online Learning
Why Online Mammography Education Matters for Your Career
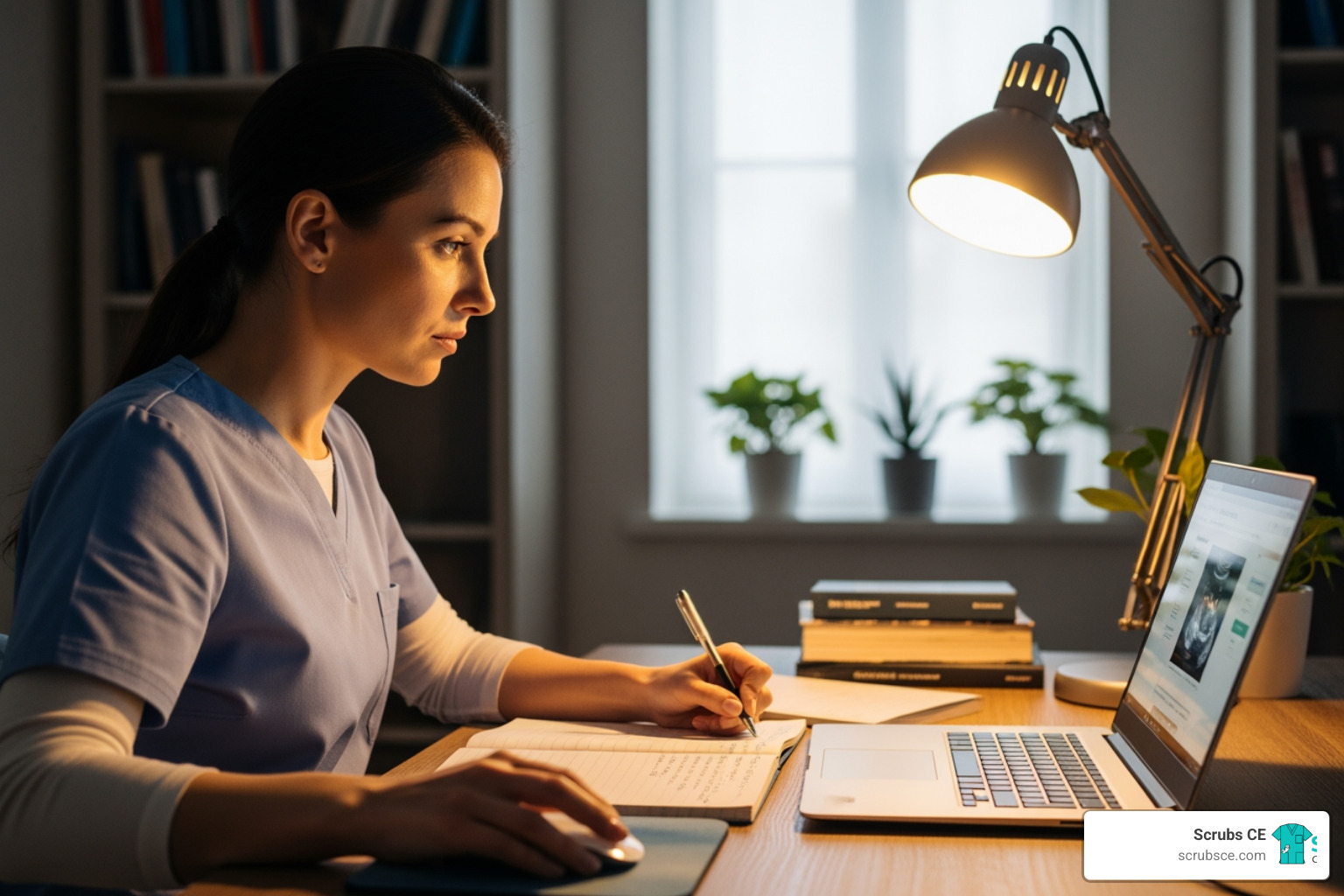
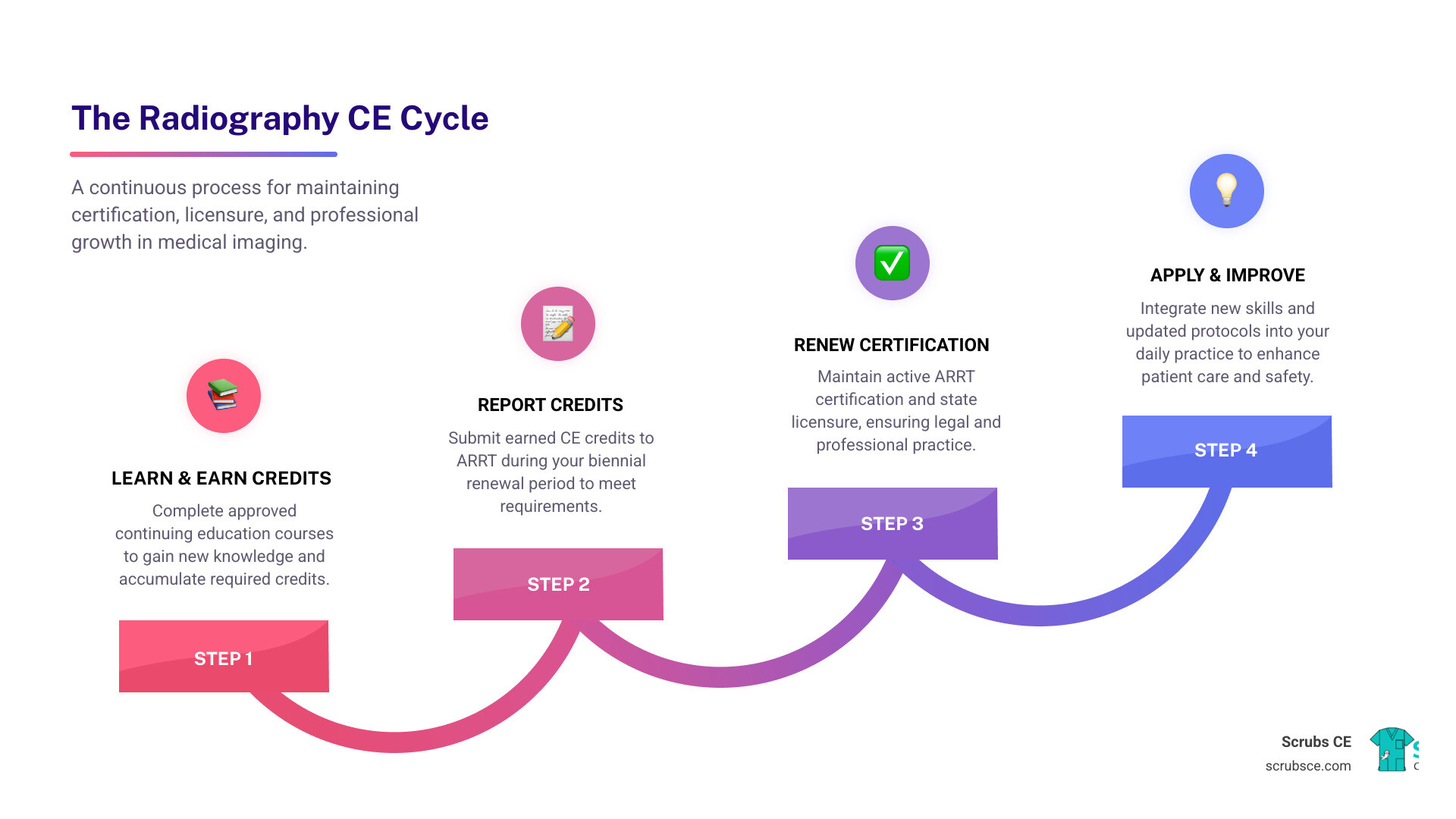
Mammography education online provides healthcare professionals with flexible, accredited training to master breast imaging skills, earn required continuing education credits, and advance their careers—all without leaving home.
Quick Answer: What You Need to Know
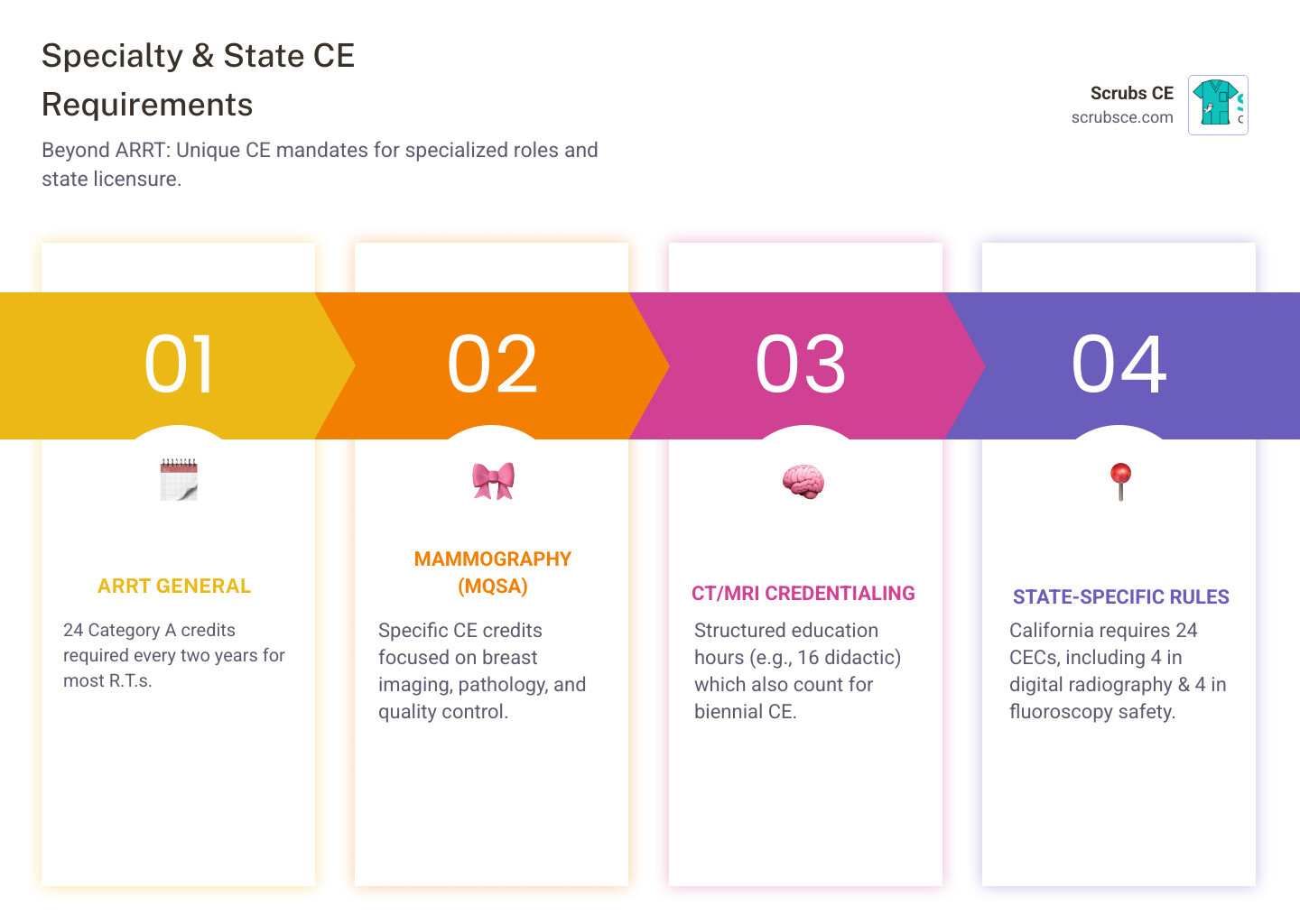
- Initial Training: 40-hour MQSA-mandated programs prepare aspiring mammographers for ARRT® certification
- Continuing Education: ASRT-approved Category A credits fulfill state licensure and professional development requirements
- Formats Available: Self-paced courses, live webinars, and comprehensive training packages
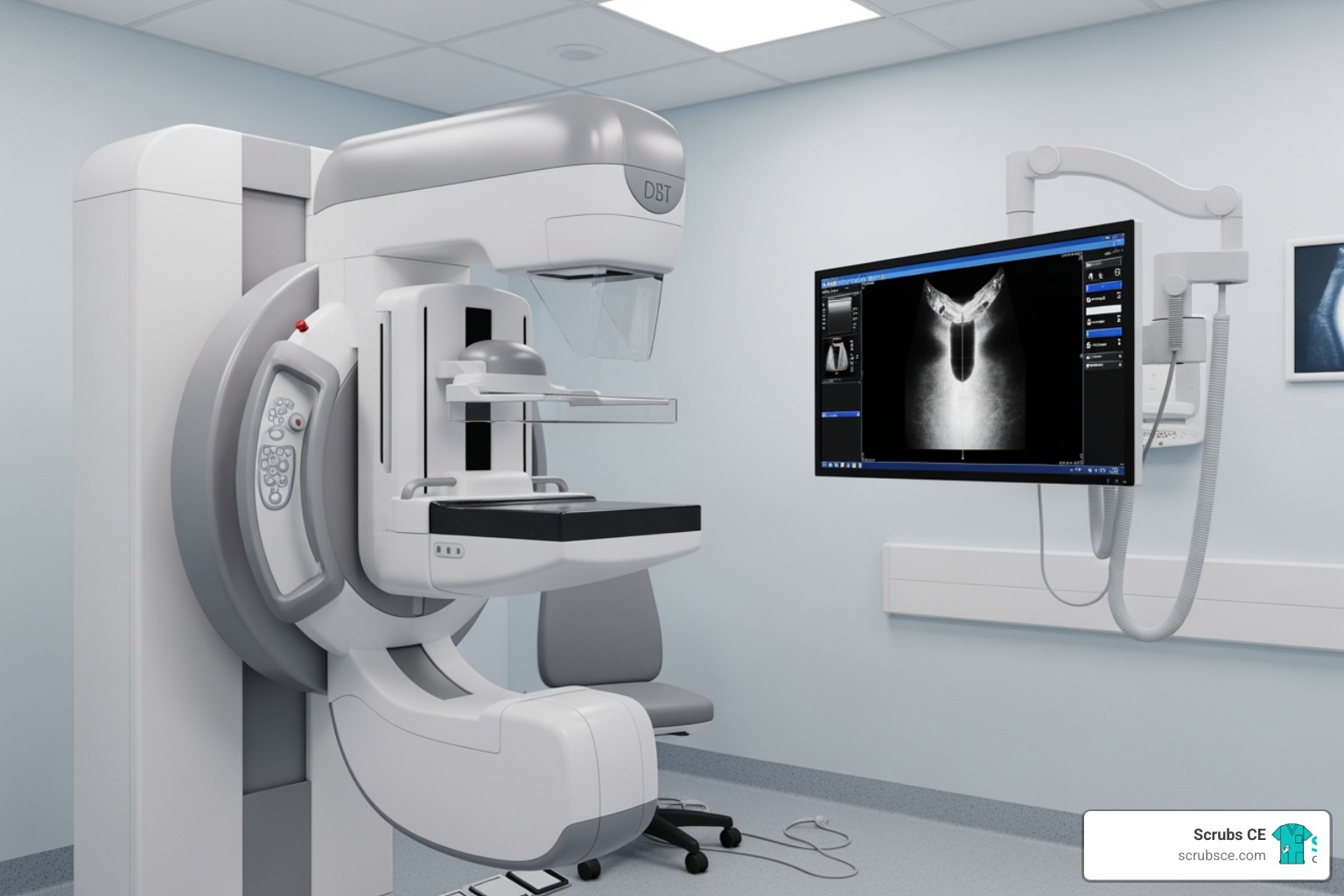
- Key Topics: Breast anatomy, patient positioning, digital mammography, DBT, quality control, and biopsy techniques
- Career Impact: 98% board exam pass rates and pathways to higher-paying specialized roles
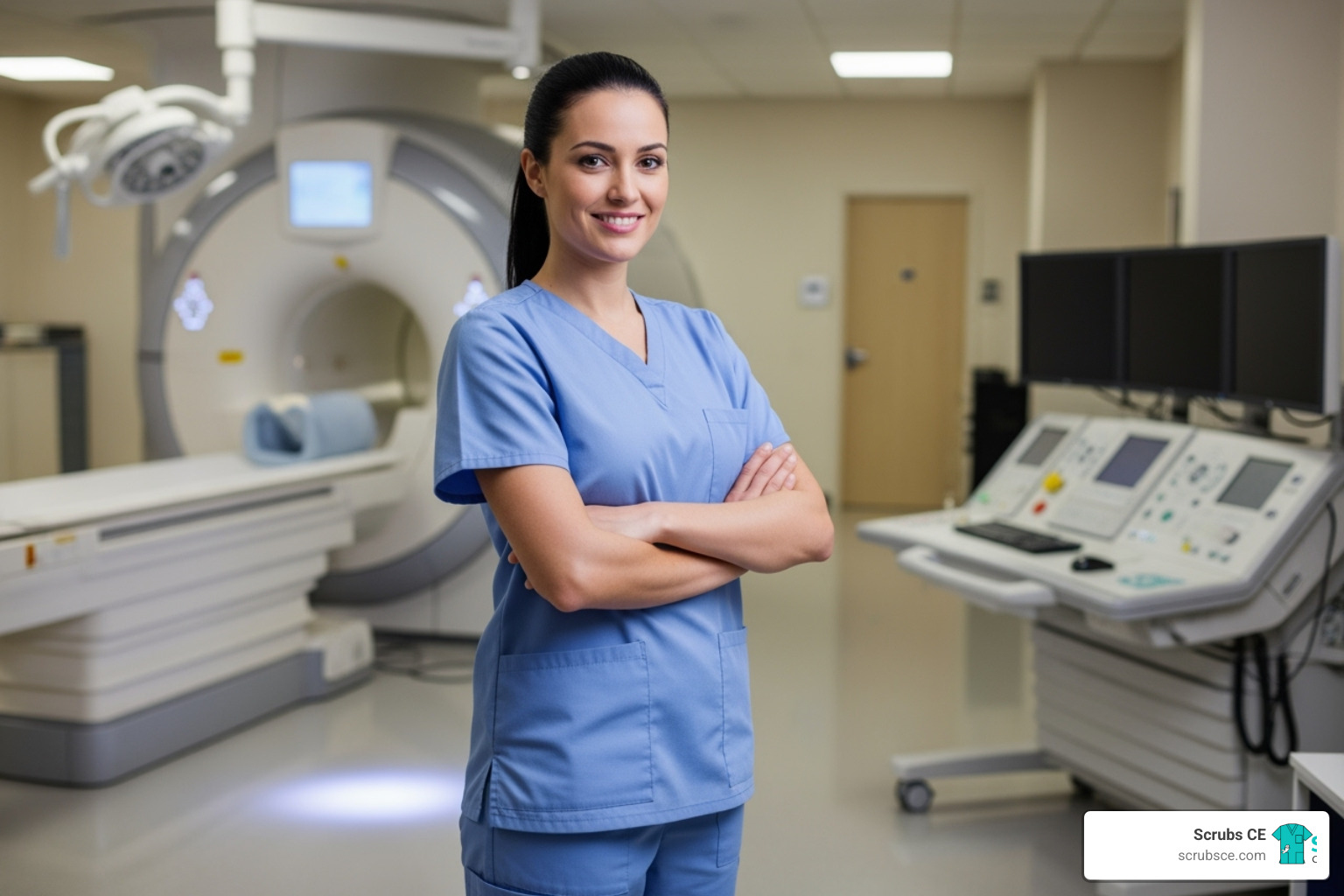
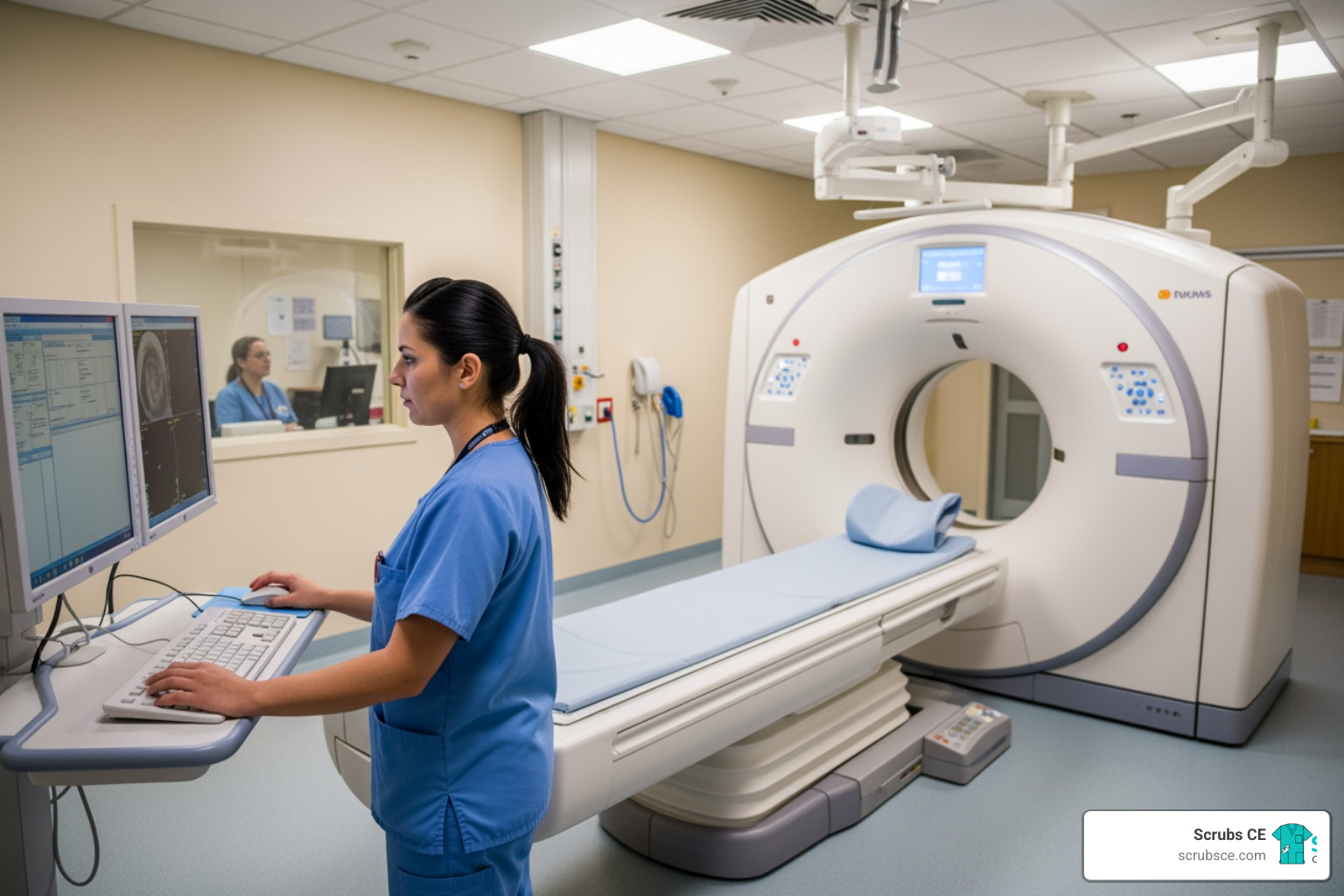
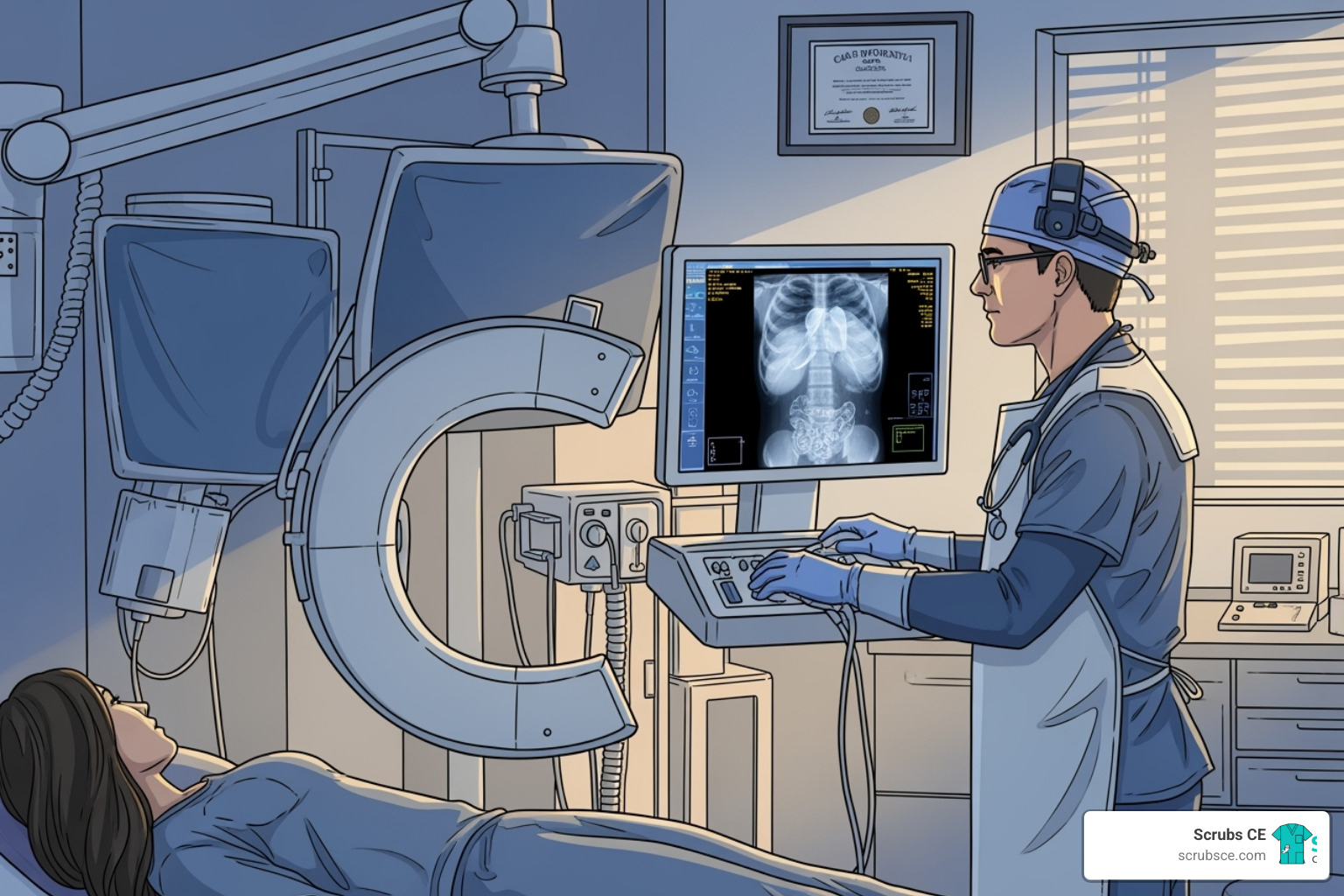
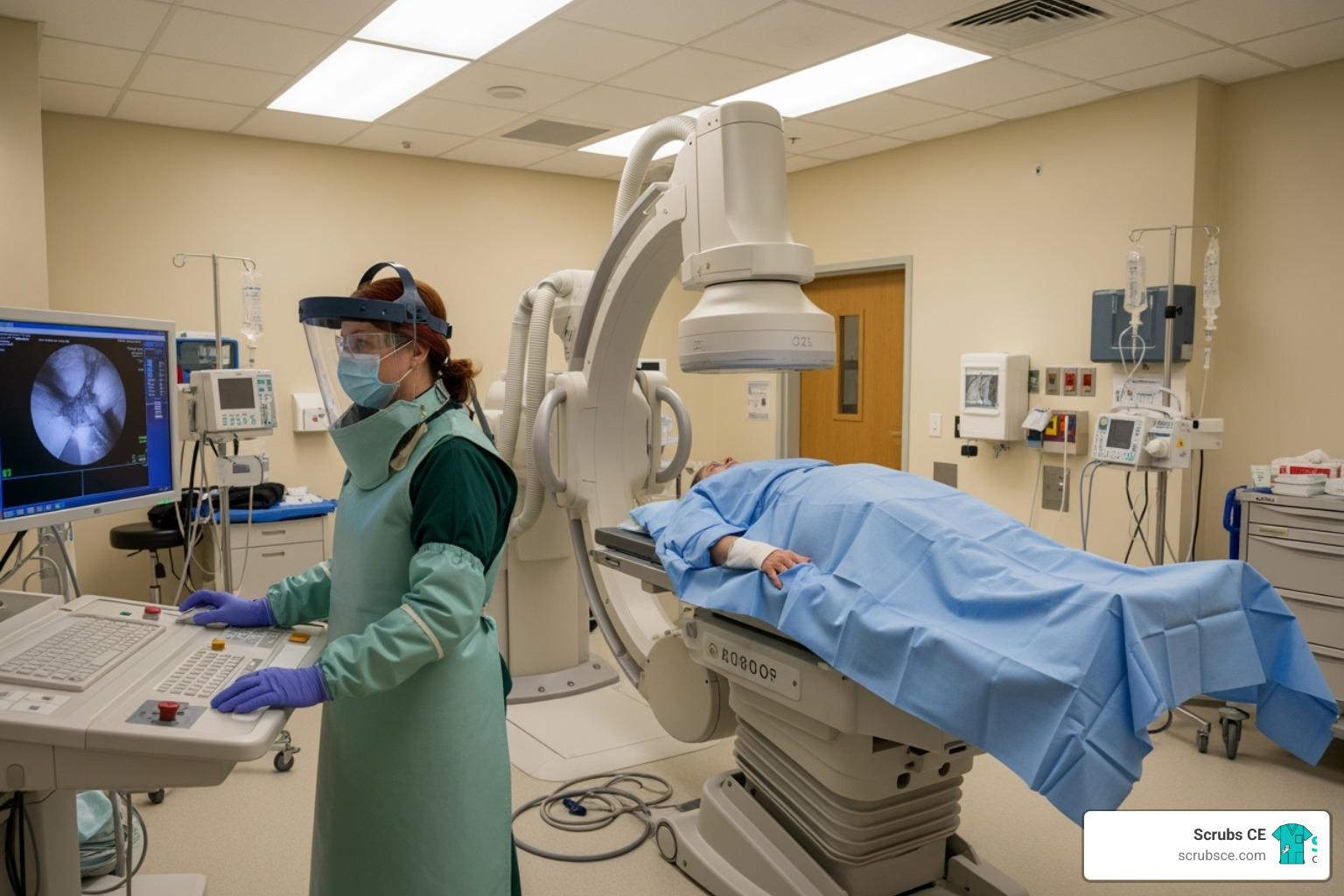
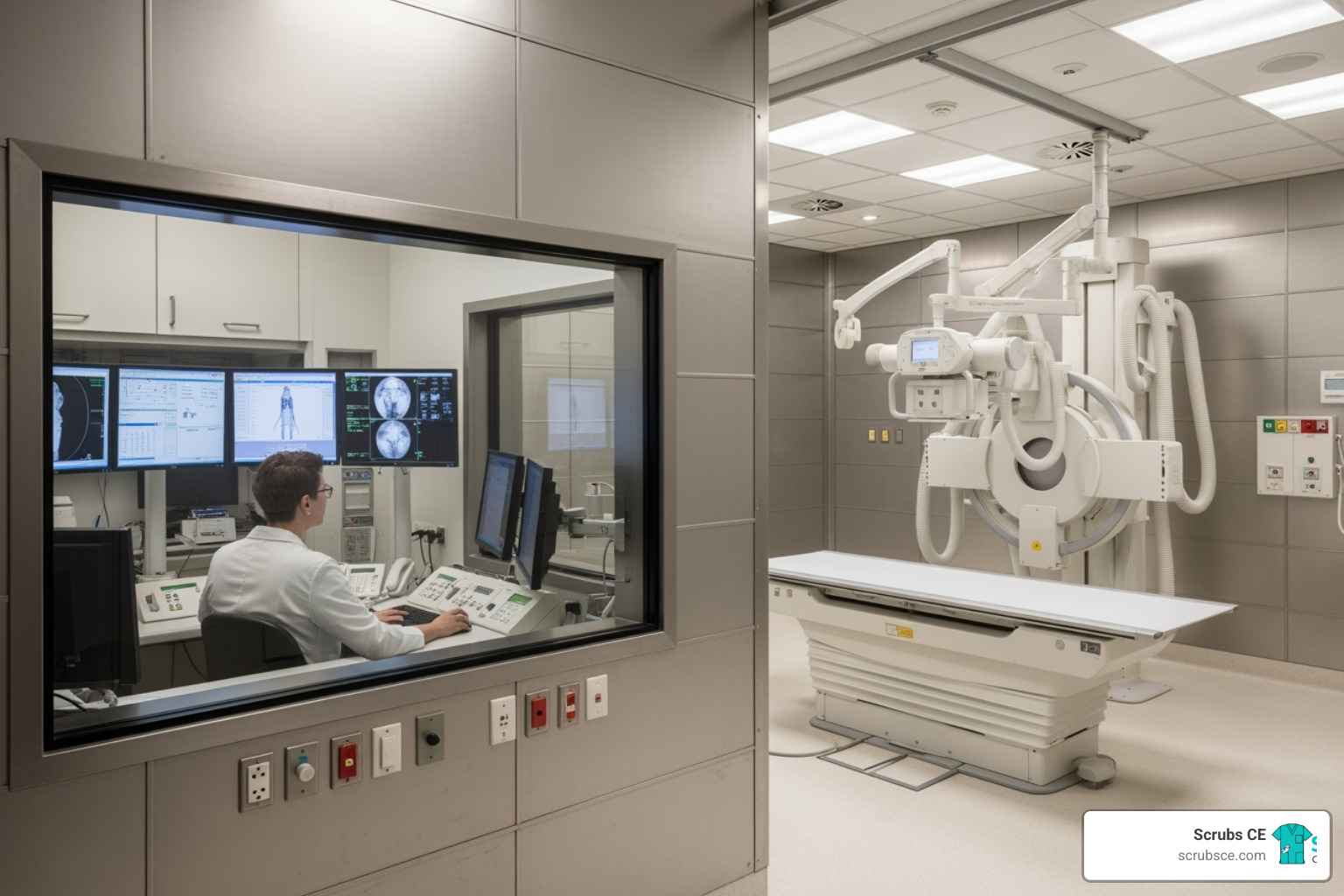
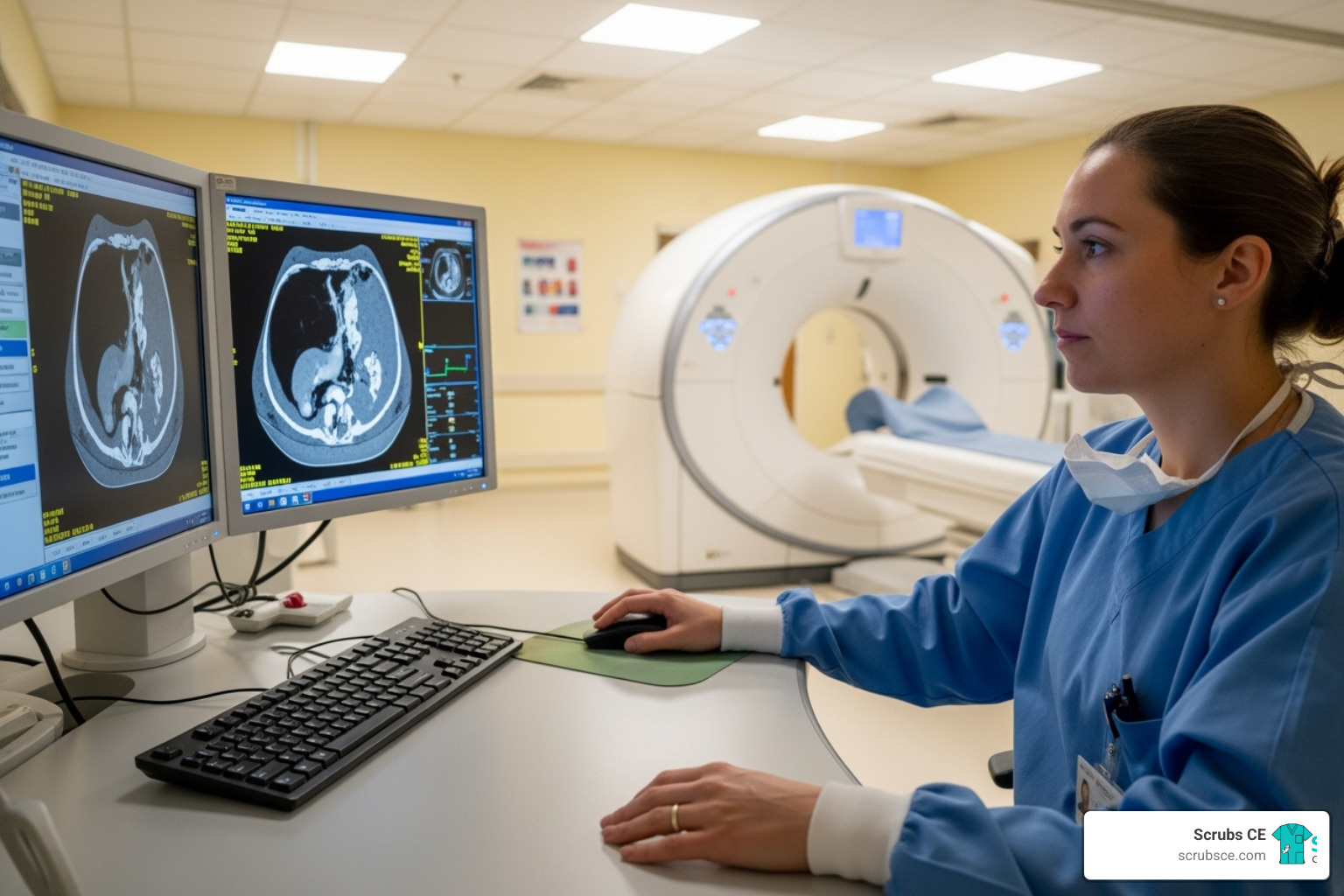
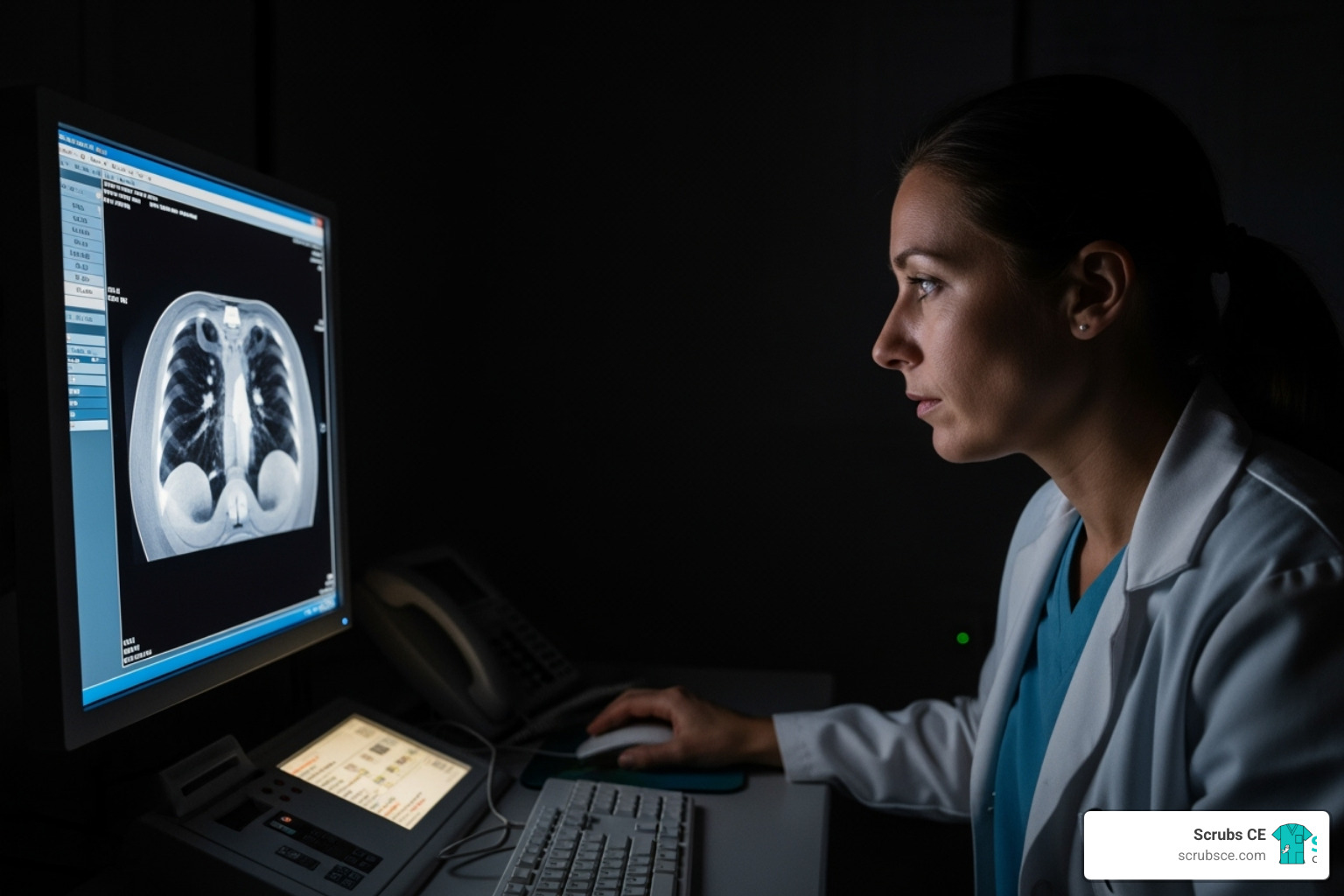
With breast cancer being the most diagnosed cancer among women worldwide, early detection through mammography is life-saving. This critical tool requires highly skilled professionals, and the educational landscape has transformed to meet this need. Today, mammography education online offers a practical solution for healthcare professionals constrained by time and budget.
Online courses provide the same rigorous, accredited training as traditional classrooms but with added flexibility. You can learn at your own pace, access materials 24/7, and study between shifts. With leading programs reporting 98% pass rates on the ARRT® mammography board exam, it’s clear that distance learning delivers results for aspiring and practicing mammographers alike.
Who Benefits from Online Mammography Training?
Mammography education online benefits a wide range of professionals in the breast imaging field. It serves as a gateway for aspiring mammographers with RT(R) certification and helps practicing radiologic technologists meet CE requirements. Radiologists and medical physicists use it to deepen their expertise in diagnostics and quality assurance. It also provides flexible options for postgraduate students, valuable insights for healthcare managers, and a pathway for career changers entering this high-demand field.
For all these professionals, staying current is critical as regulations and technology evolve. As detailed in our guide to Mammography Technologist License Renewal: What You Need to Know, online education makes keeping up manageable.
For Aspiring Mammographers
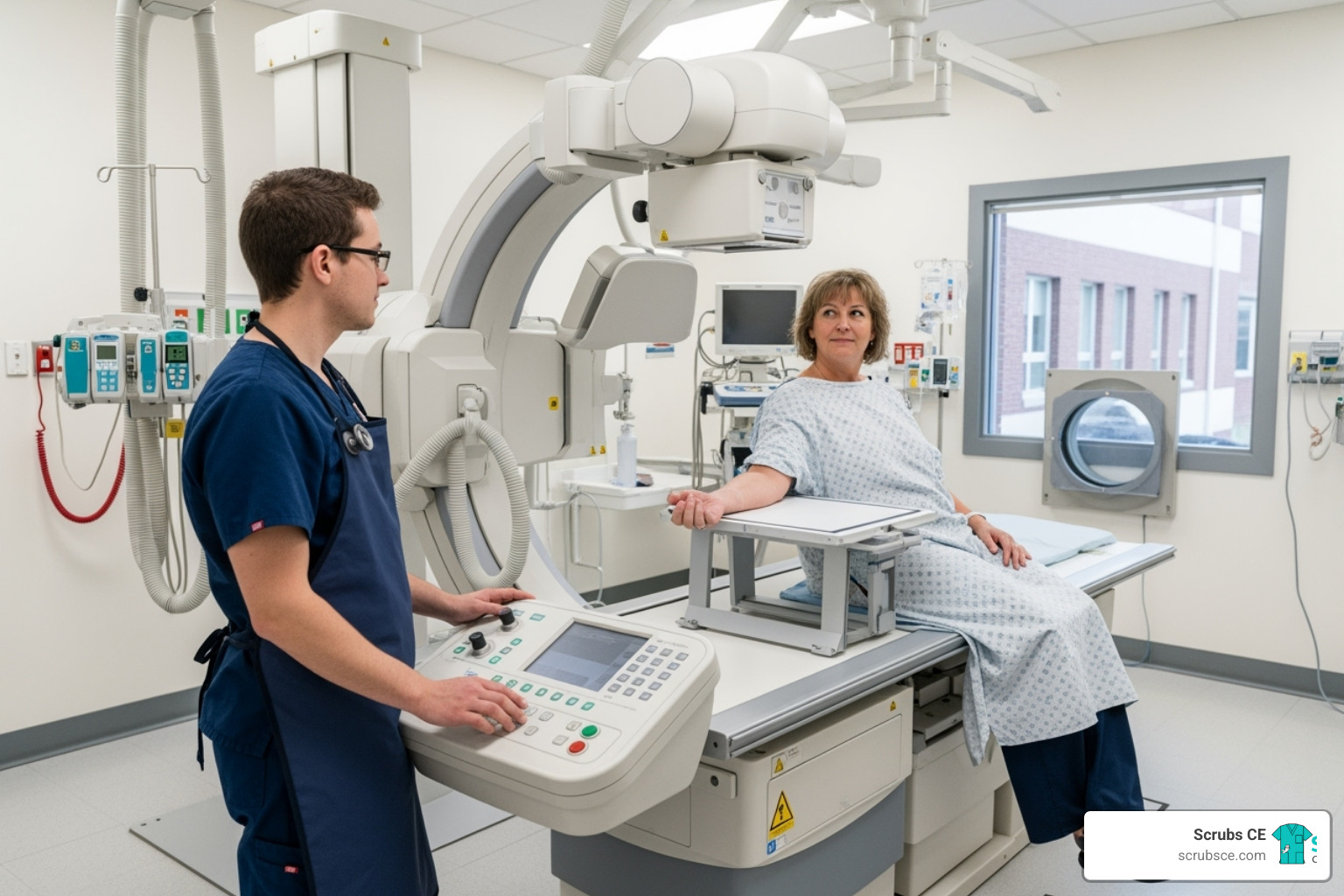
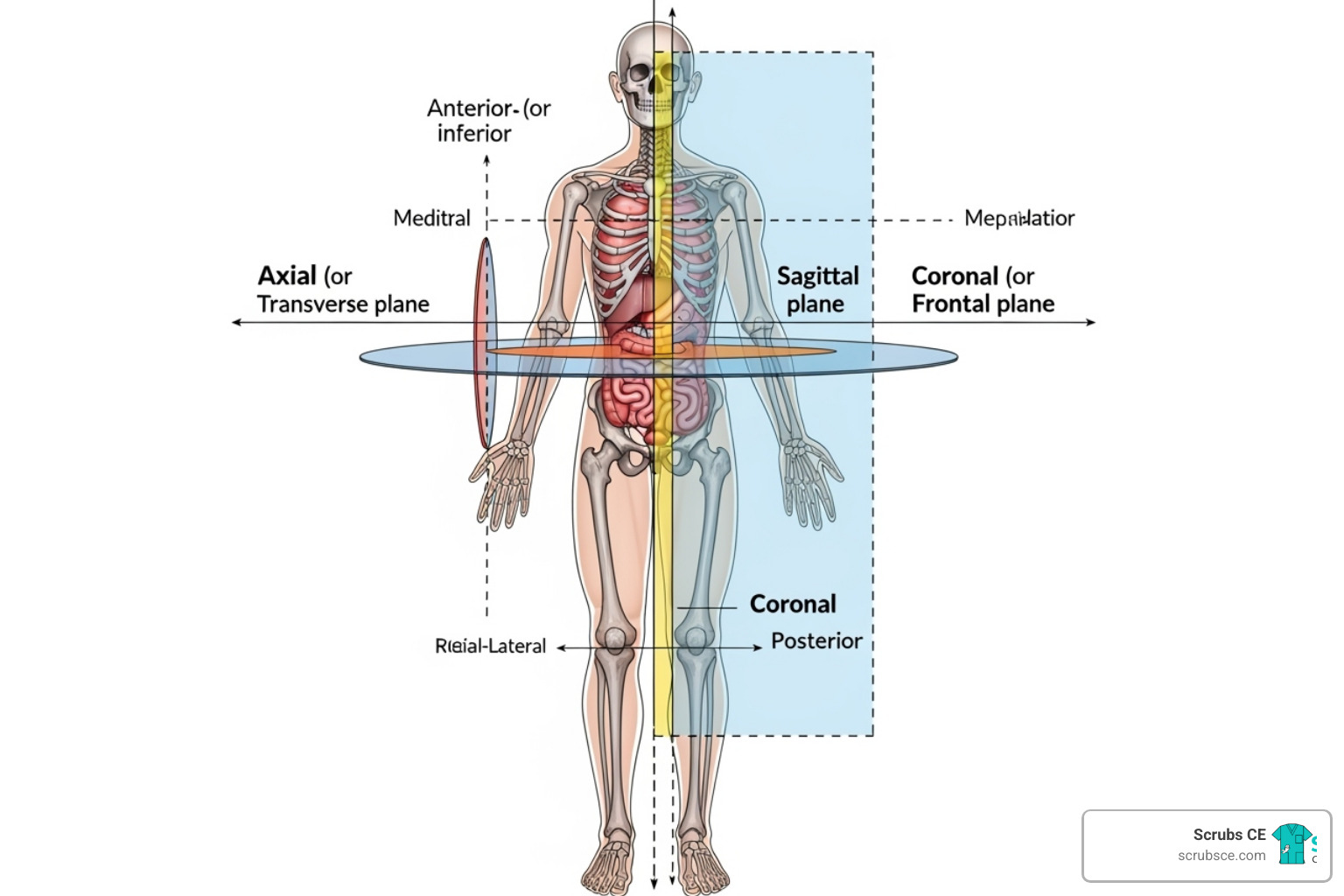
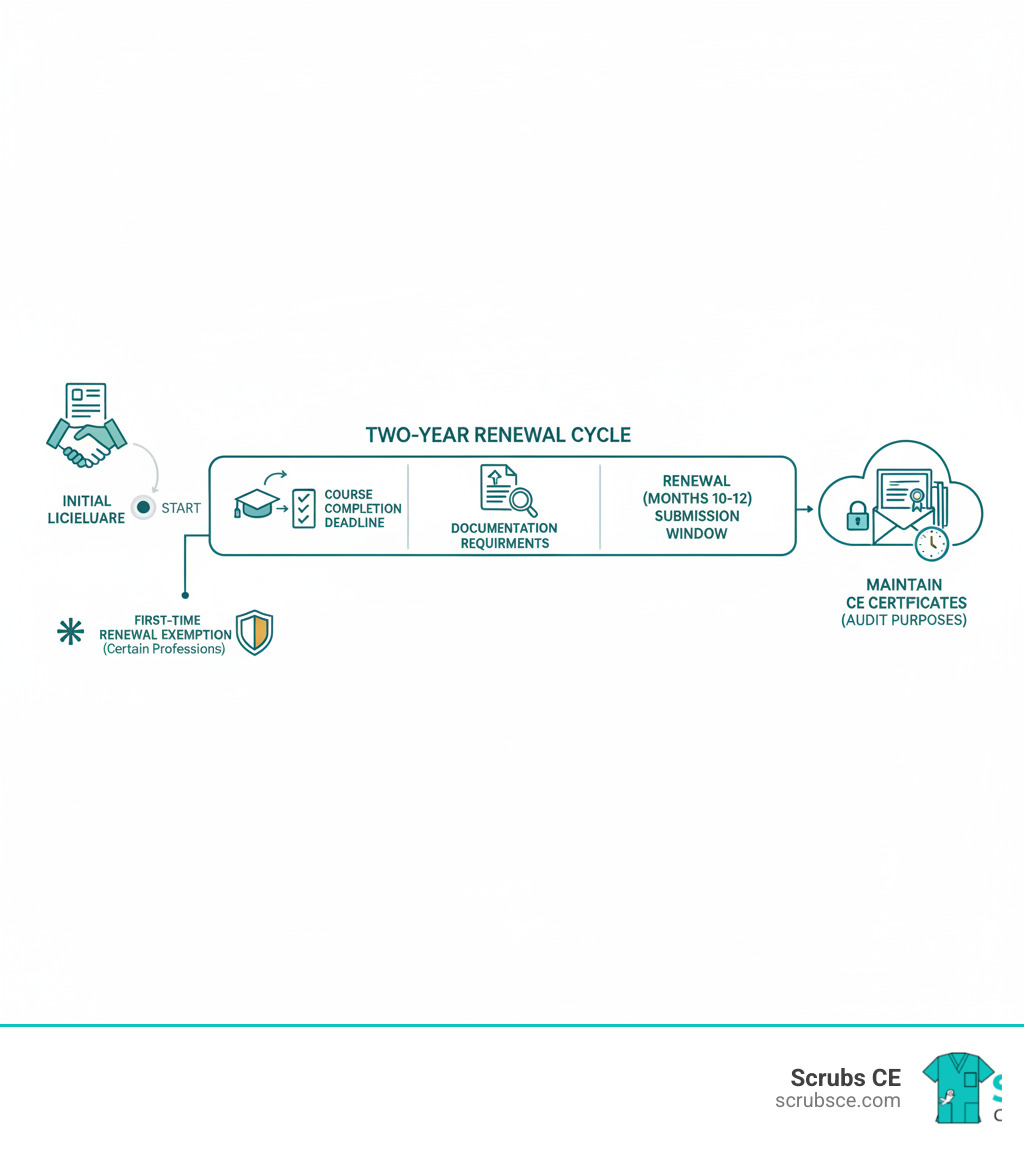
For RT(R)s passionate about women’s health, becoming a mammographer is a rewarding path made more accessible by online programs. The Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) requires 40 hours of specialized education in breast anatomy, physiology, patient positioning, and quality assurance. This foundational knowledge is crucial for patient safety and diagnostic accuracy.
Online courses designed for the ARRT® certification pathway fulfill these MQSA requirements and fit into your work schedule. They often include registry review and test prep to build confidence for the certification exam. While online learning provides the theoretical backbone, MQSA also requires 25 hands-on mammography exams performed under direct supervision. This essential clinical experience is where theory meets reality.
Ready to explore your options? Check out our Mammography Courses to see what’s available to launch your new career path.
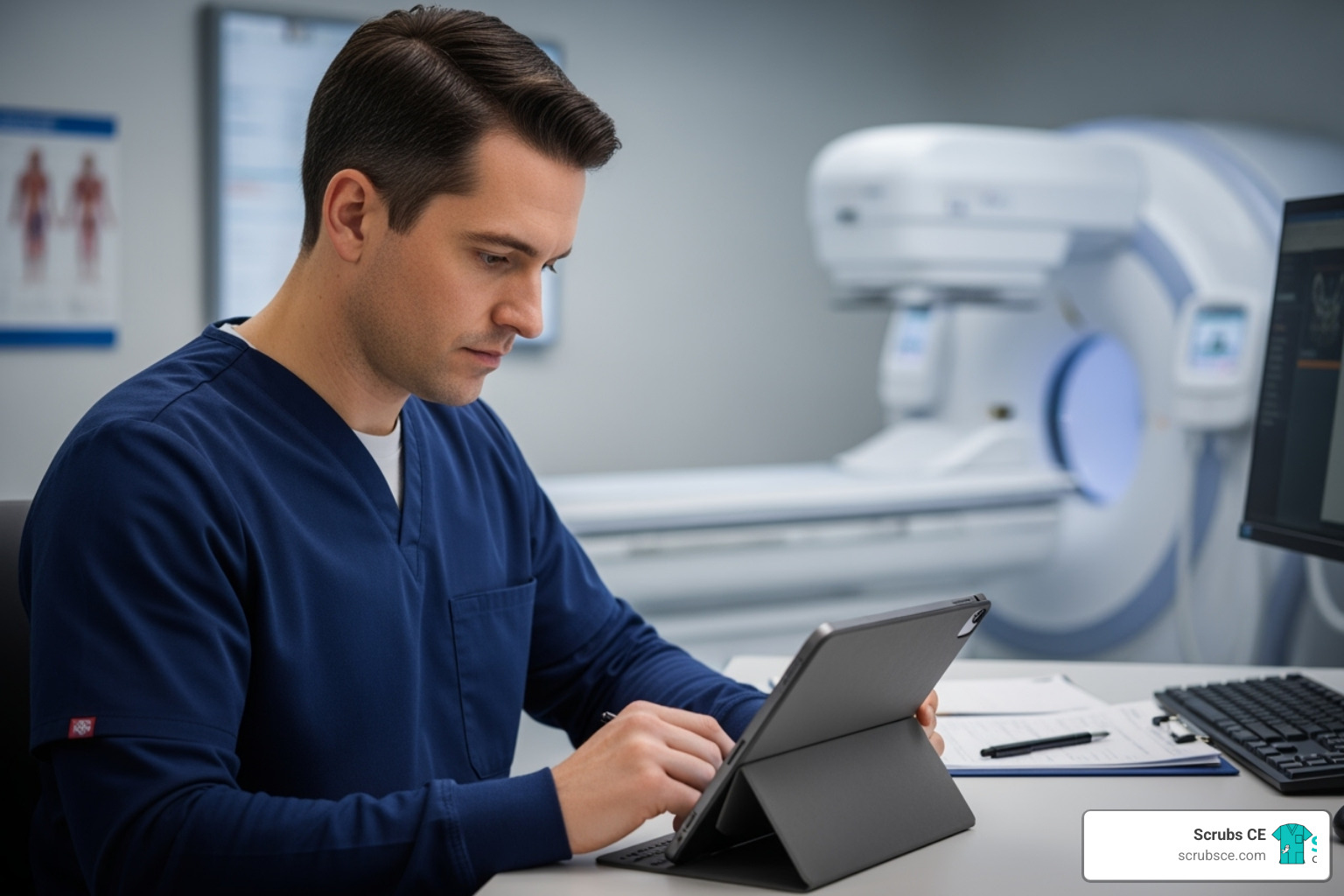
For Practicing Professionals
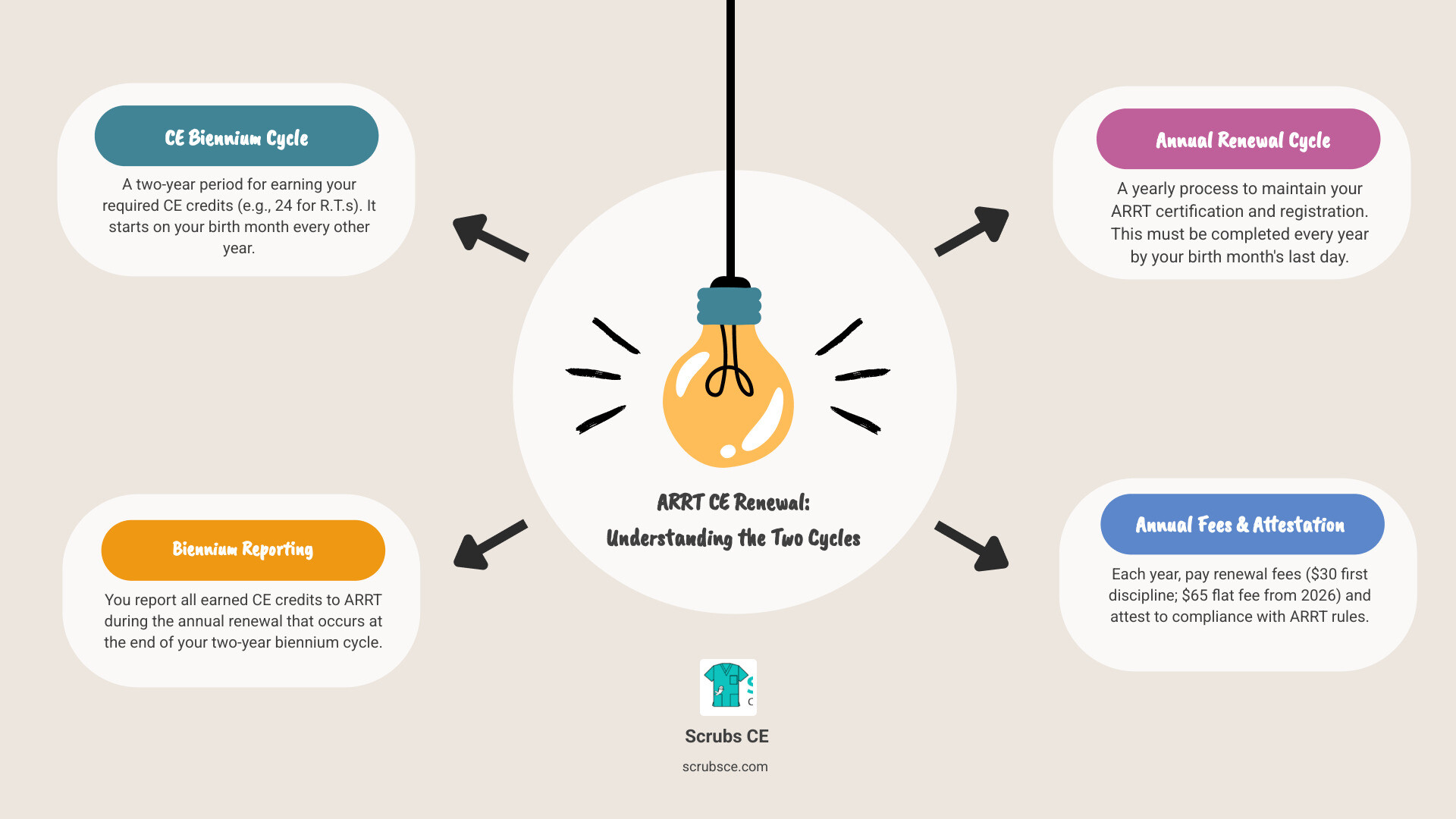
For practicing professionals, the learning never stops, and mammography education online is essential for career growth. Online courses provide a convenient way to earn the continuing education credits needed to maintain your license and ARRT® certification, as detailed in our article on Mammography Continuing Education Requirements.
Beyond fulfilling CE requirements, online modules allow you to refine specific skills, such as positioning or digital image acquisition. You can also specialize further with training in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) or breast biopsy techniques, which often leads to career advancement and higher pay.
Online training is also key to staying current with technology, from advanced tomosynthesis systems to new quality control protocols. It keeps you ahead of the curve in a fast-moving field, allowing you to grow your skills one course at a time.
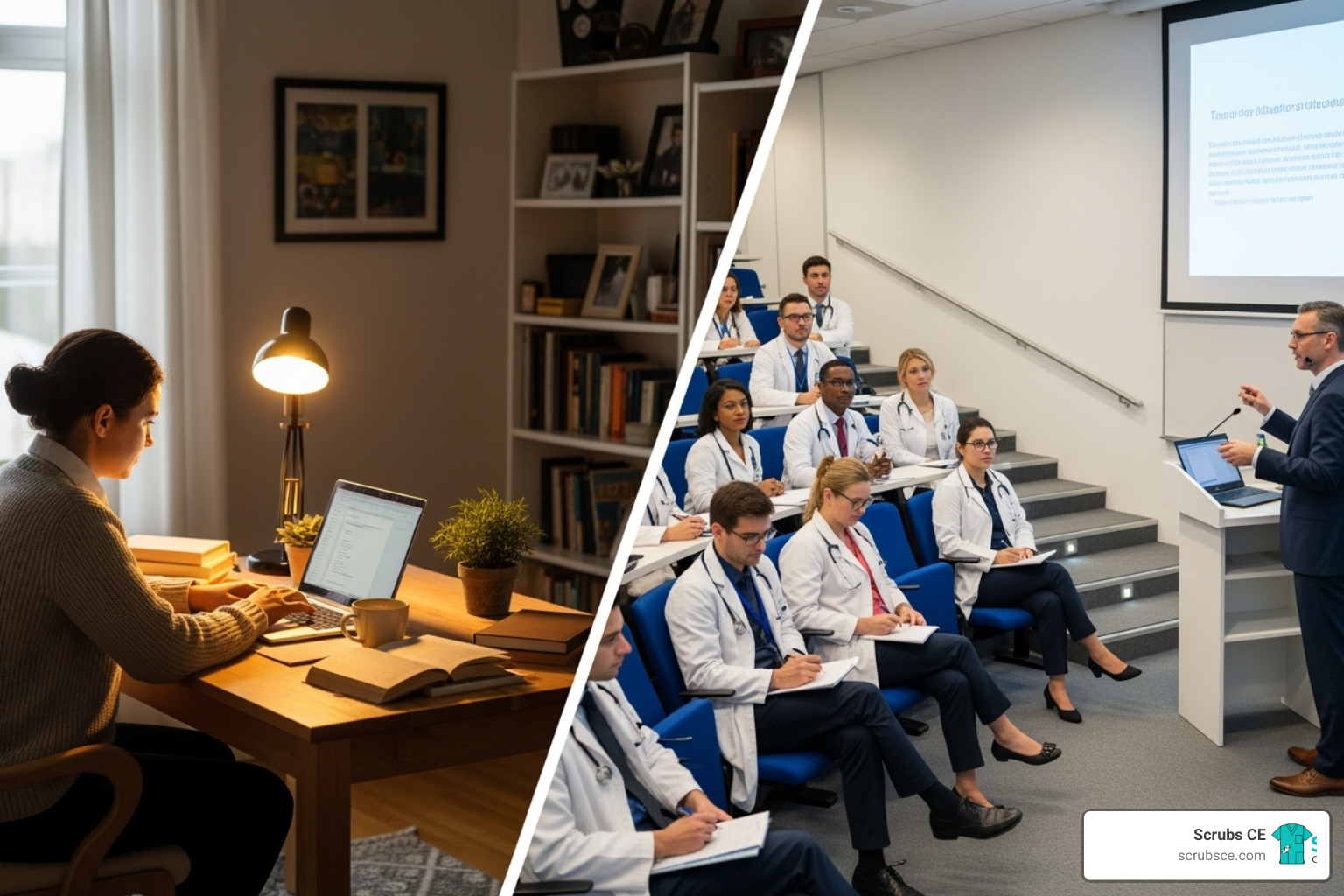
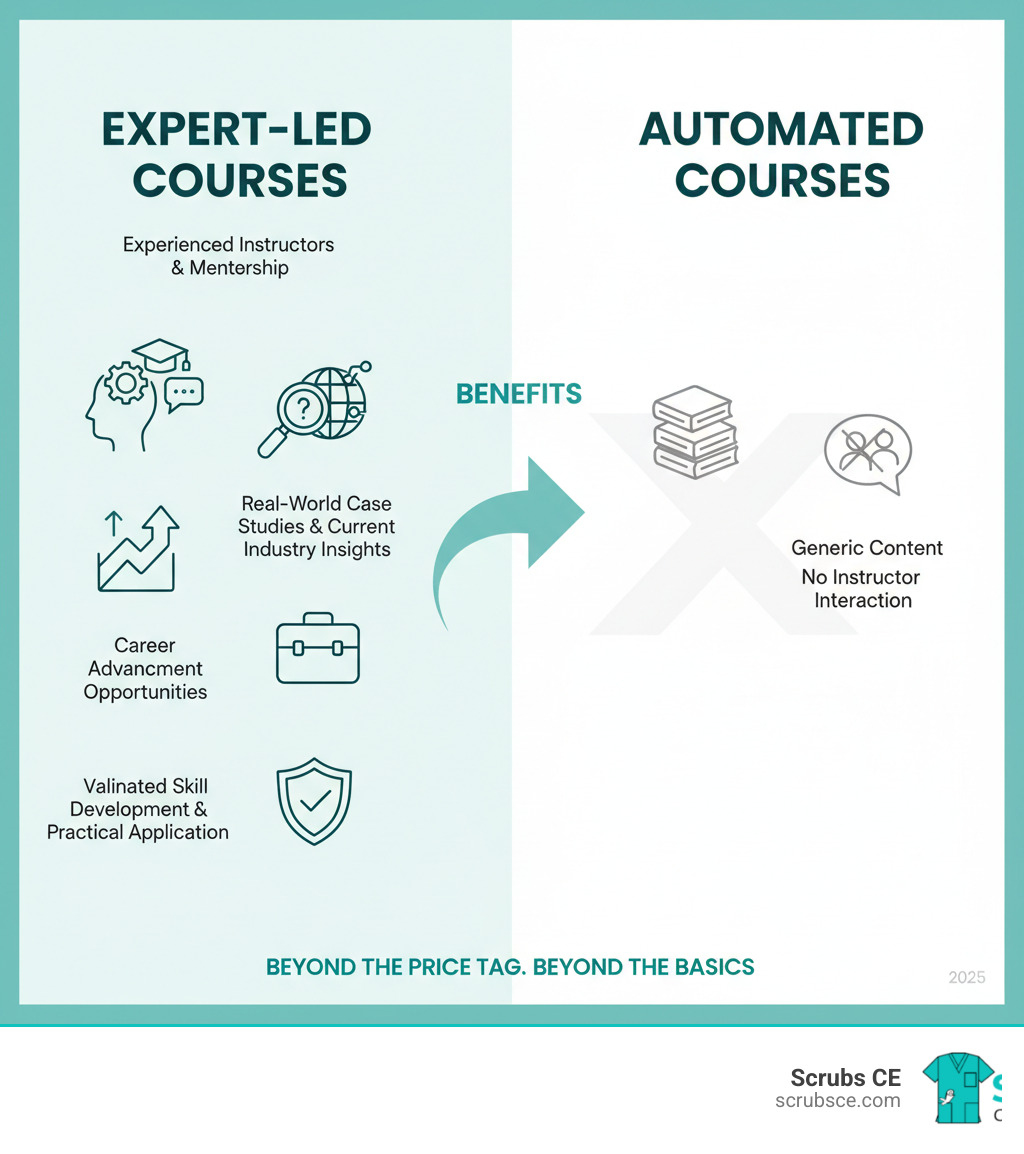
The Advantages of Learning Mammography Online
Finding time for professional development while working in healthcare is a major challenge. Juggling shifts, patient care, and personal responsibilities makes attending traditional classes difficult. This is why mammography education online has become a game-changer, making quality education accessible to busy professionals.
| Feature | Online Mammography Training | Traditional In-Person Training |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Learn anytime, anywhere, at your own pace. | Fixed schedules, specific locations. |
| Cost | Often more affordable; saves on travel, accommodation, lost wages. | Higher costs for tuition, travel, accommodation, time off work. |
| Accessibility | Available globally, to anyone with internet access. | Limited by geographic location and class capacity. |
| Pacing | Self-paced; review complex topics as needed. | Instructor-led; pace set by the class. |
| Content | Wide range of specialized courses, regularly updated. | Broader curriculum, updates may be less frequent. |
| CE Credits | Conveniently earn ASRT Category A credits. | Earn credits, but often requires travel and time commitment. |
| Networking | Online forums, virtual communities. | In-person interactions, direct mentorship. |
Flexibility and Convenience
With mammography education online, you can learn anytime, anywhere—during a lunch break or late at night. Courses are available 24/7, allowing you to set a self-paced schedule that fits your life. This flexibility makes it possible to balance work and education without requesting time off or rearranging shifts.
The no travel required benefit saves significant money on flights, hotels, and meals associated with traditional training. Furthermore, immediate access to materials means you can enroll and begin learning instantly, without waiting for a new semester to start.
Career Advancement and Professional Development
Online education offers tangible career benefits. Fulfilling CE requirements is a primary advantage, as online platforms make earning ASRT Category A credits straightforward and stress-free. For those seeking new credentials, online programs provide the structured education required for ARRT® certification, with top programs reporting pass rates of 97-98% on the board exam.
Specialized training also opens up more job opportunities. As the demand for skilled mammographers grows, professionals current with technology like digital breast tomosynthesis become highly sought-after. This expertise often translates to higher pay potential. Investing in advanced training in modalities like Advanced Breast Imaging increases your earning power. Online learning removes barriers, allowing any professional to access education that advances their career.
Navigating the Landscape of Mammography Education Online
Once you decide to pursue mammography education online, you’ll find a rich landscape of learning opportunities. Understanding the different formats and topics available will help you chart the right course for your career. The digital revolution in healthcare education has democratized access to specialized training, with some global initiatives like the IAEA’s e-learning course benefiting professionals in nearly 70 countries. These resources empower health professionals with skills in digital mammography, operational standards, and teamwork.
Types of Mammography Education Online
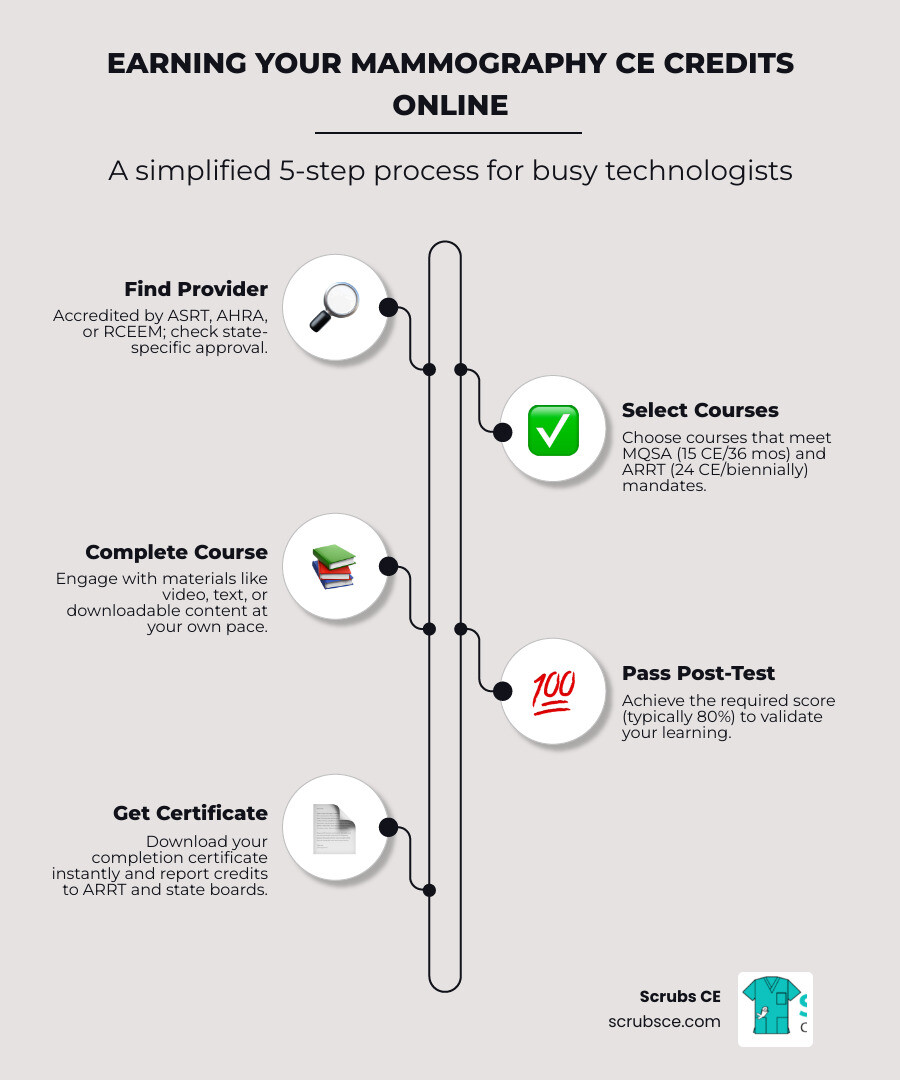
Online learning offers a variety of formats to suit different needs. Initial Training Programs are 40-hour courses that meet MQSA mandates and prepare radiologic technologists for ARRT® certification. Continuing Education courses are ideal for practicing professionals needing to fulfill annual CE requirements, ranging from short refreshers to deep dives. Live webinars offer interactive, real-time sessions with instructors, which is valuable for learning new technologies. On-demand lecture series, like Professor László Tabár’s renowned series, provide expert instruction with the flexibility to learn at your own pace.
At Scrubs CE, we offer self-paced online courses with instant certificates, e-books with tests, test-only options, and comprehensive packages to meet your specific credit requirements and schedule.
Key Topics and Skills Covered
Quality mammography education online programs cover a comprehensive curriculum. Essential areas include:
- Breast anatomy and pathology: Learn the structure of breast tissue and how to recognize benign and malignant conditions. Our guide to 7 Topics You Will Cover in Mammography Continuing Education provides more detail.
- Patient positioning: Master standard and supplementary views to ensure optimal image quality and patient comfort.
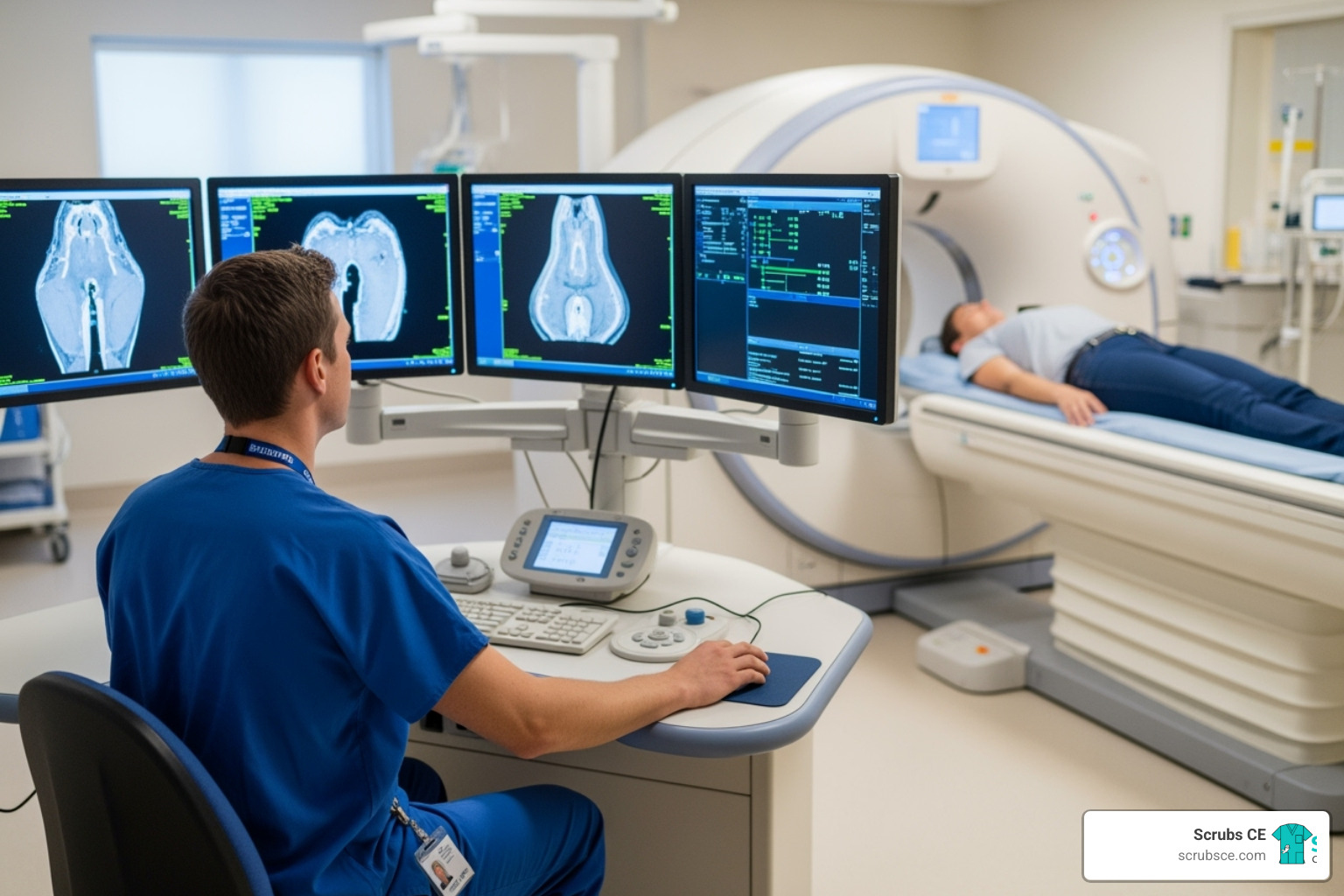
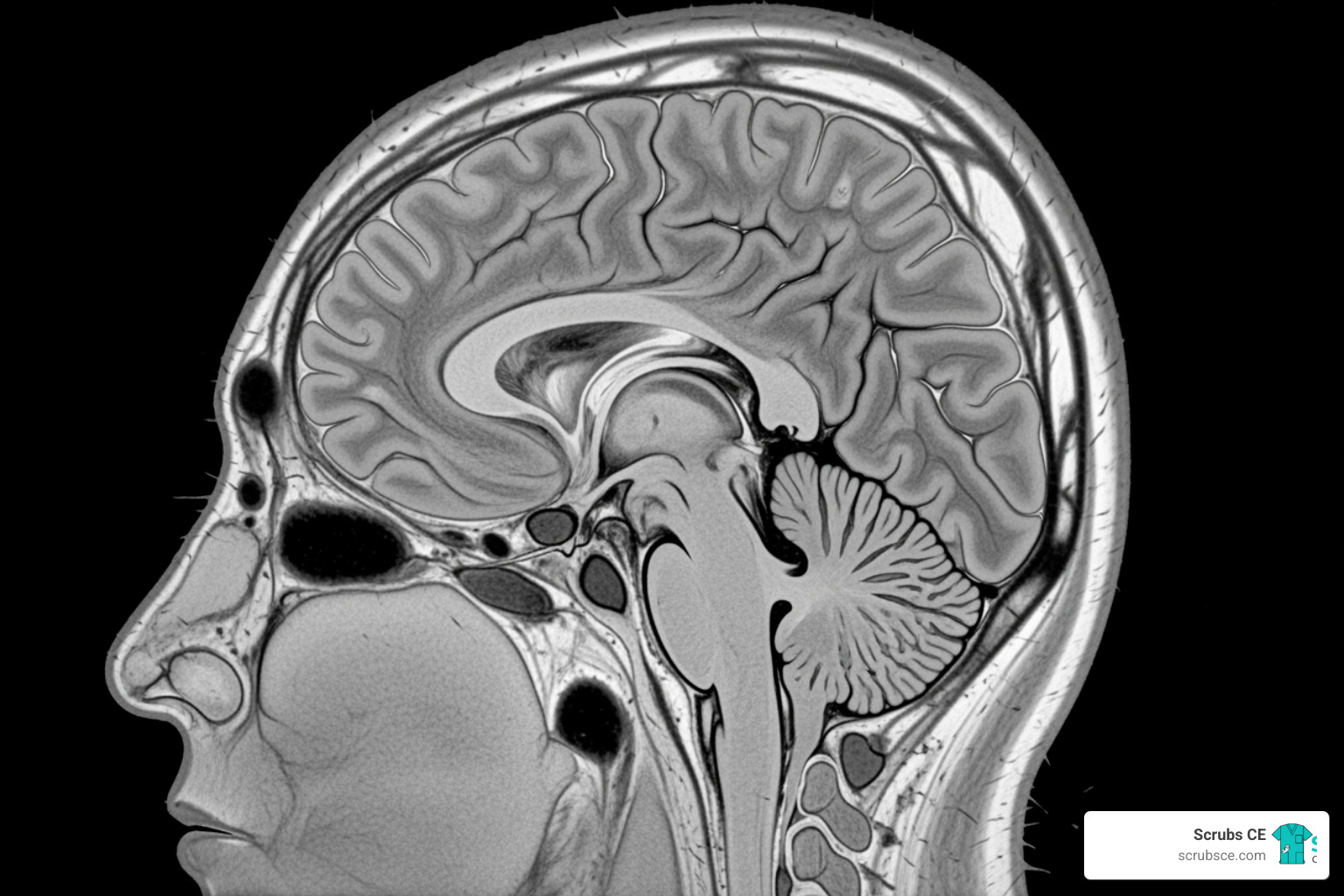
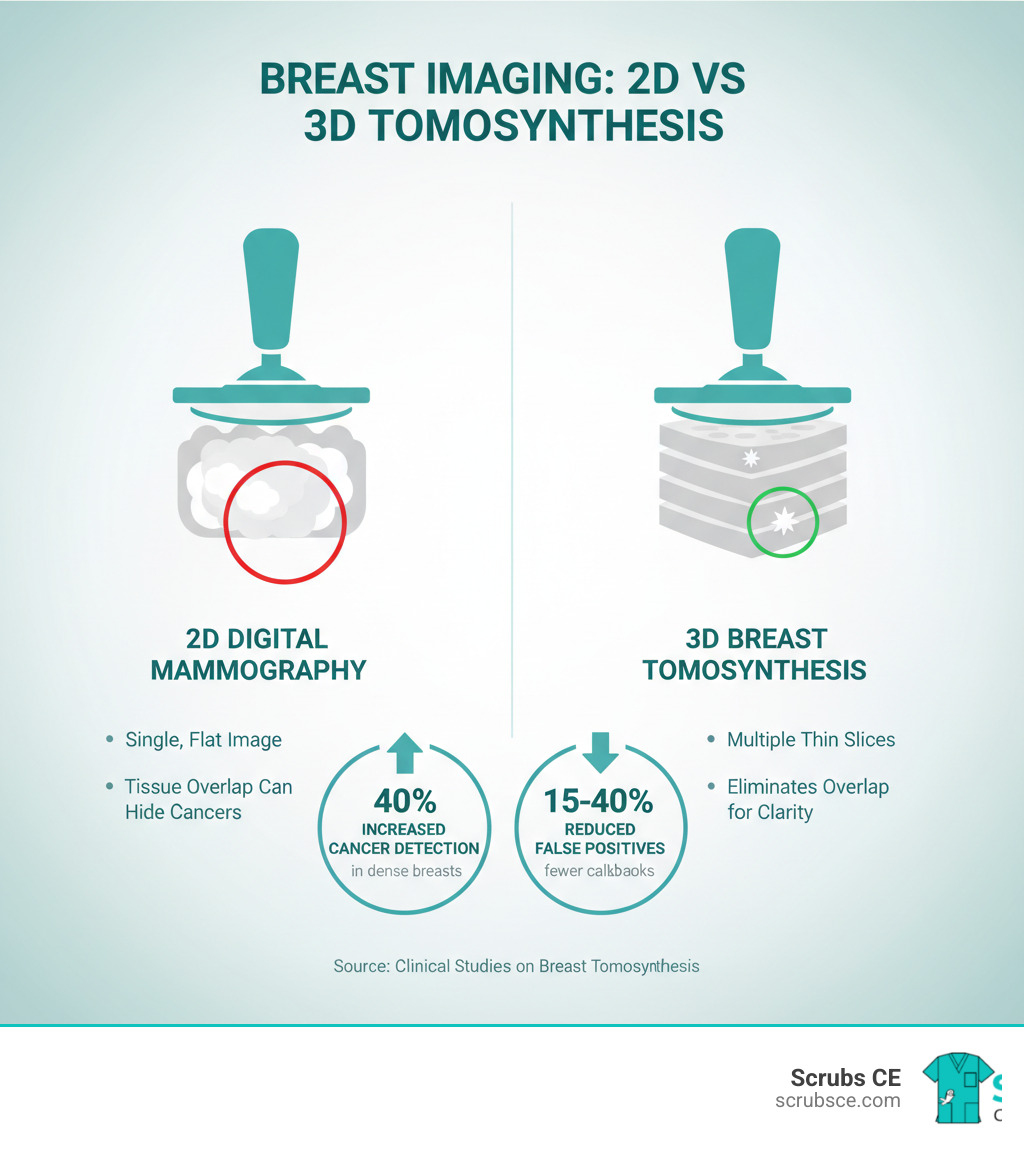
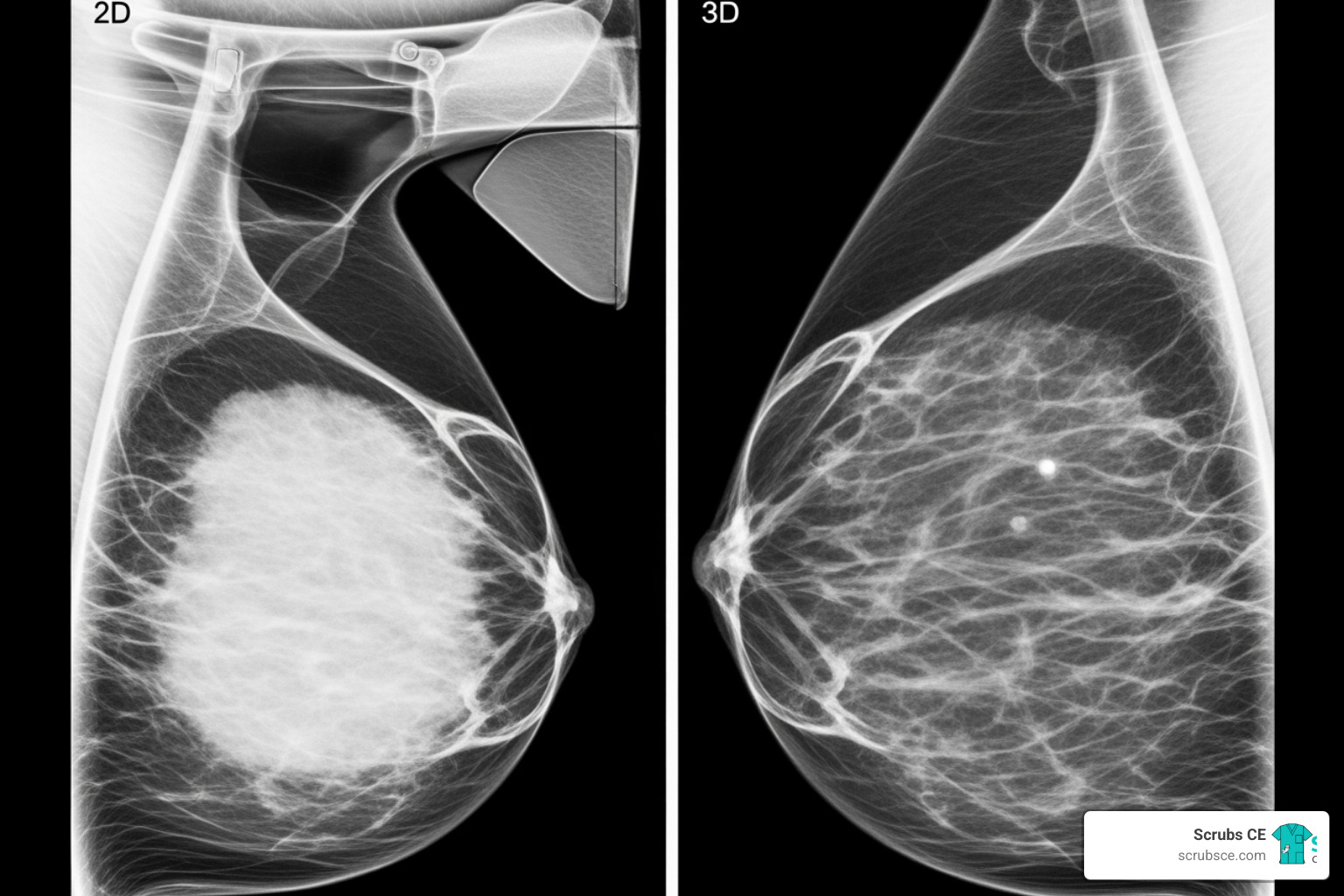
- Digital mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT): Understand the principles of modern digital imaging, including 3D mammography, which is now the screening standard.
- Quality control (QC): Dive into QC programs, MQSA regulations, and ACR guidelines that ensure equipment performance and patient safety.
- Breast biopsy techniques: Learn about procedures like stereotactic breast biopsy, which mammographers often assist with. We explore this in our guide to Breast Biopsy Targeting Techniques.
Comprehensive programs also cover equipment, patient communication, and ethical considerations to ensure well-rounded expertise.
Choosing the Right Program for Your Career Goals
With many options for mammography education online, choosing the right one can feel overwhelming. The key is to find a program that aligns with your career goals while meeting all regulatory and professional standards.
Understanding Accreditation and CE Credits
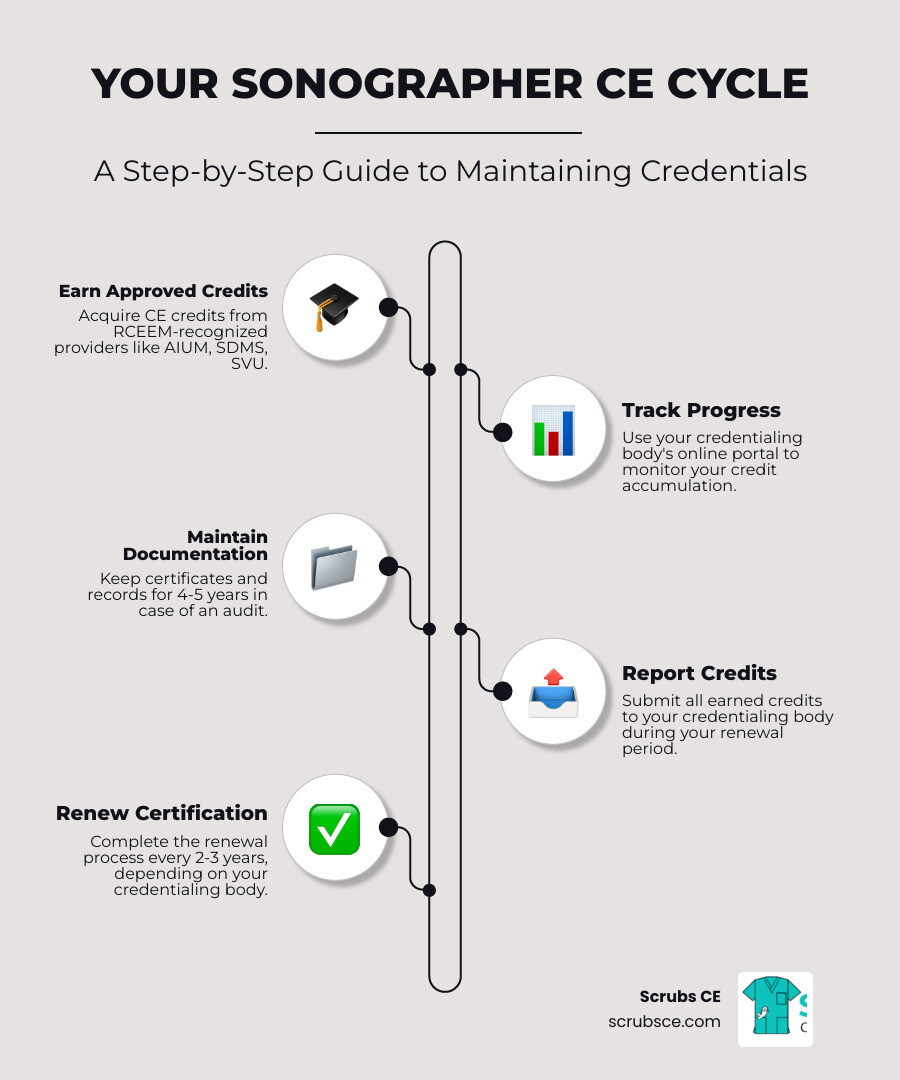
Accreditation is the foundation of a quality online program, ensuring your education counts. For initial certification, programs must meet Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) requirements, including 40 hours of didactic education and 25 supervised clinical exams. For ARRT® certification in mammography, you must satisfy specific structured education requirements, which many online courses are designed to meet. We recommend you download the ARRT® Mammography Certification Handbook for specifics.
For continuing education, ASRT Category A credits are the gold standard, accepted by the ARRT® and most states. Our courses at Scrubs CE are all ASRT-approved. However, state licensure requirements can vary, so always double-check your state’s specific mandates. To simplify this process, our Mammography CE Credits Online Guide breaks everything down.
How to Evaluate a Provider of Mammography Education Online
After confirming accreditation, evaluate the providers themselves. Not all online programs are created equal. Look for these signs of a quality provider:
- Course Curriculum: Ensure the content is detailed, current with technologies like Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT), and aligns with your learning needs.
- Instructor Expertise: Check the credentials of instructors. Learning from experienced professionals in the field is invaluable.
- User Testimonials and Reviews: Look for feedback from past students on instruction quality, material clarity, and board pass rates.
- Learning Platform and Support: The platform should be user-friendly and intuitive. Good technical support is also essential.
- Instant Certificate Availability: For CE, this is a critical feature for meeting renewal deadlines. Scrubs CE offers instant certificates upon completion.
- Instructional Design: Effective courses use engaging multimedia and interactive elements, not just static PDFs.
Choosing a high-quality program means you’re gaining valuable skills to advance your career, not just collecting credits.
Frequently Asked Questions about Online Mammography Education
Here are answers to some of the most common questions we hear about mammography education online.
What are the initial training requirements to become a mammographer?
To ensure patient safety and image quality, the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) sets specific initial training requirements. You must complete 40 hours of specialized education covering breast anatomy, physiology, patient positioning, equipment operation, and quality assurance. Many online programs are designed to meet this mandate, often providing the necessary ASRT-approved credits and structured education for ARRT® certification.
In addition to the didactic training, MQSA requires 25 supervised mammography examinations. This hands-on clinical component must be performed under the direct supervision of a qualified instructor and is arranged separately from the online coursework. Both the 40 hours of education and the 25 supervised exams are essential to become a qualified mammographer.
Can online courses fully prepare me for the ARRT® mammography exam?
Yes, high-quality mammography education online courses can fully prepare you for the ARRT® mammography exam. The best programs are designed to cover all topics in the ARRT® content specifications and include comprehensive registry review materials and mock exams. The proof is in the results: leading online providers report pass rates of 97-98% on the board exam, demonstrating that online learning is highly effective.
Success depends on choosing an accredited program that aligns with ARRT® requirements and your own dedication to studying the material. With the right program, you will have the tools needed to pass with confidence.
What is Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) and is training required?
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT), also known as 3D mammography, is a technology in breast imaging. Unlike 2D mammography, DBT captures multiple low-dose images from different angles, which are reconstructed into a 3D view. This allows radiologists to examine breast tissue layer by layer, reducing issues with overlapping tissue and improving cancer detection.
As DBT becomes the screening standard, the demand for trained technologists is growing. The MQSA mandates that before independently performing DBT exams, technologists must complete an initial 8 hours of training specific to the modality. This training covers equipment operation, positioning, image acquisition, and QC for 3D imaging. Many online providers offer convenient DBT training modules that fulfill this requirement. DBT training is essential for staying current in the field of breast imaging.
Conclusion
In the life-saving field of mammography, continuous learning is key. Mammography education online has transformed professional growth, offering a flexible and effective pathway to excellence that fits into your real life.
As we’ve explored, online learning allows you to study at your own pace, avoid travel costs, and balance your career and personal life. With board pass rates as high as 97-98%, these programs are proven to be effective. Investing in online courses helps you meet CE requirements, open up better job opportunities, increase your earning potential, and ultimately provide the best possible patient care.
Lifelong learning is a commitment to your patients and your career. At Scrubs CE, we understand the demands of healthcare professionals. Our platform offers ASRT-approved, self-paced courses with instant certificates to make your continuing education straightforward and stress-free.
Ready to take the next step in your mammography career? Whether you need CE credits, specialization, or initial certification prep, we have a course for you.
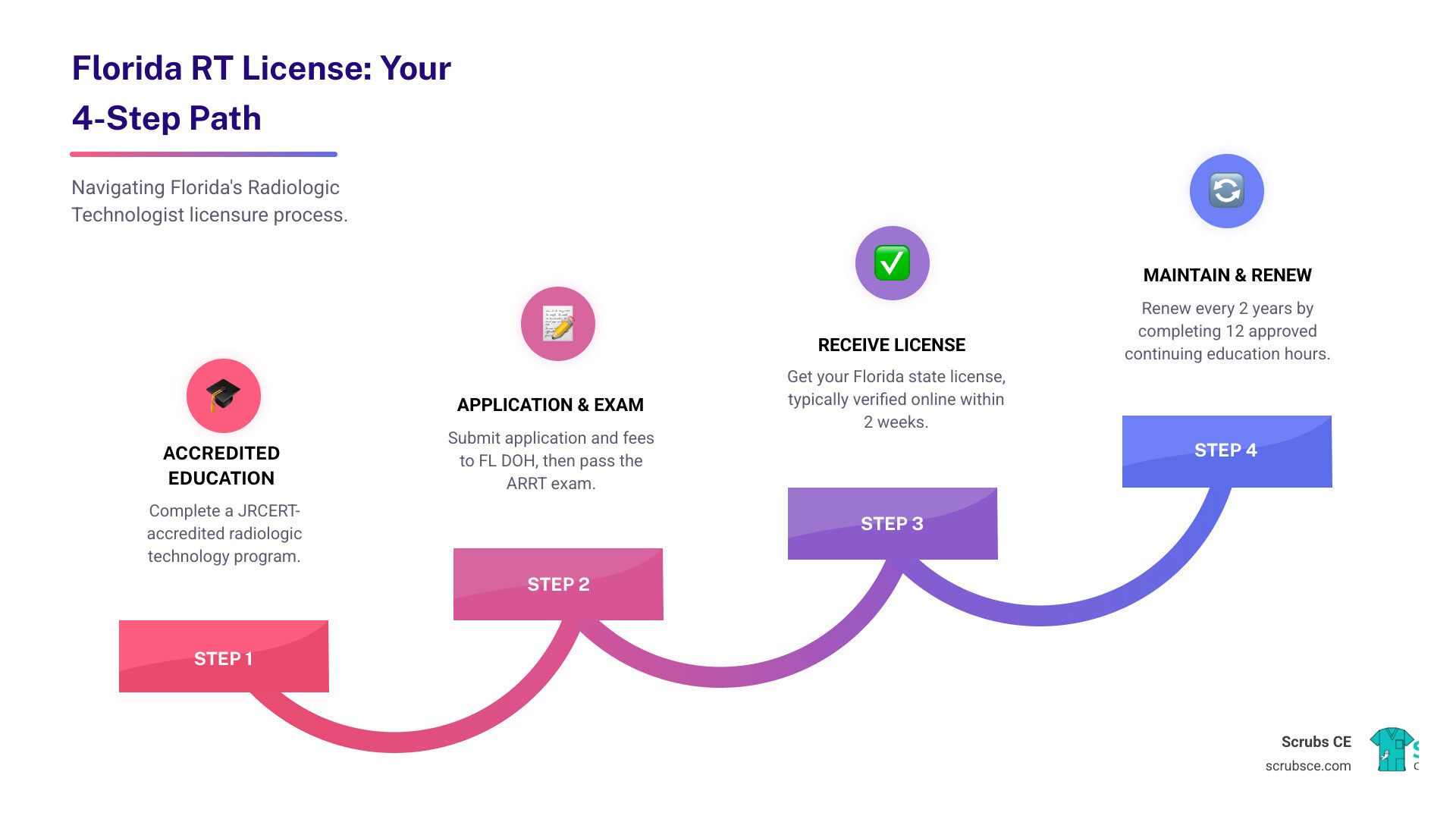
Florida Radiologic Technologist License: Requirements, Types, and More
Why Your Florida Radiologic Technologist License Matters
If you work with ionizing radiation in Florida, holding a florida license radiologic technologist certificate is mandatory. These requirements are regulated by the Florida Department of Health’s Bureau of Radiation Control, and an ARRT registration alone is not sufficient.
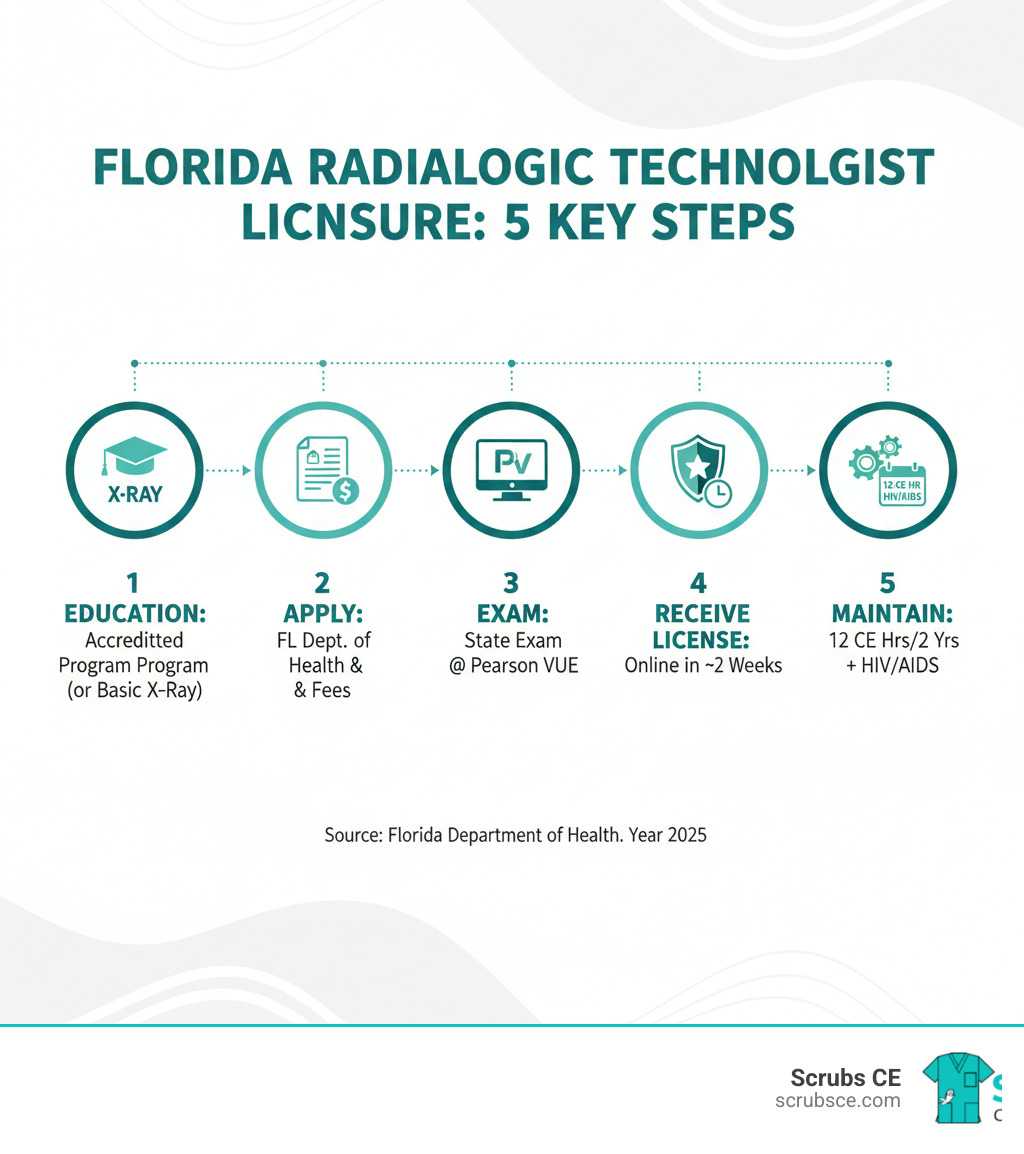
Quick Answer: To obtain a Florida radiologic technologist license, you must:
- Be at least 18 years old with a high school diploma or GED
- Complete an accredited radiologic technology program (for most certifications)
- Pass the ARRT examination or equivalent state exam
- Submit a complete application with fees to the Florida Department of Health
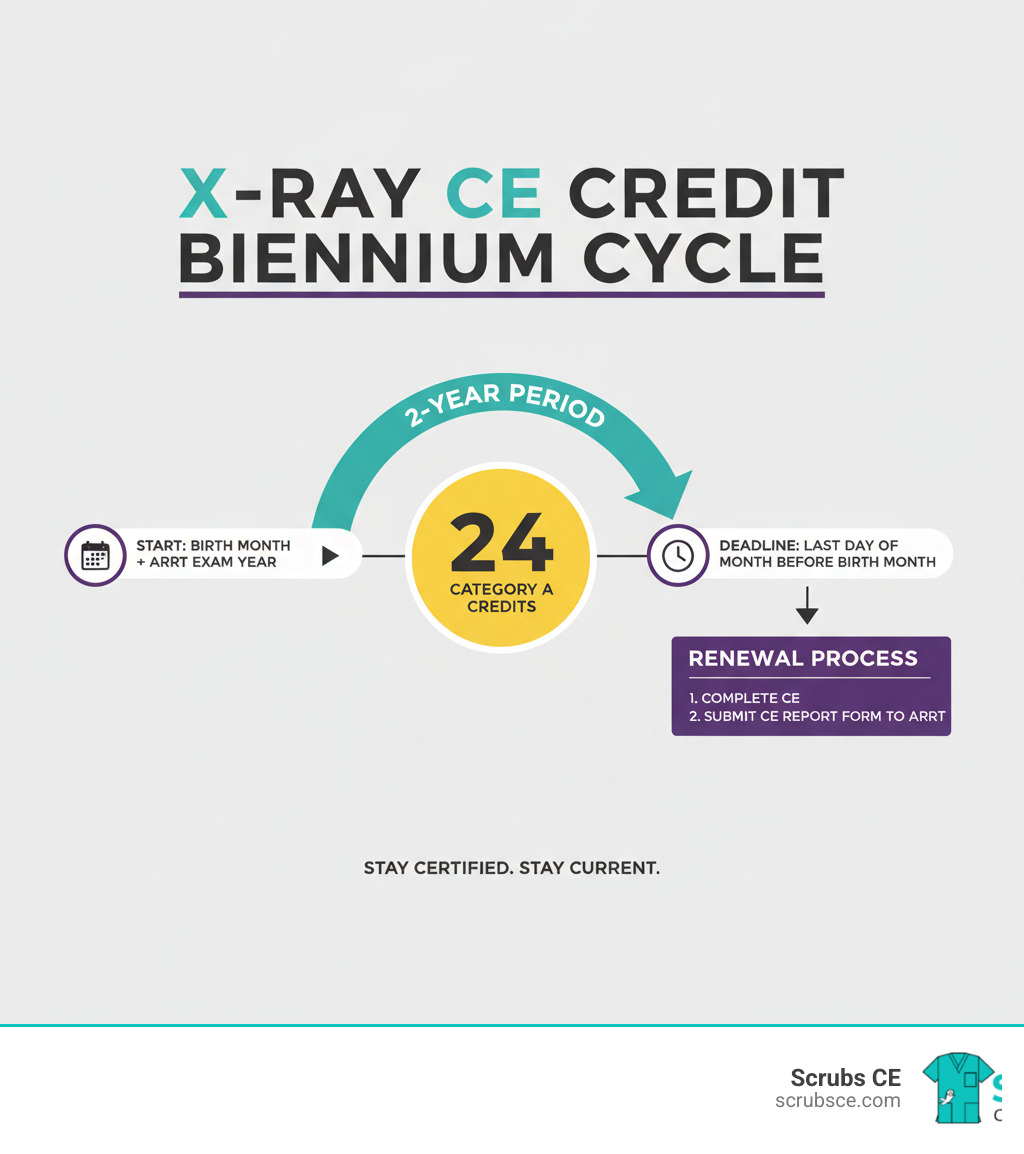
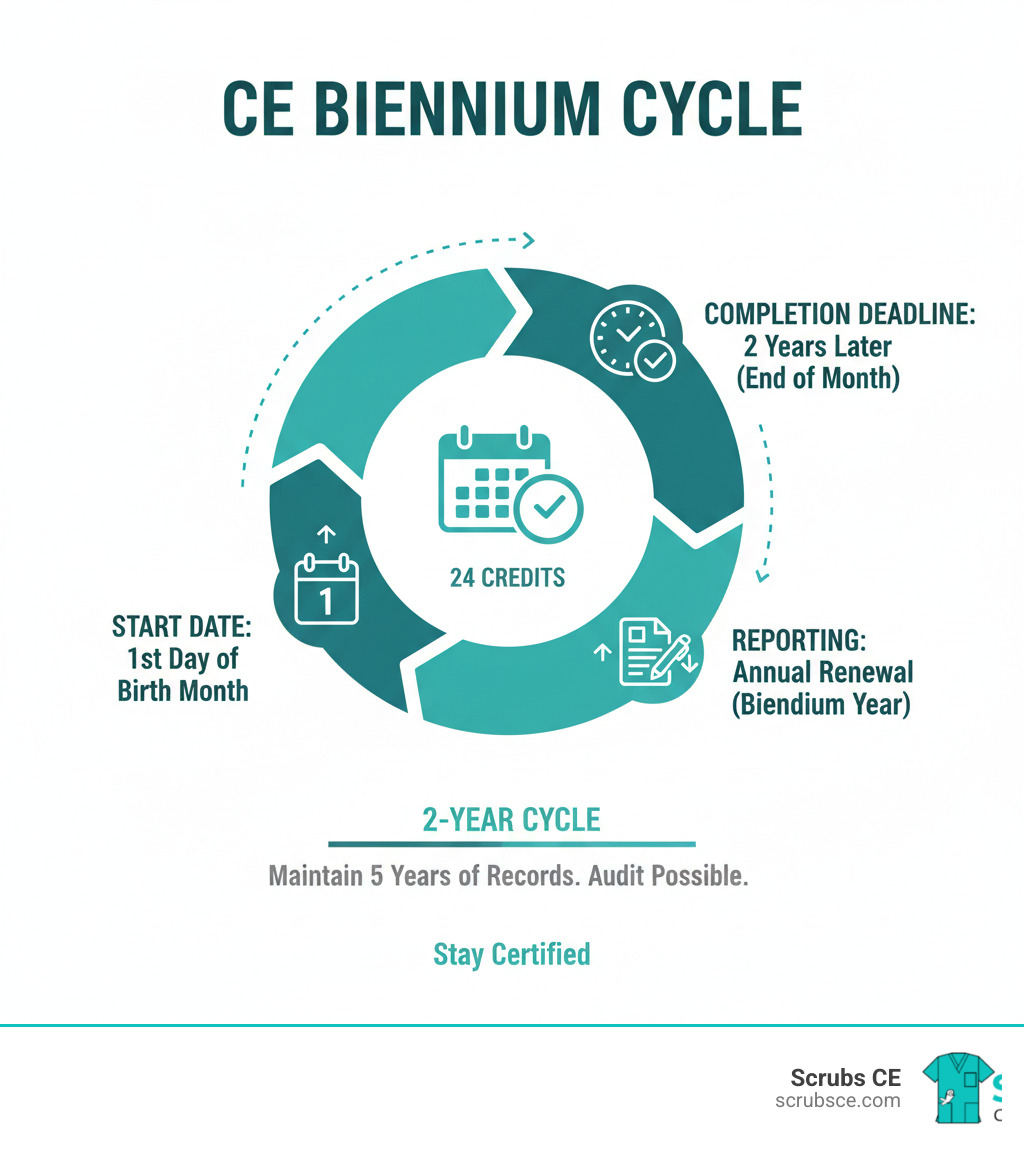
- Maintain 12 CE hours every 2 years for renewal
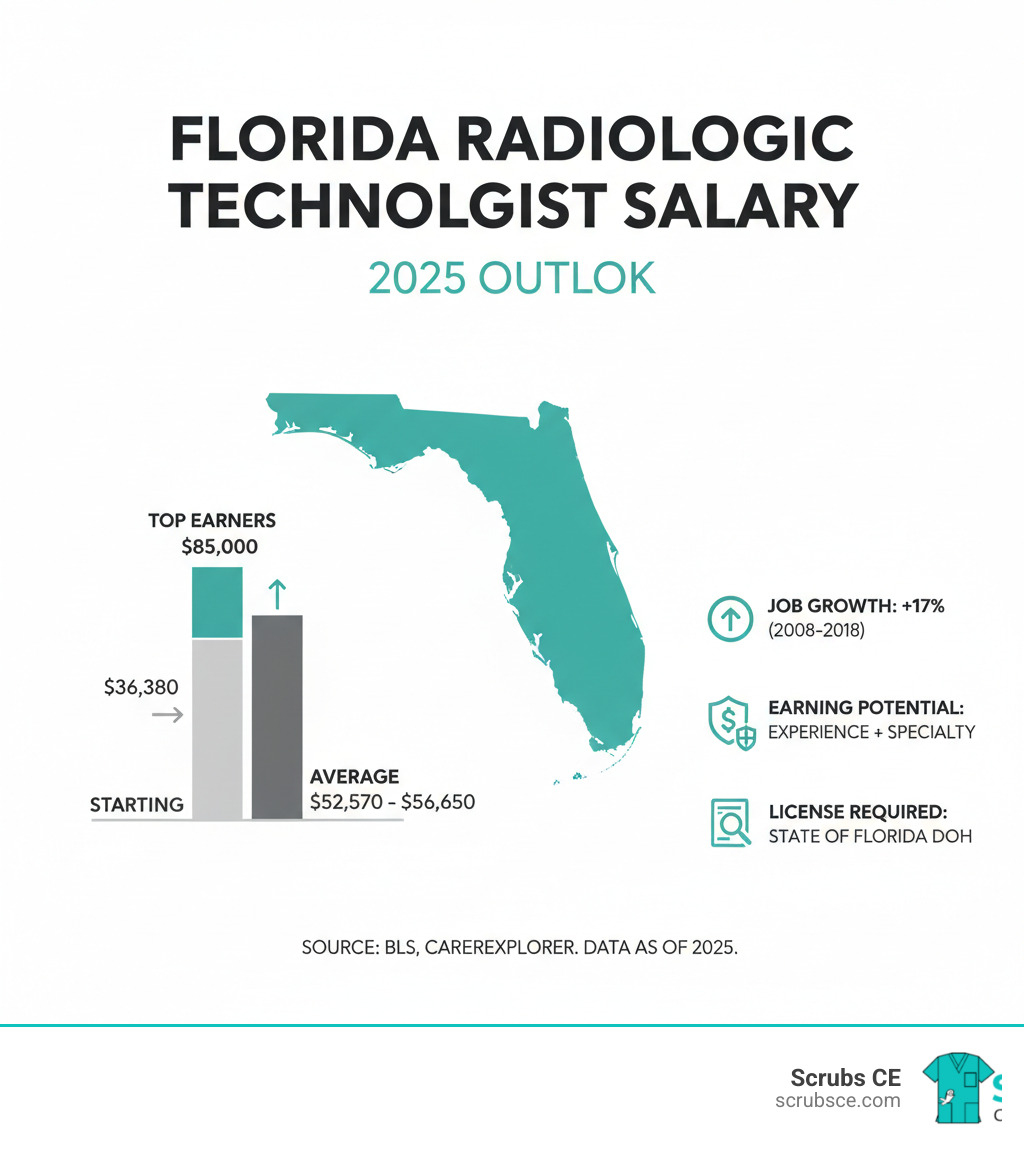
Florida has licensed radiography practitioners since 1978, and today over 27,000 professionals hold active certificates. Each certificate is valid for two years and requires continuing education for maintenance.
The demand for radiologic technologists in Florida is strong, with an average salary of $56,650 and top earners reaching $85,000 annually. With significant projected growth, it’s a promising career field.
This guide covers everything you need to know about obtaining and maintaining your Florida license, from choosing a certification to meeting renewal requirements. Understanding Florida’s specific rules is the first step, whether you’re a new graduate or transferring from another state.
Types of Radiologic Technology Certifications in Florida
Becoming a florida license radiologic technologist involves choosing a specific career path. The Florida Department of Health offers distinct certification categories for professionals working with ionizing radiation to ensure specialized expertise and patient safety. With over 27,000 active professionals in Florida, there are numerous options, each with unique training requirements and responsibilities.
Before applying, you must decide which certification fits your goals. For a detailed breakdown, see our guide: Want to Get a Florida Radiologic Technology License? 6 Types of Radiologic Technology Certification Options.
Main Certification Categories
Florida offers five primary certification categories, each representing a distinct career path.
The General Radiographer is what most people think of as a radiologic technologist. They perform a wide range of diagnostic X-ray procedures in hospitals and clinics, typically after completing a two-year accredited program.
The Basic X-Ray Machine Operator (BXMO) certificate is a more focused entry point. BXMOs work under supervision to perform specific imaging, such as podiatric or chiropractic X-rays. Educational requirements are less extensive, and you can learn more in our article How to Become a Limited License Radiologic Tech in Florida.
Nuclear Medicine Technologists administer small amounts of radioactive materials to patients and use special cameras to diagnose conditions like heart disease and cancer. This role requires a strong understanding of radiation safety and patient care.
Radiation Therapy Technologists are on the front lines of cancer treatment. They work with oncology teams to deliver targeted radiation treatments, a role that demands technical precision and compassion.
The Radiologist Assistant is the most advanced level, requiring additional education beyond initial training. They work under a radiologist’s supervision to assist with procedures and patient assessment, but they do not interpret images.
Specialty Certification Categories
Florida also recognizes three specialty certifications for focused expertise.
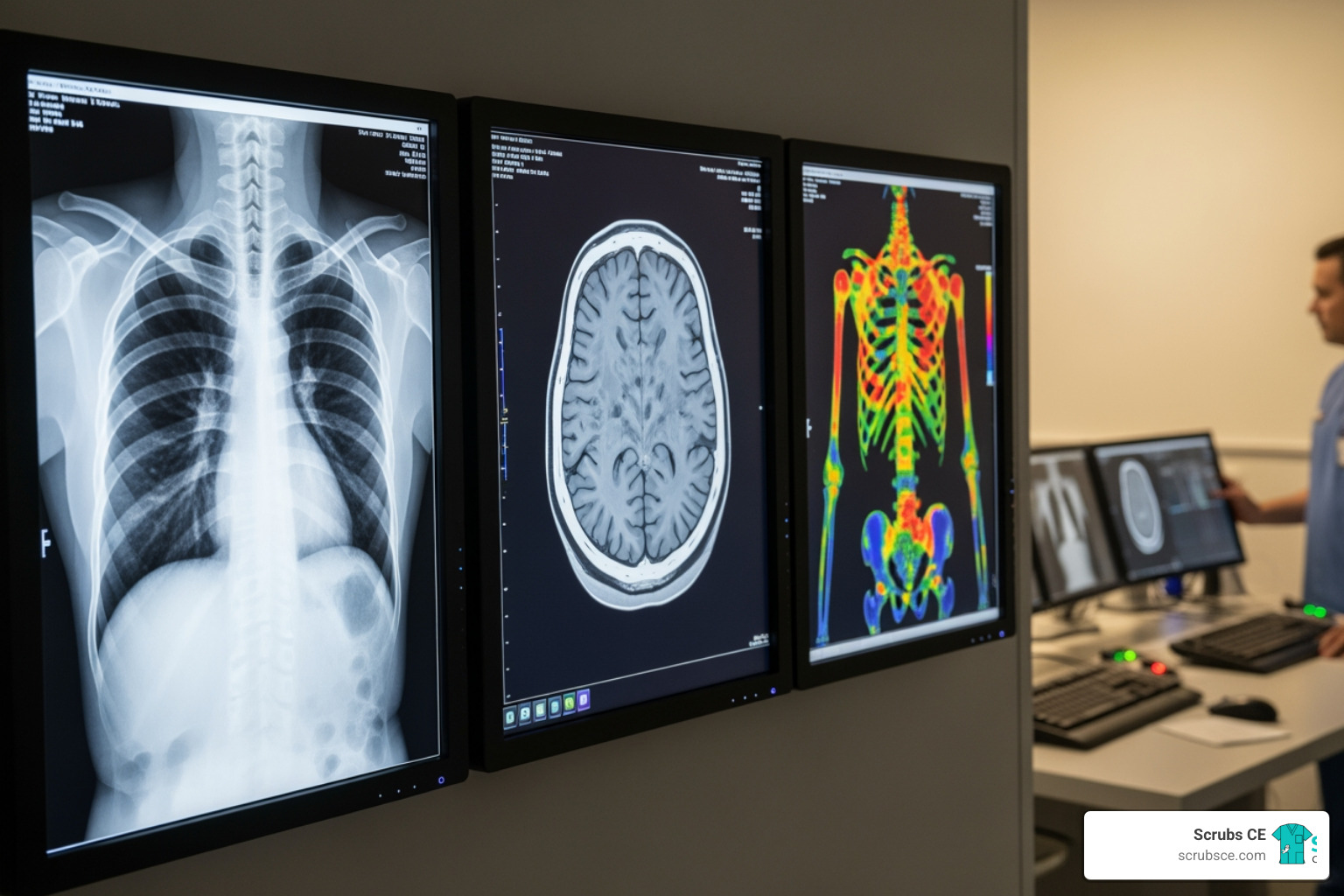
Computed Tomography (CT) specialists operate scanners that create detailed cross-sectional body images, essential for diagnosing complex diseases and injuries.
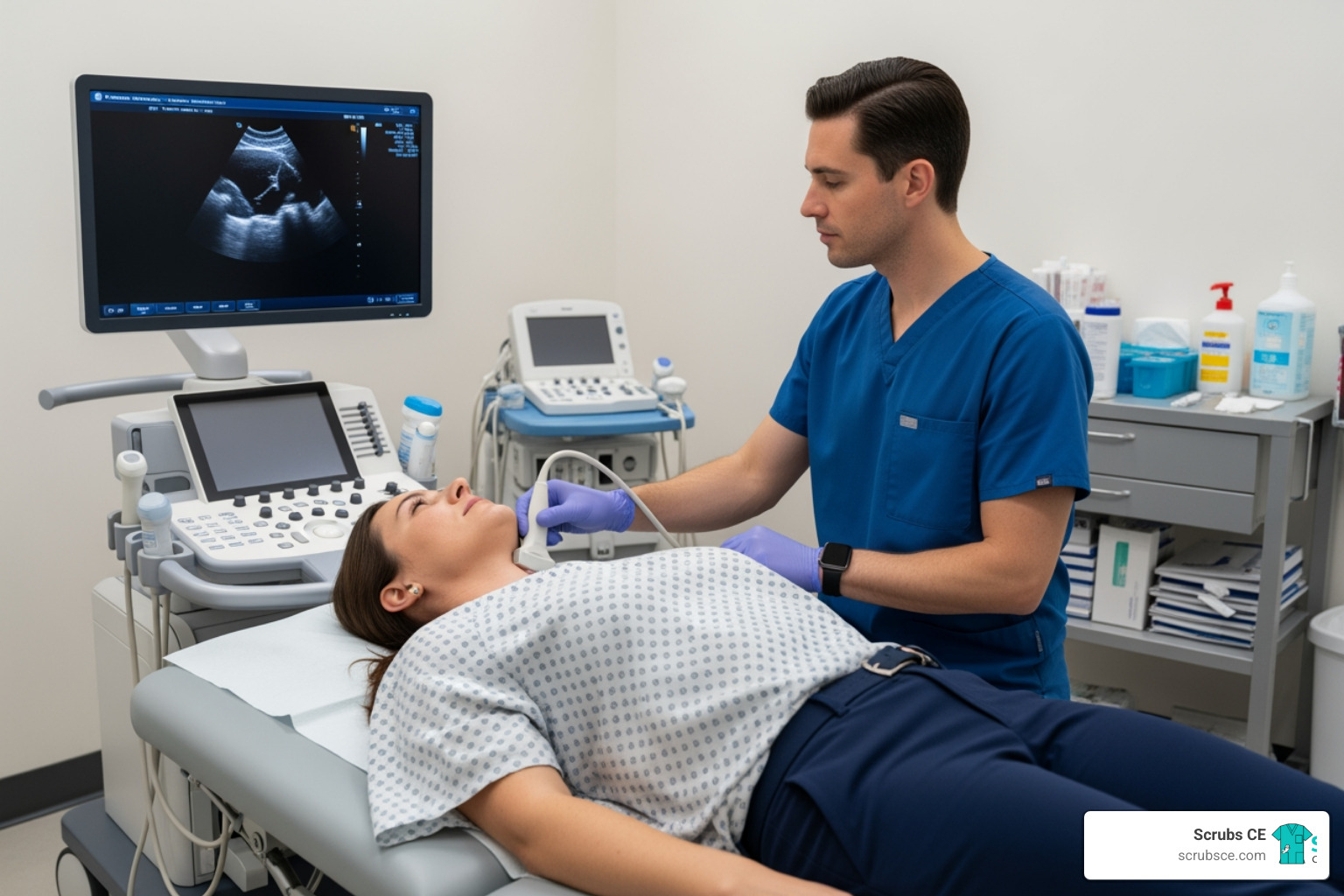
Mammography technologists perform vital breast cancer screenings. This specialty requires specific training in patient positioning and communication, as patients are often anxious.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) technologists use advanced imaging to see how organs function at a cellular level, which is valuable for detecting cancer and brain disorders. This field involves radioactive tracers and requires deep knowledge of radiation safety.
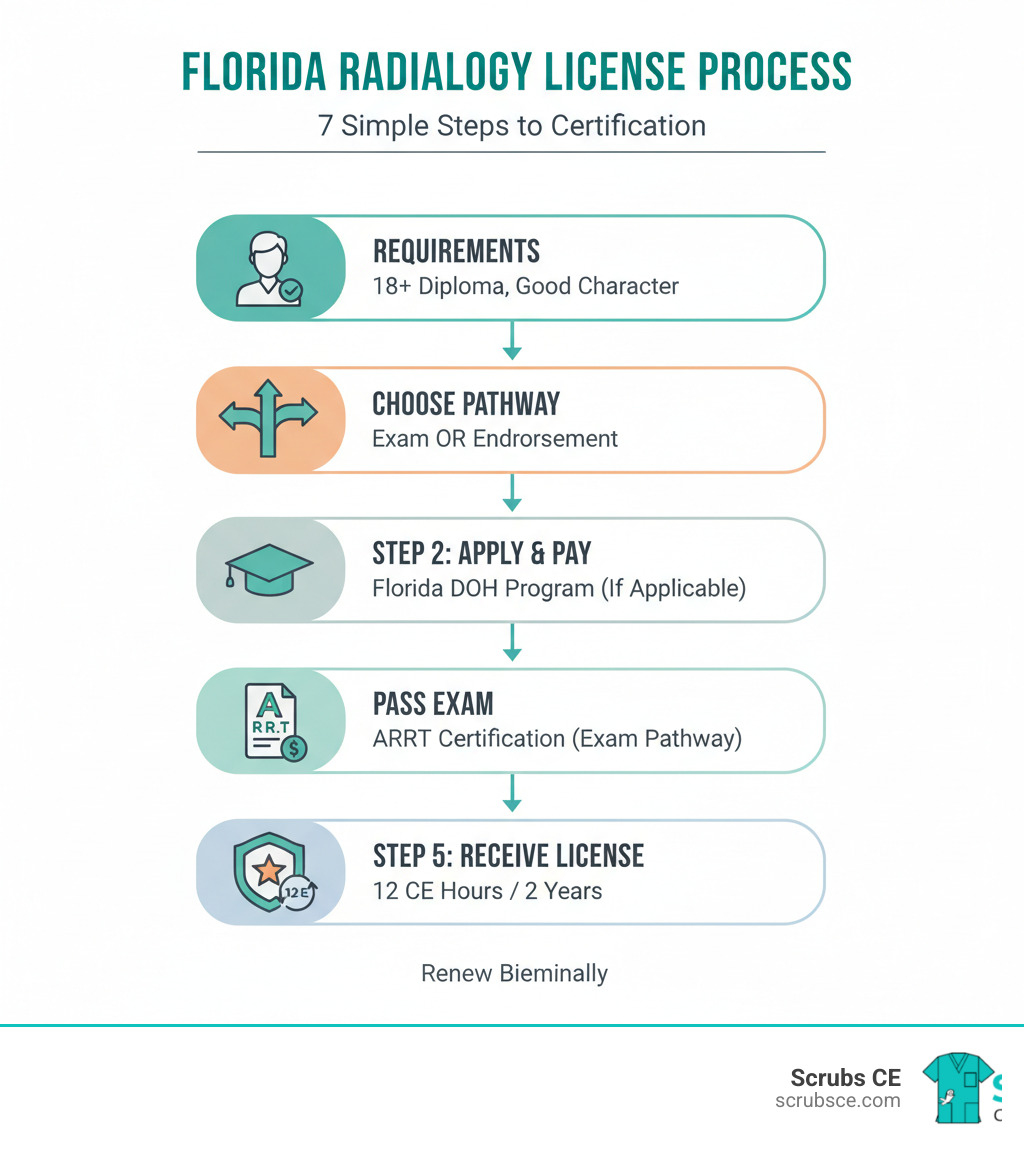
How to Get Your Florida License Radiologic Technologist
After choosing your certification path, the next step is applying for your florida license radiologic technologist. The Florida Department of Health’s Medical Quality Assurance (MQA) Services manages this process, which is straightforward once you know the requirements.
Florida offers two routes to licensure: by examination for new applicants or by endorsement for those licensed in another state. Both pathways are outlined in Florida Statutes (sections 468.304 and 468.3065). You can complete most of the process online through the MQA Online Services portal. To begin, visit Apply for a License.
Educational and Exam Requirements for a Florida License Radiologic Technologist
Education is the cornerstone of your license. Most certifications require completing an accredited program before taking the exam.
General Radiographers, Nuclear Medicine Technologists, and Radiation Therapy Technologists typically finish a two-year accredited program. Florida recognizes programs accredited by JRCERT (for radiography/radiation therapy) and JRCNMT (for nuclear medicine). These programs include extensive hands-on clinical training in patient positioning, equipment operation, and safety protocols.
Basic X-Ray Machine Operators (BXMO) have a different path. While formal programs exist, some routes involve a structured review of materials like the “Radiography Essentials for Limited Practice” textbook. Always verify current BXMO requirements with the Florida DOH. Learn more in our guide: How to Become a Limited License Radiologic Tech in Florida.
After your education, you must pass a certification exam, usually administered by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT). This includes specialty exams (CT, Mammography, PET) and the Limited Scope exam for BXMOs. Exams are held at Pearson VUE testing centers.
Applying by Examination
If this is your first certification, you’ll apply by examination. You must be at least 18, have a high school diploma or GED, and be of good moral character.
- Submit your application and fees via the Florida DOH portal. You’ll also need to provide proof of completing an approved educational program.
- Undergo a background screening. All applicants are subject to a background check. You must disclose any criminal history, as certain offenses can disqualify you. An exemption may be possible if you can demonstrate rehabilitation.
- Receive exam approval. Once your application is approved, the DOH will email you an “Exam Approval” letter with instructions.
- Register for the exam. Follow the letter’s instructions to register with ARRT or State RHC. You will be assigned a 90-day testing window.
- Schedule and take the exam. Contact Pearson VUE to schedule your appointment. On exam day, bring two forms of current, unexpired ID. One must be a government-issued photo ID with a signature (e.g., driver’s license), and the second must also have your signature (e.g., credit card). Crucially, the name on your IDs must exactly match your application name, or you may be denied entry.
For full details, review the Examination Handbook for Florida State Certification Examinations.
Applying by Endorsement
If you’re already a licensed technologist in another state, you can apply by endorsement to transfer your credentials without retaking exams.
Start by submitting your application and fees. You must prove you hold a current, active license from another jurisdiction that was based on “substantially equivalent” requirements, meaning you completed an approved program and passed an appropriate exam.
If you are registered with the ARRT or NMTCB, the process is generally straightforward. You will still need to request license verification from any other states where you have been licensed. Like all applicants, you will also undergo a background screening and must disclose any criminal or disciplinary history.
If you’re unsure if your credentials qualify, contact the Florida DOH for guidance.
Maintaining and Verifying Your License
Obtaining your florida license radiologic technologist certificate is a major achievement, but it requires ongoing maintenance. Your certificate is valid for two years and requires continuing education (CE) to keep it active. The Florida Department of Health provides online tools to manage this process.
The MQA License Verification portal is your hub for checking your expiration date, confirming CE hours, or verifying another professional’s license.
Continuing Education for Your Florida License Radiologic Technologist
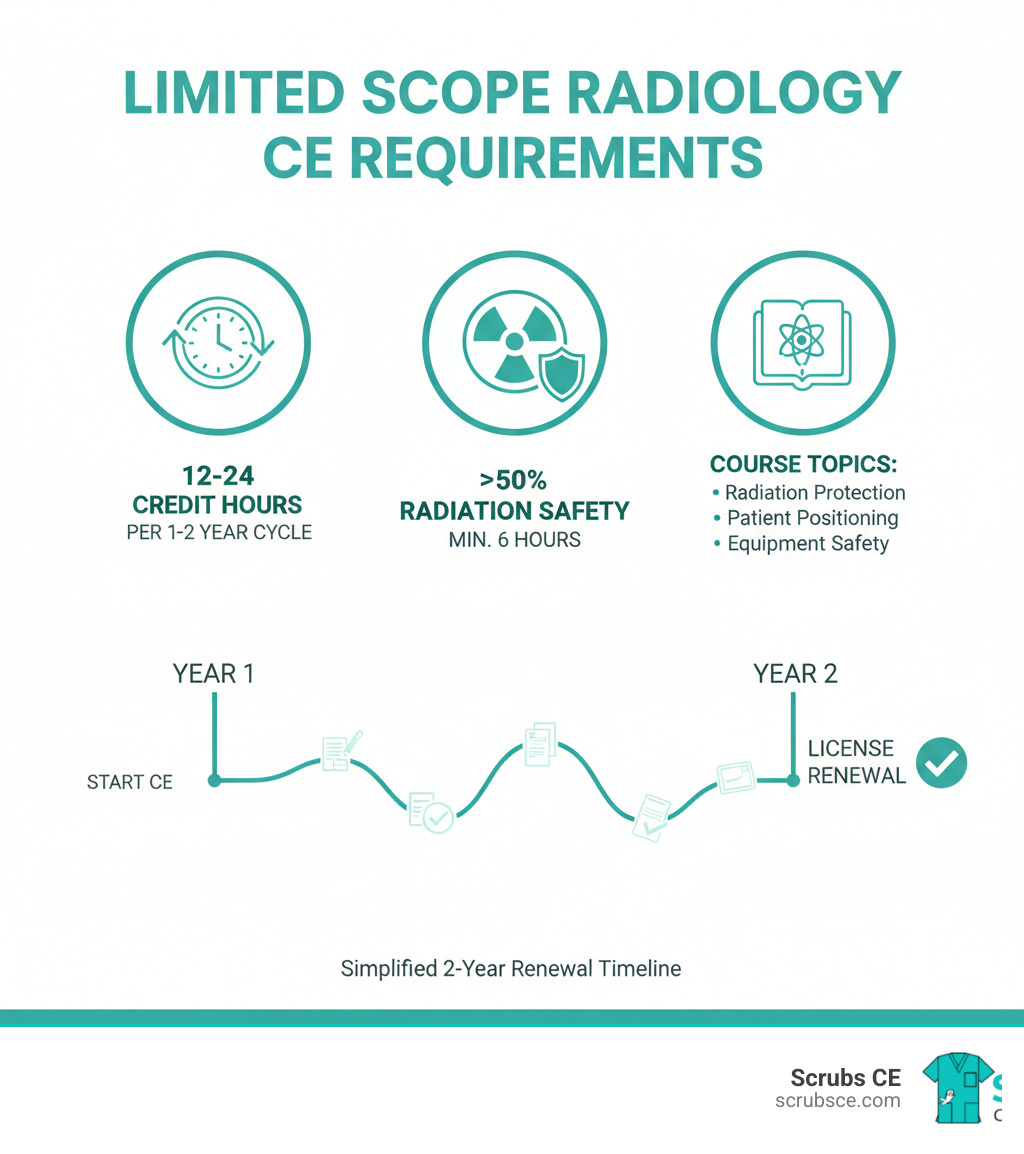
Continuing education keeps your skills sharp and ensures high-quality patient care. Florida requires 12 CE hours every two years for renewal.
These hours must come from providers approved by the Florida Department of Health. You can find a list here: Find Continuing Education (CE) and HIV/AIDS Course Providers.
The 12 hours must include:
- A minimum of 9 technical hours (e.g., radiation protection, image production).
- A maximum of 3 personal development hours (e.g., CPR, ethics).
- A required HIV/AIDS course for renewal.
When you complete a course, give the provider your Florida certificate number (not your ARRT number) for reporting. Always keep copies of your certificates for your records.
License Renewal and Reactivation
Florida’s renewal process is simple if you plan ahead. You’ll receive a renewal notice about 60 days before your certificate expires. The easiest way to renew is online through the FL HealthSource portal, where you’ll complete the application, pay fees, and confirm your 12 CE hours are on file.
Renew on time to avoid late fees. A certificate not renewed by its expiration date automatically becomes expired, and you cannot legally practice until it is reactivated.
If your certificate lapses, you can reactivate it for up to 10 years. The process is similar to renewal but requires more CE: generally 3 CE hours for every six months of inactivity, earned within the 24 months before you apply. You can also request duplicate licenses or update your name and address through your online account.
How to Verify a Florida Radiologic Technologist License
Verifying a florida license radiologic technologist is quick and easy for employers, patients, or colleagues. The state’s MQA Search Services portal promotes transparency.
Go to Verify a License and search by name, license number, or profession. The results show the license status (e.g., CLEAR/Active, Expired), expiration date, original issue date, and certification category. Any disciplinary actions are also publicly listed.
The portal also displays the total CE hours received for the current renewal cycle, allowing technologists and employers to confirm compliance. This system builds trust and protects the public.
Career Outlook and Professional Regulations in Florida
As a florida license radiologic technologist, you can expect a robust job market and solid earning potential. The field is growing due to advancing technology and Florida’s aging population. However, this opportunity comes with the responsibility of adhering to strict professional regulations designed to protect patients.
Salary and Career Growth in Florida
Radiologic technologists in Florida earn an average salary of $56,650 per year, with a typical range between $36,380 and $71,290. With experience and specialty certifications, the top 20% of earners can make up to $85,000 annually. Salaries can vary by location within the state.
The growth outlook is strong. Florida’s workforce projections have historically shown high demand, with a 17% growth forecast between 2008 and 2018. The underlying factors driving this growth—an aging population and advancing medical technology—remain, indicating a continued need for qualified professionals.
For a detailed salary breakdown across different Florida regions, check out the CareerExplorer salary data.
Important Regulations and Updates
Your florida license radiologic technologist is your legal authority to work with ionizing radiation, and the state enforces its rules strictly.
Practicing without a license in Florida is illegal. Administering ionizing radiation to humans without a valid state certificate is a crime with severe penalties, including fines and being barred from future licensure. The Department of Health actively investigates unlicensed activity.
If you suspect someone is practicing without a license or witness other violations, you should report it through the state’s confidential complaint portal: Filing a complaint. Provide as much detail as possible to help protect patients and uphold professional standards.
A technical note: ARRT no longer supports Internet Explorer. To access ARRT websites, use a modern browser like Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox, or Safari.
Finally, a key distinction: MRI and ultrasound technologists do not need a Florida license. State law (Chapter 468, Part IV) only covers professionals using ionizing radiation. Since MRI and ultrasound do not, they fall outside this regulation. Employers may still require national certifications (like ARRT for MRI or ARDMS for ultrasound), but this is a facility policy, not a state mandate.
Frequently Asked Questions about Florida Radiologic Technologist Licensing
Navigating licensing requirements can raise many questions. Here are answers to some of the most common ones about getting and maintaining your florida license radiologic technologist certification.
Do MRI or Ultrasound Technologists need a license in Florida?
No, MRI and Ultrasound Technologists do not need a state license in Florida. State law (Chapter 468, Part IV, F.S.) only regulates professionals who use ionizing radiation. Since MRI (magnetic fields) and ultrasound (sound waves) do not use ionizing radiation, they are not licensed by the Florida Department of Health. However, employers often require national certifications like ARRT (for MRI) or ARDMS (for ultrasound) as a condition of employment.
How long does it take to get a license after passing the exam?
After passing your exam, it typically takes about two weeks for the Florida Department of Health to process the results and issue your license. You can start working as soon as your license status appears as “Active” on the state’s online verification portal, even before your physical certificate arrives in the mail. You can check your status anytime at Verify a License. Processing may take slightly longer around holidays.
Can I get CE credit for passing a post-primary ARRT exam?
Yes. Passing a post-primary examination with the ARRT or NMTCB (such as for CT, Mammography, or PET) during your renewal cycle earns you twelve contact hours of continuing education credit. This is enough to satisfy your entire two-year requirement. You must submit proof of passing the exam to the Florida Department of Health to receive the credit. It’s an excellent way to advance your career while staying compliant with renewal requirements.
Conclusion
Obtaining and maintaining your florida license radiologic technologist certificate requires careful attention to state requirements, but it opens the door to a rewarding career in a thriving field. We’ve covered the key steps: choosing a certification, applying by examination or endorsement, and fulfilling ongoing renewal duties like the 12 biennial CE hours.
Florida’s regulations exist to ensure high standards of patient safety, and your compliance demonstrates a commitment to professional excellence. With competitive salaries and strong job growth, your license is a valuable asset in the Sunshine State’s healthcare community.
When it’s time to renew, Scrubs CE is here to help. We offer convenient, Florida-approved courses with instant certificates and affordable pricing, designed for busy professionals.
Ready to fulfill your continuing education requirements? Explore Florida-approved CE courses to maintain your license and keep your career moving forward with confidence.
The Beat Goes On: Mastering Cardiology Through CME
Why Cardiology CME Matters for Your Professional Journey
Cardiology cme is continuing medical education focused on cardiovascular medicine that helps healthcare professionals maintain licensure, stay current with clinical advances, and improve patient outcomes.
Quick Overview: Your Cardiology CME Options
- Online Courses – Self-paced learning with hundreds of CME credits available.
- Live Events – In-person conferences and virtual meetings with networking opportunities.
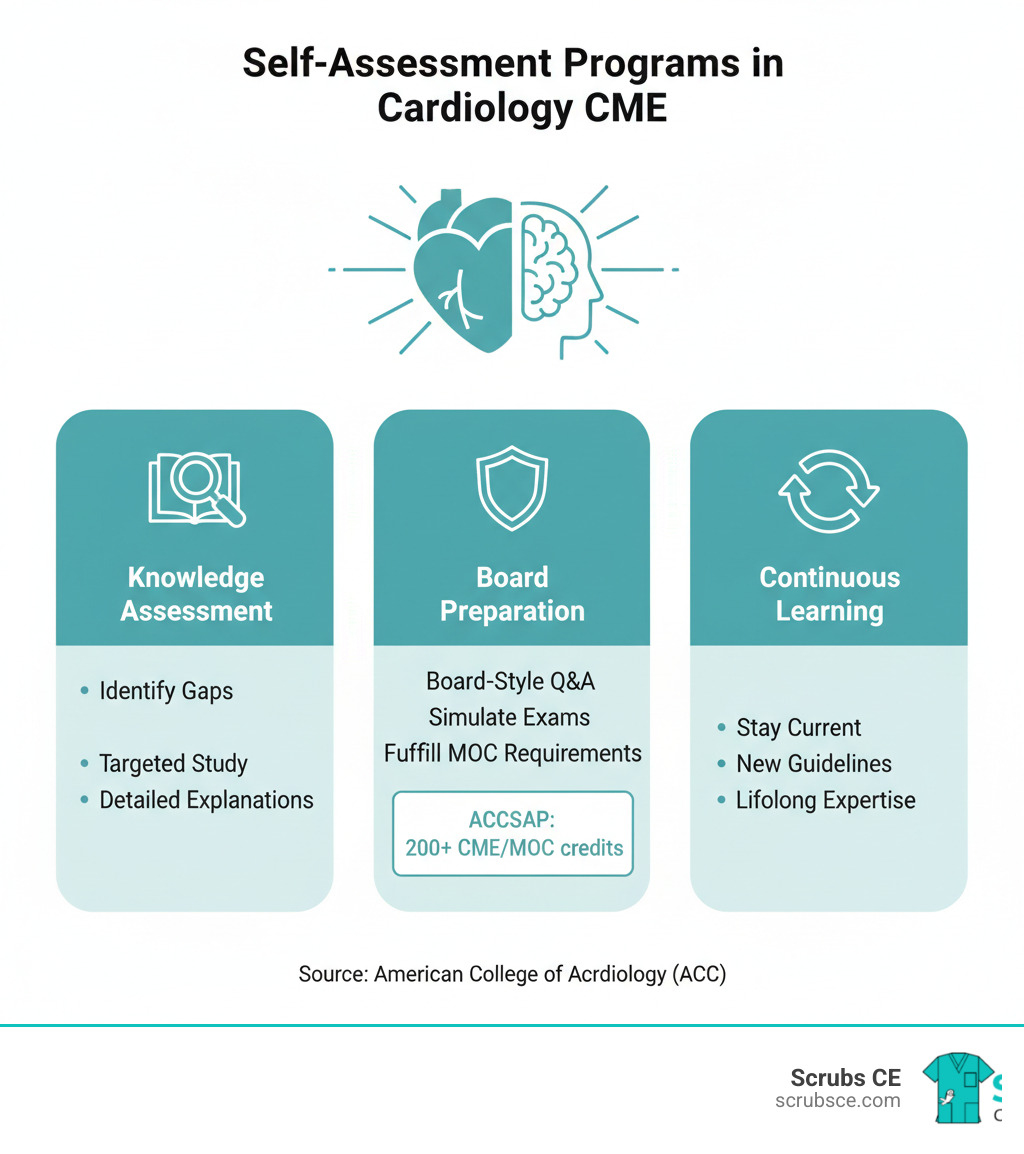
- Self-Assessment Programs – Board preparation tools offering CME/MOC credits.
- Free Options – Webinars, archived grand rounds, and journal activities.
- Mobile Learning – Apps and on-demand video libraries for learning on the go.
- Specialized Topics – Interventional cardiology, electrophysiology, heart failure, imaging, and more.
Cardiovascular medicine changes fast as new treatment guidelines emerge and clinical trials reshape how we manage heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and coronary disease. The challenge is finding time to learn while managing a demanding patient schedule. The solution is a landscape of flexible, accredited educational options designed for busy healthcare professionals.
Whether you’re a cardiologist preparing for board recertification, a nurse practitioner expanding your cardiovascular skills, or a primary care provider managing cardiac patients, cardiology CME keeps you sharp. It’s not just about checking boxes for licensure—it’s about providing better care and advancing your career. Platforms like Scrubs CE make it easy to access courses that fit your schedule and budget.
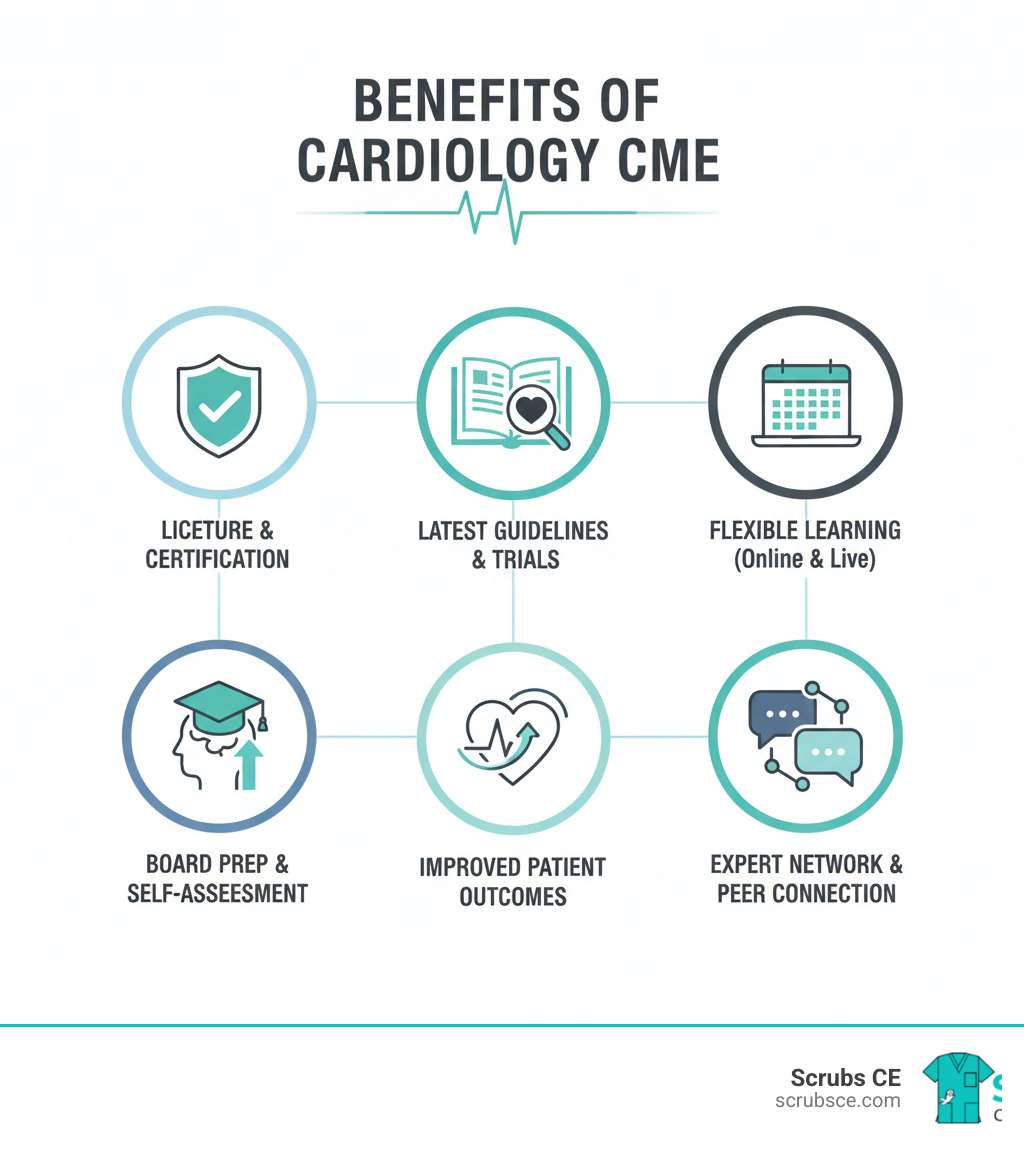
Why Cardiology CME is Essential for Your Career
Let’s be honest—when you’re managing a full patient schedule, tracking down CME credits can feel like a chore. But cardiology cme isn’t just another box to check. It’s what keeps us sharp, keeps our licenses active, and ultimately keeps our patients safe.
Continuing education is the foundation of your practice. Without it, your medical license is at risk, as every state has its own requirements for hours and credit types. Beyond state licensure, board certification adds another layer with Maintenance of Certification (MOC) requirements. These are designed to ensure we maintain our expertise. The good news is that many cardiology cme activities count toward both state requirements and MOC points.
Most importantly, staying current with cardiovascular medicine directly impacts patient care. New treatment guidelines, clinical trials, and novel therapies emerge constantly. Understanding these advances helps you make better decisions for your patients. Resources like Cardiology Secrets 5th Ed. Test Only E-Mailed can help you reinforce core concepts while earning the credits you need.
The Benefits of Staying Current
Practicing cardiology without current education is like using an outdated GPS. The field moves fast, and patient safety depends on up-to-date knowledge. Understanding the latest clinical trials and guidelines for managing complex cases like heart failure and arrhythmias helps you optimize outcomes. It’s about applying the best available evidence to help your patients live longer, healthier lives. For example, the role of SGLT2 inhibitors in heart failure has become a game-changer, an advance you might miss without ongoing cardiology cme. Staying current means you’re confident implementing new guidelines and technologies.
Meeting Board and State Requirements
Keeping track of requirements can feel overwhelming. Your state medical board sets specific CME mandates, which can vary widely in hours and topics. For board-certified cardiologists, the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) requires ongoing learning to maintain certification. Many cardiology cme activities offer MOC points alongside traditional credits, making it easier to meet both requirements.
Credit tracking is crucial. Keep organized records of every course, certificate, and credit statement. Platforms like Scrubs CE simplify this by providing instant certificates you can download and file. Viewing continuing education as an investment in your career and patients—rather than a chore—makes it a priority. With flexible online options, staying compliant doesn’t have to disrupt your practice.
Navigating the Landscape of Cardiology CME/CE Content
The beauty of modern cardiology cme is its variety. Whether you prefer learning late at night or thrive on the energy of a conference, there’s a format that fits your life.
Online Courses and Self-Paced Learning
For most busy professionals, online courses are a perfect fit due to their unbeatable flexibility. You can tackle a module during lunch, finish a chapter before rounds, or take a test after hours. Modern platforms offer video lectures, interactive case studies, and mobile-friendly e-books. You work at your own pace, replaying complex topics as needed.
Scrubs CE specializes in this model, offering quality education without the hassle. You complete your course, pass the test, and get an instant certificate. For those diving into specialized areas, resources like Cardiac Imaging The Requisites E-Book Test offer focused learning.
Live and Virtual Learning Opportunities
While self-paced learning is convenient, live events offer real-time interaction. Conferences and workshops provide direct access to expert faculty for Q&A and hands-on practice. The networking is also invaluable, connecting you with colleagues who share your challenges.
Virtual meetings have bridged the gap, offering expert sessions and live interaction without the travel. Many organizations now offer hybrid events, so geography doesn’t limit your access to top-tier education. Scrubs CE also hosts webinars and virtual events, combining online convenience with live engagement.
Key Topics in Modern Cardiology Education
The scope of cardiovascular medicine is vast, and cardiology cme reflects that. Key areas of focus include:
- Interventional Cardiology: Covering techniques from basic catheterization to complex interventions. Resources like the Cardiac Catheterization Handbook offer comprehensive guidance.
- Electrophysiology (EP): Managing atrial fibrillation, device therapy, and complex arrhythmias.
- Heart Failure (HF): Understanding guideline-directed medical therapy and new medications like SGLT2 inhibitors.
- Prevention: Focusing on hypertension, lipid optimization, and lifestyle interventions.
- Cardiac Imaging: Interpreting echocardiograms, nuclear studies, cardiac CT, and MRI.
- Emerging Topics: Including cardio-oncology, valvular heart disease, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and health equity.
The breadth of available CME allows you to focus on your specific interests and practice needs, ensuring you can find educational activities that match your career goals.
The Role of Professional Organizations and Self-Assessment
Think of professional organizations and self-assessment programs as your personal GPS and fitness tracker. They guide you through cardiology cme while showing you where you’re strong and where you need more work.
Staying Connected with Professional Communities
Joining professional societies connects you to a network of peers who face the same challenges and share the same passion for patient care. The benefits go beyond CME credits, offering access to prestigious journals, networking at conferences, and a collective voice in shaping healthcare policy. Being part of a larger community can be uplifting and professionally rewarding.
Mastering Knowledge with Self-Assessment
Self-assessment programs are sophisticated learning tools that reveal your knowledge gaps. By working through board-style questions with detailed explanations, you can identify areas that need review and focus your learning where it matters most.
These programs are excellent for board preparation and often fulfill MOC requirements. Many organizations offer specialty-specific self-assessment programs that provide substantial CME and MOC credits. They feature questions written by experts, comprehensive rationales, and current references to deepen your understanding. Scrubs CE also offers self-assessment modules and practice tests to help you identify areas for improvement while earning credits on your schedule.
Lifelong Learning and Maintenance of Certification
Lifelong learning doesn’t have to be a burden. When woven into your practice, it becomes an ongoing conversation with your field. Many certification bodies are moving toward a continuous learning model, where instead of cramming for an exam every ten years, you focus on specific areas annually. This approach feels more manageable and stays relevant to your daily practice.
This shift recognizes that we learn best by engaging with new information regularly and applying it to real patients. When you can access educational content on demand—through platforms like Scrubs CE—you can learn when you’re most motivated. This transforms MOC from a checkbox exercise into genuine professional development, helping you become the best clinician you can be.
Finding and Accessing the Right Cardiology CME for You
With so many cardiology cme options, finding the right courses can feel overwhelming. But with a clear game plan, you can find exactly what you need to keep your credentials current and your skills sharp.
How to Find Courses and Meet State Requirements
First, understand your specific needs. Check your state medical board and specialty board websites for their exact requirements. Knowing your targets saves you from scrambling later.
Next, explore your options.
- Online Catalogs: The Scrubs CE course catalog lets you browse convenient, affordable options. You can filter by credit type (CME, CNE, AAPA, CPE) and specialty to zero in on relevant topics.
- Professional Societies: These organizations are treasure troves of quality education, offering extensive online learning catalogs.
- Academic Medical Centers: University hospitals often host scientific sessions and grand rounds, many of which are now available online.
Platforms like Scrubs CE simplify the process with high-quality, self-paced courses and instant certificates.
Are There Free Cardiology CME Options?
Yes, and you don’t have to sacrifice quality. While comprehensive courses have a cost, many excellent no-cost cardiology cme opportunities exist.
- Webinars: Professional organizations regularly host complimentary webinars on timely topics like new guideline updates.
- Archived Grand Rounds: Many academic institutions provide free online CME credits through their archived presentations.
- Journal-based Activities: Medical journals frequently offer free online CME linked to published articles.
While free options are great for supplementing your education, always verify they provide the type of accredited credit you need for your specific state and board requirements.
Future Trends in Cardiology CME
The future of medical education is evolving rapidly.
- Personalized Learning: Artificial intelligence is beginning to shape personalized learning paths that analyze your practice patterns and recommend specific courses to fill knowledge gaps.
- Mobile & Microlearning: Education is becoming truly portable, with a trend toward short, focused modules you can complete in just a few minutes between patients.
- Immersive Technologies: Virtual and augmented reality are on the horizon, promising hands-on learning for complex procedures in a risk-free environment.
- Health Equity: Courses are increasingly addressing cultural competence, bias mitigation, and strategies for reducing cardiovascular health disparities.
- Interdisciplinary Content: Expect more content on topics like cardio-oncology and cardio-obstetrics, reflecting an integrated approach to patient care.
Learning is becoming more accessible, engaging, and relevant. Whether you prefer traditional online courses from platforms like Scrubs CE or are eager to explore new technologies, the educational tools at your disposal will only get better.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cardiology CME
Let’s tackle some of the most common questions about cardiology cme.
How many CME credits do I need for cardiology?
There’s no single answer. Credit requirements vary significantly by your state medical board and specialty certification body. Most physicians need between 20 to 50 CME hours annually, but this can vary. Some states require a certain number of Category 1 credits or mandate training in specific topics like ethics or pain management.
For Maintenance of Certification (MOC), some pathways require focused learning over a multi-year cycle. Self-assessment programs can offer a substantial number of CME/MOC credits. The best advice is to check with your specific state medical board and certification body for their exact requirements.
Can I use online cardiology CME for my MOC requirements?
Yes, many online activities are fully approved for Maintenance of Certification (MOC) points. Self-assessment programs and journal-based activities are often designed to provide both CME and MOC credits.
The key is to look for explicit MOC approval before starting a course. Reputable providers will clearly state if the activity is approved for MOC by the relevant board (typically ABIM MOC for cardiologists). Always verify before investing your time, and use MOC approval as a filter when browsing courses on platforms like Scrubs CE.
What’s the difference between CME and CE?
This distinction is simple but important.
- CME (Continuing Medical Education) is specifically for physicians (MDs, DOs).
- CE (Continuing Education) is the broader term for all healthcare professions. It breaks down into specific types, such as CNE for nurses, AAPA credits for physician assistants, and CPE for pharmacists.
It’s crucial to get the right type of credit for your license. A nurse needs CNE, not CME. Many educational platforms, including Scrubs CE, offer courses that provide multiple credit types, which is convenient for interdisciplinary teams. Always double-check that your credential type is listed before starting a course.
Conclusion
Your journey through cardiovascular medicine doesn’t end—it evolves with every patient encounter, every clinical breakthrough, and every hour of learning you invest. Cardiology cme represents far more than checking off boxes for licensure. It’s about waking up each day knowing you’re equipped with the latest knowledge to make life-changing decisions for your patients.
Think about it: when you understand the newest heart failure guidelines, you’re not just memorizing protocols—you’re potentially adding years to someone’s life. When you master the latest interventional techniques through continuing education, you’re giving a patient the chance to walk their daughter down the aisle. That’s the real power of lifelong learning in cardiology.
The landscape of cardiovascular education has never been more accessible or diverse. Whether you prefer the flexibility of self-paced online courses, the energy of live conferences, or the focused preparation of self-assessment programs, there’s a path that fits your schedule and learning style. The key is making that commitment to continuous growth, not just for your career, but for every patient who trusts you with their heart health.
At Scrubs CE, we get it. We know you’re juggling patient care, family commitments, and the constant pressure to stay current. That’s why we’ve built our platform around your needs—offering convenient, affordable online courses that deliver high-quality education without the hassle. You can earn your credits on your schedule, get instant certificates, and get back to what matters most: caring for patients.
Your professional development deserves the same attention and care you give your patients every day. Whether you’re exploring advanced cardiac imaging, refreshing your knowledge on heart failure management, or branching into related specialties, investing in education is investing in excellence.
Ready to expand your learning beyond cardiology? Explore our Nuclear Medicine Continuing Education courses and find how convenient continuing education can be.
Don’t Get Zapped: Mastering Your Texas Radiology CEU Credits
Why Texas Radiology CEU Matters for Your License Renewal
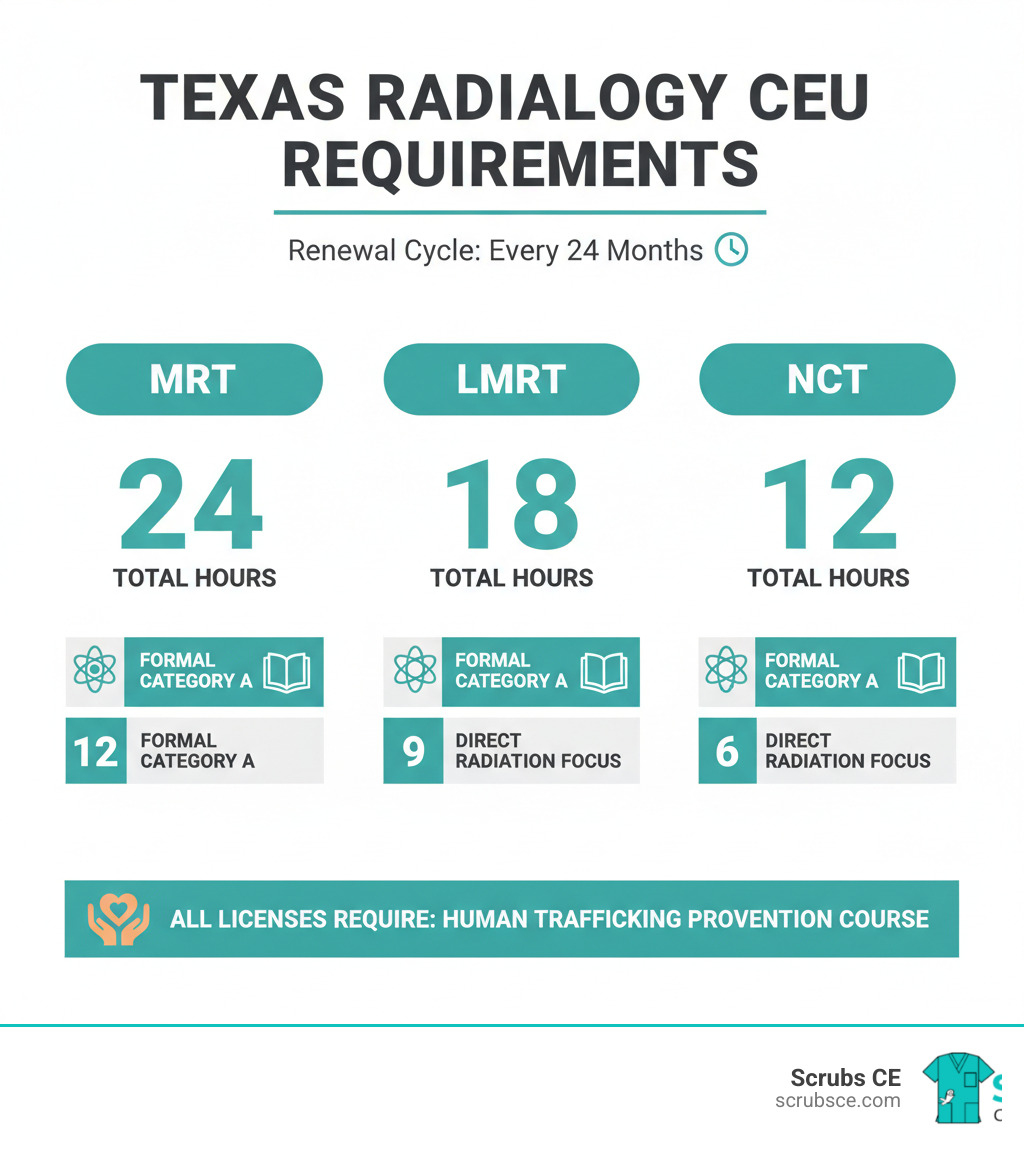
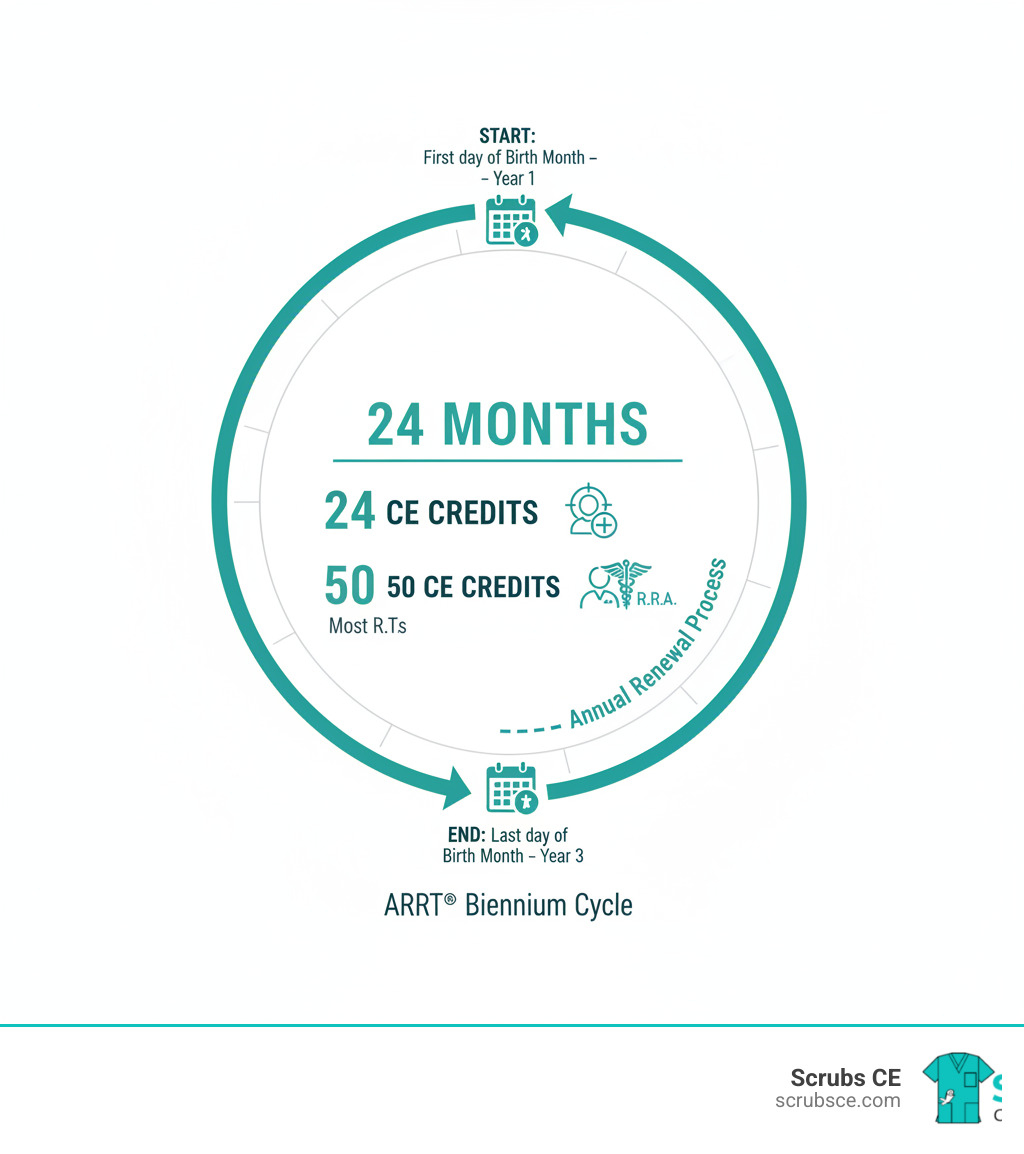
Texas radiology CEU is the continuing education you need to keep your radiologic technologist license active in Texas. Every 24 months, you must complete specific hours of approved courses to renew with the Texas Medical Board.
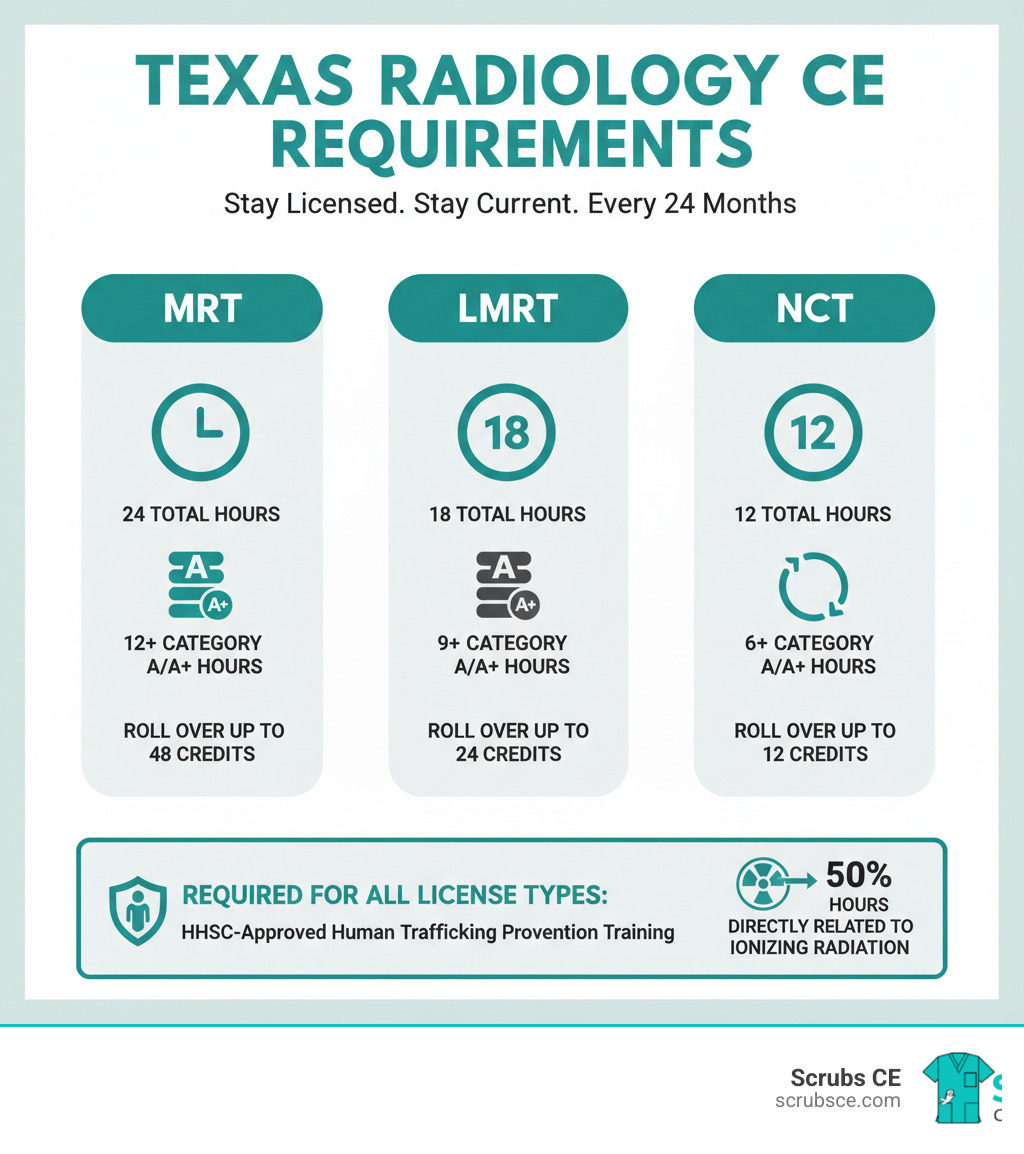
Quick Requirements by License Type:
| License Type | Total CE Hours | Formal Category A Hours | Direct Radiation Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRT (Medical Radiologic Technologist) | 24 hours | At least 12 hours | At least 12 hours |
| LMRT (Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist) | 18 hours | At least 9 hours | At least 9 hours |
| NCT (Non-Certified Technician) | 12 hours | At least 6 hours | At least 6 hours |
Plus: All license types must complete a mandatory human trafficking prevention course.
If you’re juggling shifts, patient care, and family responsibilities, finding time for continuing education probably feels like one more thing on an already packed to-do list. But here’s the good news: Texas has eliminated the requirement for in-person or live webinar courses. You can now complete your CEUs entirely online, on your own schedule.
The Texas Medical Board sets clear rules about what counts toward your renewal. At least 50% of your CE hours must focus on ionizing radiation for diagnostic imaging or treatment. That means courses on radiation safety, anatomical positioning, CT techniques, and mammography applications. The other half can cover broader topics like patient care, ethics, or computer applications in radiology.
Understanding these requirements upfront saves you from last-minute scrambling when your renewal date approaches. Let’s break down exactly what you need to know.
Understanding Your Texas Radiology CEU Requirements by License Type
Think of your Texas radiology CEU requirements like a prescription—the right dose depends on your specific license type. The Texas Medical Board (TMB) sets different continuing education requirements for Medical Radiologic Technologists (MRTs), Limited Medical Radiologic Technologists (LMRTs), and Non-Certified Technicians (NCTs).
Your license renewal runs on a biennial cycle, which is just a fancy way of saying every 24 months. During this two-year period, you’ll need to complete a specific number of CE hours based on your license type. The TMB’s Board Rule 186.19 spells out these requirements in detail, covering not just how many hours you need, but also what types of courses count.
The good news? The TMB has made life easier by eliminating the requirement for in-person or live webinar courses. You can now complete all your continuing education online, on your own schedule—whether that’s during your lunch break or at 11 PM in your pajamas.
Here’s how the requirements break down across license types:
| License Type | Total CE Hours | Formal Category A/A-plus Hours | Direct Ionizing Radiation Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRT (Medical Radiologic Technologist) | 24 hours | At least 12 hours | At least 12 hours |
| LMRT (Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist) | 18 hours | At least 9 hours | At least 9 hours |
| NCT (Non-Certified Technician) | 12 hours | At least 6 hours | At least 6 hours |
Notice the pattern? No matter which license you hold, at least 50% of your total CE hours must focus on ionizing radiation. This ensures you’re staying sharp on the core skills that matter most in your daily work.
Medical Radiologic Technologist (MRT) Requirements
As a Medical Radiologic Technologist, you’re looking at 24 CE hours every two years. This is the most common license type in Texas, and it comes with the most comprehensive continuing education requirements.
Of those 24 hours, at least 12 must be formal Category A or A-plus credits. These formal courses have been evaluated by an ARRT-recognized RCEEM (Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism) or RCEEM-plus. Organizations like the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT) provide this evaluation, which guarantees the courses meet professional standards.
The other critical piece is that at least 12 hours must directly relate to ionizing radiation for diagnostic imaging or medical treatment. This includes courses on radiation safety, CT techniques, fluoroscopy, mammography applications, and anatomical positioning. These are the bread-and-butter topics that keep you competent in your core responsibilities.
The remaining 12 hours can cover broader professional topics like patient care, ethics, medical terminology, or computer applications in radiology. This balanced approach keeps you well-rounded while ensuring you maintain expertise in radiation-related skills.
Looking for courses that check all these boxes? Our Radiology CE Courses are designed specifically to meet Texas requirements while helping you grow professionally.
Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist (LMRT) Requirements
If you hold an LMRT license, your requirements reflect your more focused scope of practice. You’ll need 18 total CE hours per biennium, with at least 9 hours coming from formal Category A or A-plus courses.
Just like MRTs, you need at least 50% of your hours—that’s a minimum of 9 hours—focused on ionizing radiation for diagnostic imaging or medical treatment. These radiation-focused hours should also be formal credits, ensuring you’re getting high-quality instruction in the specialized areas where you practice.
The beauty of the current rules is their flexibility. While formal courses are required, you’re no longer tied to attending in-person sessions or logging into live webinars at specific times. You can complete your entire CE requirement through self-paced online courses that fit around your work schedule and personal life.
This makes it much easier to stay current without sacrificing your weekends or taking time off work. You can spread your learning throughout the 24-month period instead of cramming everything in at the last minute.
Non-Certified Technician (NCT) Requirements
Non-Certified Technicians have the most streamlined requirements, but they’re no less important. You’ll need 12 total CE hours every two years to maintain your license.
Following the same 50% rule, at least 6 hours must focus on ionizing radiation for diagnostic imaging or medical treatment. These 6 hours need to be formal Category A or A-plus courses, ensuring you’re getting properly evaluated content even with the reduced hour requirement.
Even though NCTs typically work within a more limited scope, the TMB still requires regular refreshers on radiation safety and application. This protects both you and your patients by making sure everyone working with ionizing radiation maintains current knowledge.
The biennial renewal cycle applies to you too, so pacing yourself throughout the 24-month period is smart. With online learning, you can knock out a course here and there as your schedule allows. No need to block out entire days or travel anywhere—just log in, learn, and download your certificate when you’re done.
The Nitty-Gritty: Course Content and Special Mandates
Now that we’ve covered the basics of how many hours you need, let’s talk about what actually counts toward your Texas radiology CEU requirements. The Texas Medical Board doesn’t just care about quantity—they’re equally focused on making sure your continuing education genuinely improves your skills and keeps patients safe.
Think of it this way: you wouldn’t accept a poorly positioned X-ray, and the TMB won’t accept just any course for your license renewal. There are specific rules about course content, mandatory state requirements, and limits on certain types of learning. Let’s bring all of this into sharp focus.
The Mandatory Human Trafficking Prevention Course
Here’s something every Texas radiologic technologist needs to know, regardless of whether you’re an MRT, LMRT, or NCT: you must complete a human trafficking prevention course to renew your license. This requirement came from House Bill 2059, passed by the 86th Legislature, and it applies to all healthcare professionals who provide direct patient care.
This isn’t just another box to check. As healthcare providers, we’re often the first people who might notice signs of trafficking in vulnerable patients. The training equips us to recognize these signs and know how to respond appropriately.
The good news is that this course counts toward your total CE hours, even if it comes from a provider that isn’t ARRT-recognized. The Texas Health and Human Services Commission (HHSC) approves these courses, and many are available for free. For renewals on or after September 1, 2020, this became a non-negotiable requirement.
We recommend tackling this requirement early in your renewal cycle. You can find an approved Human Trafficking Prevention Training course through the HHSC website. It’s usually quick to complete and provides genuinely valuable information for your practice.
Directly vs. Indirectly Related Topics for your Texas radiology CEU
Here’s where the TMB gets specific about content. 50% Rule we mentioned earlier? At least half of your required CE hours must be directly related to ionizing radiation for diagnostic imaging or medical treatment. This ensures you’re continuously sharpening the core skills that define our profession.
Directly related topics are the courses that make you better at what you do every day in the imaging suite. These include radiation safety and protection, radiation biology and physics, anatomical positioning and radiographic exposure technique, and emerging imaging modalities like advanced CT or interventional radiology techniques. Patient care that’s specifically associated with radiologic procedures counts here, as does anything involving radio-pharmaceuticals, contrast media, computer applications in radiology systems, mammography applications, nuclear medicine applications, and radiation therapy applications.
These are the courses that keep you current with technology and techniques, making you a more skilled and confident technologist.
Indirectly related topics still support your professional growth, but they’re not specifically about ionizing radiation. No more than 50% of your required hours can come from these areas. These might include general patient care skills, basic computer literacy, communication and ethics courses, management and administration training, or broader medical sciences topics. While these courses are valuable for your overall development as a healthcare professional, the TMB wants to ensure you’re spending most of your CE time on your core competencies.
The balance makes sense when you think about it. You need to be an expert in radiation and imaging, but you also need to communicate well with patients, work effectively with your team, and understand the ethical dimensions of your work. For the official TMB definition and complete list of what counts as directly versus indirectly related content, check the TMB definition of CE content.
Formal vs. Self-Study: Understanding the Limits
The TMB also sets rules about how you earn your Texas radiology CEU hours. There’s an important distinction between formal credits and self-study, and understanding this difference will save you headaches at renewal time.
At least 12 hours for MRTs, 9 hours for LMRTs, and 6 hours for NCTs must come from formal courses designated as Category A or Category A-plus credits. These courses have been evaluated by an ARRT-recognized RCEEM (Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism) or RCEEM-plus. Organizations like the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT) provide this evaluation, ensuring the courses meet rigorous quality standards.
Self-study courses offer wonderful flexibility for busy professionals, but there’s a cap. No more than 12 hours in your two-year renewal period can come from self-study or courses not approved for formal CE. So if you’re an MRT needing 24 total hours, you could do 12 hours of self-study, but the other 12 must be formal Category A credits. For LMRTs needing 18 hours, that’s 9 formal and up to 9 self-study. For NCTs needing 12 hours, that’s 6 formal and up to 6 self-study.
Here’s the great news: the TMB eliminated the requirement for in-person or live webinar courses. Your formal Category A credits can now be earned entirely online through approved providers, as long as they meet the quality standards. You get structured, evaluated education without sacrificing the convenience of learning on your own schedule.
If you’re ready to knock out those formal credit requirements with courses that fit your busy life, explore X-Ray Radiology Continuing Education options designed specifically for Texas radiologic technologists. We make staying compliant simple, so you can focus on what you do best—taking care of patients.
How to Fulfill Your Texas and National CEU Requirements Simultaneously
If you’re like most radiologic technologists in Texas, you probably hold both your state license and a national certification from the ARRT®. Here’s something that’ll make your life easier: you don’t have to complete separate continuing education for each one. With smart planning, the same courses can satisfy both your Texas radiology CEU requirements and your national certification needs. It’s the ultimate professional efficiency move.
Finding Approved Texas Radiology CEU Courses
The secret to dual compliance is choosing courses from recognized continuing education providers whose offerings meet both Texas Medical Board standards and ARRT® requirements. When a course earns Category A or A-plus credits from an ARRT®-recognized evaluation mechanism like the ASRT, it typically satisfies Texas’s formal credit requirements too.
Look for courses that clearly state their approval status. The provider should specify that their courses are approved as Category A or A-plus by ARRT®-recognized third-party accreditation mechanisms. This designation means the courses have undergone rigorous review and meet established quality standards. As long as the content aligns with Texas’s requirements, particularly that 50% ionizing radiation focus we discussed earlier, you’re covering both bases with one course.
The Texas Medical Board has partnered with CE Broker to help licensees find, track, and report continuing education more easily. This platform can be a helpful starting point, though you’ll always want to verify courses meet all TMB requirements, especially that critical ionizing radiation content rule.
Online providers offer the flexibility most of us desperately need. You can complete courses between shifts, during quiet evenings at home, or even during your lunch break. No travel required, no rigid schedules to juggle. We’ve designed our courses at Scrubs CE with exactly this kind of flexibility in mind. Our Texas radiology CEU courses are self-paced, accessible anytime, and you receive instant certificates upon completion. To make your planning even simpler, check out our Radiology CE Course Combos where we’ve bundled complementary courses that work perfectly together for both state and national requirements.
Tracking and Documentation: Staying Audit-Ready
Here’s something important: while the TMB doesn’t require you to submit CE certificates with your renewal application, they absolutely do conduct random audits. And if your name comes up, you’ll need to produce documentation quickly. Think of good record-keeping as your insurance policy against renewal headaches.
The Texas Medical Board requires you to keep proof of completion for at least two renewal periods, which typically means four years. Your certificates of completion are your primary evidence. Make sure each one clearly shows the course title, provider name, completion date, and the number of CE hours with their category designation.
Beyond certificates, consider keeping course descriptions or outlines. If an auditor questions whether a course meets the “directly related” criteria for ionizing radiation content, having the course outline readily available can resolve the issue immediately. A simple personal log tracking all your completed CEUs with dates, hours, and topics makes everything easier to reference.
The TMB Online Renewal Portal is where you’ll manage your license renewal. You won’t upload documentation there unless specifically requested during an audit, but it’s good to familiarize yourself with the portal before your renewal deadline approaches.
Smart documentation practices start with redundancy. Keep digital copies of your certificates in multiple places: your computer, cloud storage like Google Drive or Dropbox, and even email copies to yourself. Print physical backups and store them in a dedicated folder. Technology fails, files get corrupted, and computers crash at the worst possible moments. Multiple backup copies mean you’re covered no matter what happens.
Make sure everything you save is clearly dated. If you’re planning to carry over excess credits to your next renewal period (yes, you can do that, and we’ll cover it in the FAQ section), document those carefully with notes about which renewal period they’re intended for. The two-year limit on carry-over credits means you need to track when you earned each credit.
Staying organized might feel like extra work now, but it takes maybe an hour to set up a good system. Compare that to the stress of scrambling during an audit or, worse, facing delays in your license renewal because you can’t locate your documentation. The peace of mind alone is worth it, and you’ll breeze through any audit that comes your way.
Frequently Asked Questions about Texas Radiology CEUs
We’ve covered a lot of ground, but you might still have some specific questions buzzing in your head. These are the questions we hear most often from radiologic technologists across Texas, and we want to make sure you have clear, straightforward answers about your Texas radiology CEU requirements.
Can I carry over extra CE hours to the next renewal period?
Here’s some good news for the overachievers among us: yes, you absolutely can carry forward excess CE credits to your next biennial renewal period! If you’ve completed more than your required hours, those extra credits don’t just vanish into thin air.
The Texas Medical Board allows you to roll forward a maximum of 48 total excess credit hours, but these can only be applied to your immediate subsequent renewal period. In other words, you can’t stockpile credits indefinitely – they’re only good for the next two-year cycle.
There’s one important exception to keep in mind: the mandatory human trafficking prevention course cannot be carried forward as an excess credit. You’ll need to complete this required course fresh for each renewal period, even if you’ve done it before. Think of it as a regular refresher on this critical public health issue.
So if you attended an amazing conference that gave you extra credits, or if you got a little too enthusiastic browsing through CE courses one weekend, those hours will serve you well next time around. Just make sure you document them properly and use them within that two-year window.
Do I need to send my CE certificates when I renew my license?
This question comes up constantly, and the answer is refreshingly simple: no, you do not need to send copies of your CE certificates with your registration renewal.
When you log into the TMB Online Renewal Portal to renew your license, you’ll attest that you’ve completed the required CE hours. The Board trusts you initially, and that’s the end of it for most people.
But – and this is a big but – the TMB conducts random audits after each registration period. If your license number comes up in the audit lottery, or if Board staff send you a written request for documentation, you’ll need to provide your certificates of completion promptly. This is exactly why we emphasize keeping meticulous records. Those certificates should be filed away safely, easily accessible if you need them.
Think of it like keeping your old tax returns. You probably won’t need them, but if the IRS comes knocking, you’ll be really glad you saved them. Same principle applies here with your CE documentation.
Are there any exemptions from CE requirements?
Life doesn’t always go according to plan, and the Texas Medical Board recognizes that sometimes circumstances genuinely prevent you from completing your continuing education. Exemptions do exist, but they’re granted on a case-by-case basis and require you to submit a written request to TMB explaining your situation.
The most common reasons for exemption include experiencing a catastrophic illness or injury that prevented you from fulfilling your CE obligations, serving in extended military service abroad, or maintaining extended residency abroad where you couldn’t access appropriate courses. The Board also considers other extenuating circumstances under a “good cause shown” category, which gives them flexibility to evaluate unique situations.
Exemptions aren’t automatic or permanent. You’ll need to provide supporting documentation along with your written request, and approvals are typically limited to one registration period. If your circumstances continue into the next renewal cycle, you’ll need to apply again.
Most of us, thankfully, won’t need to pursue an exemption. But it’s reassuring to know that the Board has provisions for those truly difficult situations when completing your Texas radiology CEU simply isn’t possible through no fault of your own.
Conclusion: Power Up Your Career with Compliant CE
You’ve made it through the maze of Texas radiology CEU requirements, and honestly, that’s half the battle! Now you understand exactly what you need: the specific hours for your license type, the critical 50% rule about ionizing radiation content, the mandatory human trafficking prevention course, and the balance between formal and self-study credits. You know how to keep records that’ll save you during an audit, and you’ve got answers to those nagging questions about carry-over credits and exemptions.
Here’s the beautiful truth: staying compliant doesn’t have to feel like a burden. The Texas Medical Board’s decision to eliminate in-person CE requirements means you can complete everything online, on your schedule. Whether you’re winding down after a long shift, enjoying a quiet Sunday morning, or squeezing in learning during your lunch break, you have the flexibility to make continuing education work for your life.
This isn’t just about maintaining your license, though that’s certainly important. Every course you complete sharpens your skills, updates your knowledge base, and ultimately makes you a better healthcare provider for your patients. When you understand the latest radiation safety protocols or refine your positioning techniques, you’re investing in excellence. That’s something to feel good about.
At Scrubs CE, we built our platform with busy healthcare professionals like you in mind. Our self-paced courses mean you’re never rushing to catch a live webinar or scrambling to find childcare for an in-person class. Complete a module, get your instant certificate, and move on with your day. Simple as that. We’ve taken the stress out of the equation so you can focus on what matters: learning and growing in your profession.
Whether you’re working in general radiography, specializing in mammography, or expanding your skills into new modalities, we’ve got courses designed to meet your needs and keep you compliant. Ready to knock out those CEU requirements? Fulfill your requirements with our Mammography CE Courses or explore our complete catalog of radiology offerings. We’re here to support your journey every step of the way. Your career deserves it, and so do you!
How to Renew Florida Radiology License in 3 Easy Steps
Why Timely Radiology License Renewal in Florida Matters
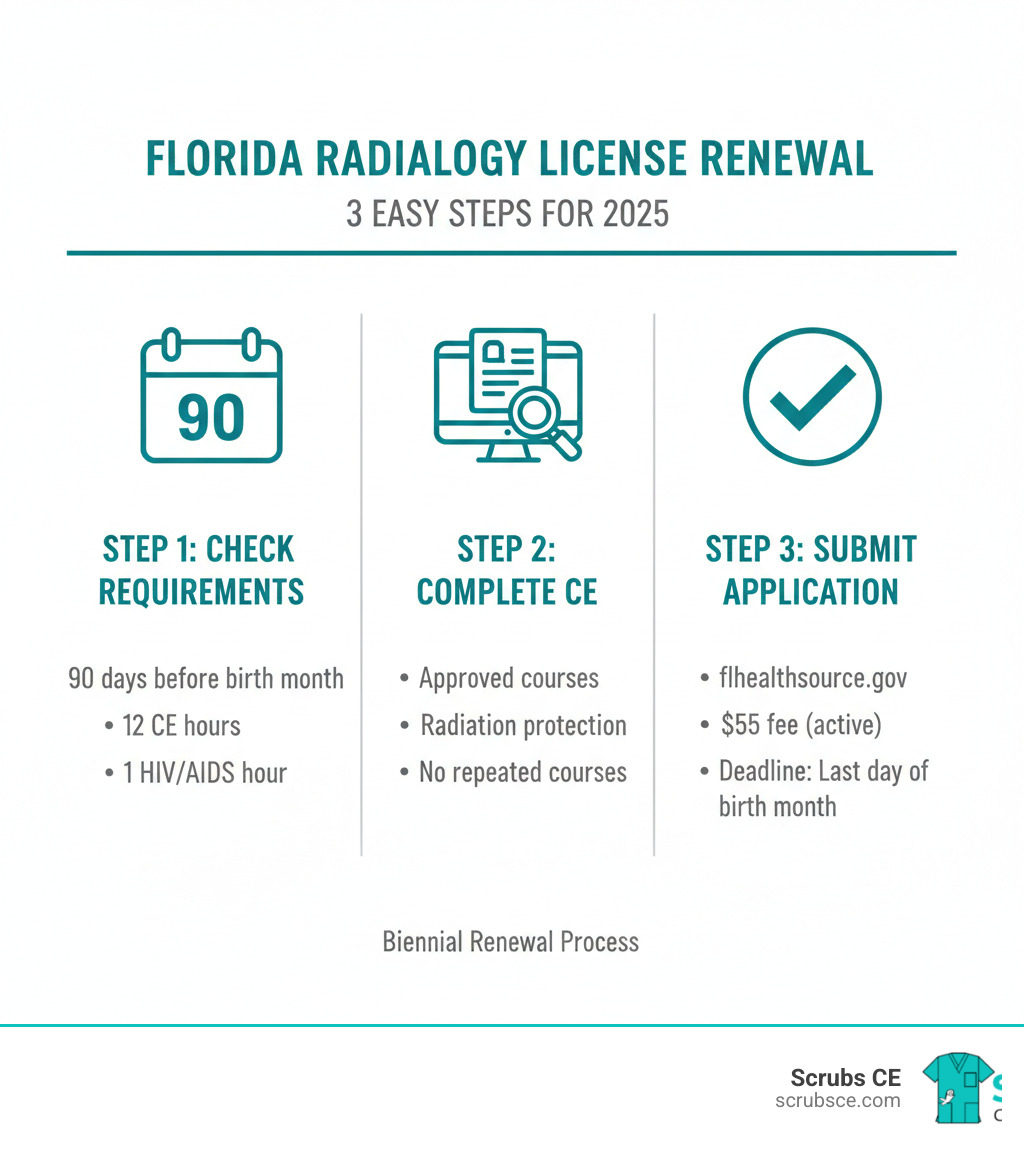
Radiology license renewal florida is required every two years to maintain your right to practice as a radiologic technologist in the state. If you’re approaching your renewal deadline, here’s what you need to know:
Quick Answer: Florida Radiology License Renewal Overview
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Renewal Frequency | Biennial (every 2 years) |
| Expiration Date | Last day of your birth month |
| CE Hours Required | 12 general hours + 1 HIV/AIDS hour |
| Renewal Fee | $55 (Active to Active) |
| Renewal Portal | www.flhealthsource.gov |
| Contact | MQAOnlineService@FLhealth.gov |
As a radiologic technologist in Florida, you’re required to renew your license with the Florida Department of Health’s Division of Medical Quality Assurance (MQA) every two years. Missing your renewal deadline can result in your license entering expired status, requiring higher fees and preventing you from practicing legally.
The good news? Renewing your Florida radiology license doesn’t have to be stressful. The process breaks down into three straightforward steps: understanding your requirements, completing approved continuing education, and submitting your application with fees.
Your renewal window opens 90 days before your license expires on the last day of your birth month. The Florida Department of Health will mail you a notification postcard, but it’s your responsibility to renew on time—even if you don’t receive the notice.
Step 1: Understand Your Renewal Timeline and Requirements
Let’s start with the basics: knowing when and what you need to renew. Your radiology license renewal florida happens every two years—that’s what “biennial” means. The Florida Department of Health requires this regular renewal to make sure everyone practicing radiologic technology stays current with the latest safety protocols and professional standards.
Here’s something that makes your renewal date easy to remember: your license expires on the last day of your birth month. So if you were born in June, your license expires on June 30th at midnight, Eastern Time. It’s like having a professional birthday to remember every two years!
The good news is that Florida gives you a heads-up. About 90 days before your license expires, the Department of Health will mail you a renewal notification postcard. But here’s the important part—even if that postcard gets lost in the mail or you never receive it, you’re still responsible for renewing on time. Think of it like paying taxes: not getting the reminder doesn’t change the deadline.
There’s one more thing you’ll need to handle: background screening. Recent changes to Florida law (specifically HB 975 from 2024) established background screening requirements for radiologic technologists. This helps protect patients and maintains the integrity of healthcare practice across the state. Don’t wait until the last minute on this one—it can take time to process. Visit Don’t Delay, Get Screened Today! to get started with your background screening.
Continuing Education (CE) Requirements
Now for the heart of your renewal: continuing education. This is where you keep your skills sharp and stay on top of new developments in radiologic technology. For your radiology license renewal florida, you’ll need to complete 12 hours of general CE plus 1 hour of HIV/AIDS education. That’s 13 hours total.
The 1-hour HIV/AIDS course must be approved by the Florida Department of Health. You can take an approved course or read “Florida’s Omnibus AIDS Act: A Brief Legal Guide for Health Care Professionals.” Even though this requirement was dropped for initial certification back in 2016, it’s still required when you renew.
Your 12 general CE hours need to be mostly technical—we’re talking about radiation protection, equipment operation, patient care, and other hands-on aspects of your job. You can include up to 3 hours of personal development topics, but no more than that. The state wants to make sure you’re focusing on skills that directly improve patient care.
A few important rules to keep in mind: you can’t repeat the same course within your current renewal cycle. Each course needs to be a new learning experience. And all your CE hours must be earned during your current renewal cycle—you can’t carry over old credits or use courses from a previous period.
If you’re wondering how to report your CE credits or need more details about the submission process, check out our guide on FL Continuing Education Self-Submission Information. We’ll walk you through everything you need to know.
Step 2: Complete Your Approved Continuing Education
Once you understand your requirements, it’s time to tackle those CE hours. And honestly? This is where things get a lot easier than they used to be.
Gone are the days of sitting in a stuffy classroom after pulling a double shift. Thanks to online learning, you can complete your radiology license renewal florida CE requirements from your couch, during your lunch break, or even at 2 AM in your pajamas (we won’t tell).
The key is choosing courses from providers approved by the Florida Department of Health, Bureau of Radiation Control. This isn’t just a suggestion—it’s essential. Only approved courses will count toward your renewal, and you definitely don’t want to find you’ve wasted time on courses that won’t be accepted.
Here’s a nice bonus: many approved providers automatically report your completed CE credits directly to Florida’s Licensure Services. This can save you a step in the renewal process, as you won’t have to manually submit proof of completion for those courses. That’s one less thing on your to-do list.
With self-paced learning, you control the schedule. Start a course on Tuesday, finish it on Thursday, or spread it across a few weeks—whatever works for your life. And when you complete a course, you’ll get an instant certificate of completion. No waiting, no wondering if it went through. Just immediate proof that you’re one step closer to renewal.
At least 9 of your 12 general CE hours must be technical in nature. This means courses covering radiation protection, equipment operation, patient care and safety, image quality and evaluation, radiographic positioning, and pathology and image interpretation. These aren’t just boxes to check—they’re opportunities to sharpen the skills you use every single day with your patients.
Where to Find Approved CE Providers for your radiology license renewal florida
Finding trustworthy, Florida-approved CE providers doesn’t have to feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. At Scrubs CE, we’ve designed our courses specifically with busy radiologic technologists in mind. We understand your schedule is packed, and we’ve built our platform to work around your life, not the other way around.
You can Browse Florida-approved Radiology CE Courses right on our website, where every course is designed to meet Florida’s specific requirements. Looking to knock out multiple requirements at once? Check out our Radiology CE Combos that bundle courses together, often saving you both time and money.
The real goal here isn’t just checking off requirements—it’s actually learning something valuable that makes you better at what you do. Your patients deserve that, and so does your career.
Step 3: Submit Your Application and Fees for Radiology License Renewal Florida
You’ve checked your requirements, completed your continuing education, and now it’s time for the final step: officially submitting your renewal application and paying your fees. Think of this as crossing the finish line of your radiology license renewal florida process!
The Florida Department of Health has made this step pretty straightforward, especially if you’re renewing online. Most radiologic technologists can complete their renewal entirely through the Florida HealthSource portal at www.flhealthsource.gov. It’s the fastest way to get everything processed and your license renewed.
Here’s how it works: Steer to the website and look for the “Renew A License” button. You’ll need to log in using your Personal Identifying Information (PII). Don’t worry if you see a “PII Failed” screen pop up – it happens! Just click the “Other Login Option” button and use your regular User ID and password instead. The system will recognize you and let you through.
Once you’re logged in, you’ll land on your MQA Services Account Dashboard. The first thing you should do is confirm or update your email address. This ensures you’ll receive important notifications about your license status and any future renewals. During your renewal window, which opens 90 days before your license expires, you’ll see a “Renew My License” option right on your dashboard. Click it, follow the prompts to complete your application, and pay your fees using a credit or debit card. The whole process typically takes just minutes.
What about renewing by mail? While online renewal is usually the quickest option, there are specific situations where you’ll need to send in a paper application instead. You’ll want to use the mail-in renewal option if you’re changing your license status (like going from active to inactive), if you prefer to pay with a cashier’s check or money order, if your license is in “Military, Active” status, or if you need to change your name during renewal. For mail-in renewals, you can still start the process online to generate your application summary, then print it out and mail it with your payment to the Division of Medical Quality Assurance.
After you’ve submitted everything, you can track your progress. The DOH provides an online portal where you can Check your application status here and see exactly where your renewal stands in the system. No more wondering if your paperwork got lost in the mail!
Renewal Fees and Status Changes
Let’s talk money. The renewal fees for your radiology license renewal florida depend on your current license status and whether you’re renewing on time. Here’s what you need to know:
If you’re renewing from active to active status, which is the most common scenario, you’ll pay $55. Planning to take a break from practice? Changing from active to inactive status costs $40. Coming back to work and reactivating? Moving from inactive to active is $55. Here’s where it gets expensive: if your license has already expired, renewing from expired to active status jumps up to $155 – that’s a $100 penalty for missing your deadline! And if you hold multiple certifications, each additional one costs $40 to renew after your first.
| Status Change | Renewal Fee |
|---|---|
| Active to Active | $55.00 |
| Active to Inactive | $40.00 |
| Inactive to Active | $55.00 |
| Expired to Active | $155.00 |
| Additional Certification (after the first) | $40.00 |
That expired license fee is no joke, which is why staying on top of your renewal timeline really matters. Mark your calendar, set a reminder on your phone, or tie a string around your finger – whatever it takes to avoid that extra $100 charge!
The good news is that paying online is simple and secure. The system accepts all major credit and debit cards, and you’ll receive confirmation immediately. Your updated license information will typically appear in the state’s verification system within a few business days after your renewal is processed.
What if Your License Expires or Becomes Inactive?
Life can get hectic, and sometimes renewal deadlines slip through the cracks. Maybe you took time off for family, dealt with a health issue, or simply got overwhelmed with everything on your plate. Whatever the reason, it’s important to understand what happens if your radiology license renewal florida doesn’t get completed on time—and how to fix it.
First, let’s clarify the difference between expired and inactive status, because they’re not the same thing.
An expired license means you missed your renewal deadline while holding an active license. This isn’t just a paperwork problem—it’s a legal one. Once your license expires, you cannot legally practice as a radiologic technologist in Florida until you get it renewed. Every shift you work with an expired license puts you at risk for disciplinary action, fines, and potentially even criminal charges. It’s simply not worth the risk.
An inactive license, on the other hand, is a status you typically choose intentionally. Maybe you’re taking a break from clinical work, pursuing further education, or stepping away from practice temporarily. Going inactive is a legitimate option that allows you to maintain your credential without meeting the full requirements of an active license. When you’re ready to return to practice, you can reactivate.
The fee structure reflects these different situations. Renewing an expired license costs $155.00—nearly three times the standard renewal fee. It’s the state’s way of encouraging timely compliance. If you’re moving from inactive to active status, the fee is $55.00, the same as a standard renewal.
Here’s where things get serious: if your license remains expired (what the DOH calls “delinquent status”) through the end of your current licensure cycle without being renewed, it becomes null and void. Even more critical, if your certificate has been inactive or expired for 10 years or more, it automatically becomes null and void and cannot be reactivated. At that point, you’re essentially starting from scratch—you’d need to apply for a brand new license, which involves meeting all current initial licensure requirements. For more information on that process, check out: How to Get a Florida Radiologic Technology License.
The reactivation process for an expired or inactive license typically involves several steps. Start by contacting MQA Licensure Services at mqa.rad-tech@flhealth.gov to request specific reactivation requirements for your situation. You’ll likely need to demonstrate that you’ve maintained your competency during the time away from active practice, which usually means completing additional continuing education hours to cover the period your license wasn’t active. Finally, you’ll pay the appropriate reactivation fee based on your status change.
The bottom line? Don’t let your license lapse. Mark your calendar, set phone reminders, do whatever it takes to stay on top of your renewal deadline. The consequences of practicing with an expired or inactive license simply aren’t worth it—both for your career and for patient safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
You’ve made it this far, which means you’re well on your way to completing your radiology license renewal florida! But we know that even with all this information, a few questions might still be lingering in the back of your mind. That’s completely normal – the renewal process involves several moving parts, and it’s better to get clarity now than to wonder later.
Let’s tackle some of the most common questions we hear from radiologic technologists just like you. These are the real concerns that come up time and again, and we want to make sure you have solid, reliable answers.
How can I verify a radiologic technologist license in Florida?
Maybe you’re starting a new job and your employer needs to verify your credentials. Or perhaps you’re curious about checking your own license status online. Whatever the reason, Florida makes it easy to verify any healthcare license through their public portal.
The MQA Search Portal is your go-to resource for this. You can search by name, license number, or profession to pull up current license status and even view any disciplinary history. This transparency is actually a good thing – it helps maintain public trust in healthcare professionals and ensures everyone is playing by the rules.
To verify any Florida healthcare license, including your own, just head to the official verification site: Verify a Florida healthcare license. The information is public and updated regularly, so you can check anytime you need confirmation of your active status.
What happens if I don’t receive a renewal notice?
Here’s something important to remember: even if that renewal postcard never shows up in your mailbox, you’re still responsible for renewing on time. The DOH sends out notifications as a courtesy, typically about 90 days before your expiration date, but the notice itself isn’t what triggers your renewal obligation. Your license still expires on the last day of your birth month, whether you got a reminder or not.
Think of it like paying your rent or mortgage – you wouldn’t skip a payment just because you didn’t get a reminder call, right? The same principle applies here. The responsibility to renew on time ultimately rests with you, regardless of whether the postcard arrives.
The best approach is to be proactive. Make sure your current mailing address is always up to date in your MQA Services Account. Mark your calendar for the last day of your birth month every two years. Better yet, set a reminder a few months in advance so you have plenty of time to complete your CE and submit your application. You can also periodically log into www.flhealthsource.gov to check your license status and see if your renewal window has opened.
Who do I contact with questions about my renewal?
When you hit a roadblock or just need clarification about your radiology license renewal florida, knowing who to contact can save you a lot of frustration. The good news is that the Florida Department of Health has dedicated staff ready to help you through the process.
For most renewal-related questions, your first stop should be MQA Licensure Services. You can reach them by email at MQAOnlineService@FLhealth.gov for general renewal process questions, payment issues, or help navigating the online portal. If you prefer talking to someone directly, the Customer Contact Center is available at (850) 488-0595. They’re typically available Monday through Friday from 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. Eastern Time, so plan your call accordingly.
If you have very specific questions about Radiologic Technology certification requirements or continuing education that seem to go beyond the general renewal process, you can also contact the MQA RT Certification Office at mqa.rad-tech@flhealth.gov or (850) 245-4910. Just keep in mind that since all renewals now go through Licensure Services, questions about actually submitting your renewal and paying fees are best directed to the MQAOnlineService email.
Don’t hesitate to reach out if something isn’t clear. These folks are there to help you maintain your license, not to make the process harder. A quick phone call or email can often clear up confusion and get you back on track toward a successful renewal.
Conclusion
You’ve made it! By now, you should feel confident about tackling your radiology license renewal florida process. Let’s recap those three essential steps one more time: first, understand your renewal timeline and CE requirements; second, complete your approved continuing education; and third, submit your application and fees through the Florida HealthSource portal.
Staying compliant with your biennial renewal isn’t just about checking boxes or avoiding late fees. It’s about something much more meaningful – maintaining the high standards that define your profession. Every CE hour you complete and every deadline you meet represents your commitment to providing exceptional care to your patients and staying current with the latest advances in radiologic technology.
We understand that juggling your professional responsibilities, continuing education requirements, and personal life can feel overwhelming at times. That’s exactly why we created Scrubs CE – to make the CE portion of your renewal as simple and stress-free as possible. Our Florida-approved courses are designed with busy healthcare professionals like you in mind. You can learn at your own pace, on your own schedule, and receive instant certificates the moment you complete a course.
Think of us as your partner in professional development. Whether you need to fulfill your 12 general CE hours, complete your mandatory HIV/AIDS course, or explore new technical topics to improve your skills, we’ve got you covered with quality courses that actually matter to your daily practice.
Ready to make your next radiology license renewal florida the easiest one yet? Don’t wait until the last minute – get started on your continuing education today and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with being ahead of your deadline. Your future self will thank you!
Buyer’s Guide: Best Digital Radiography CEs for 2025
Why Digital Radiography CE Matters for Your Career and Patient Safety
Digital radiography ce is continuing education on modern X-ray technologies like Computed Radiography (CR) and Direct Radiography (DR). Radiologic technologists must complete these courses to maintain licensure and stay current with evolving imaging standards.
Quick Answer for Your CE Requirements:
- ARRT requires 24 Category A CE credits every two years (biennium)
- California mandates at least 4 of those 24 credits specifically in digital radiography
- Most states accept ASRT-approved courses that cover CR/DR fundamentals, radiation safety, and image quality
- You need to understand exposure indicators, dose creep prevention, and proper collimation techniques
- Courses typically cover digital image processing, PACS integration, artifact management, and radiation protection
The shift from film to digital has created new challenges. Digital systems can mask exposure errors, leading to a phenomenon called dose creep, where patients may receive radiation doses three to five times higher than necessary without any visible image degradation. This makes proper training essential.
Many experts note that technologists trained on analog systems have a strong foundational understanding of exposure principles, a skill that is critical in the digital age.
Whether you’re a Certified Radiologic Technologist (CRT) renewing your California license or an ARRT registrant fulfilling biennium requirements, understanding CE can be confusing. State rules vary, and not all courses satisfy mandatory credits.
This guide cuts through the confusion to help you find high-quality, accredited digital radiography CE that meets your state requirements, fits your schedule, and improves your clinical practice.
Understanding the Core Concepts of Digital Radiography
To meet your digital radiography ce requirements, you need to understand how modern X-ray imaging works. Digital radiography is a fundamentally different way of capturing, processing, and viewing images, revolving around image capture methods, image processing, and workflow speed. Both Computed Radiography (CR) and Direct Radiography (DR) convert X-ray energy into digital data for manipulation and storage in a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS).
The difference between CR and DR directly impacts workflow, patient throughput, and image quality. Here’s how they compare:
| Feature | Computed Radiography (CR) | Direct Radiography (DR) |
|---|---|---|
| Image Capture Medium | Photostimulable Phosphor (PSP) plate | Flat-panel detector (direct or indirect conversion) |
| Workflow Steps | Expose plate → Process in CR reader → Image displayed | Expose detector → Image displayed instantly |
| Image Availability | Minutes (requires plate processing) | Seconds (immediate) |
| Image Quality/Resolution | Good, but generally lower than DR | Excellent, higher spatial resolution and contrast |
| Initial Cost | Lower (can use existing X-ray units) | Higher (integrated system) |
Understanding these differences helps explain why some facilities use CR (budget constraints) while others choose DR (high patient volume, need for speed).
The Shift from Film to Digital
The transition from film to digital eliminated the darkroom and transformed radiographic practice. Post-processing capabilities allow for adjustments to brightness, contrast, and magnification after the exposure, often salvaging a suboptimal technique and reducing repeat exposures.
This flexibility contributes to reduced patient dose potential. Digital receptors are more sensitive than film, allowing for diagnostic images with lower radiation settings and upholding the ALARA principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable). Furthermore, digital imaging simplifies data storage and archiving in PACS, eliminating physical film libraries and reducing technical issues like chemical streaks or processor artifacts.
However, digital’s forgiving nature can mask poor technique, which is why quality digital radiography ce is so important. To strengthen your foundational knowledge, see our A Guide to Continuing Education for X-Ray Technologists.
How CR and DR Systems Work
Computed Radiography (CR) acts as a bridge between film and fully digital systems. It uses a Photostimulable Phosphor (PSP) plate in a cassette to capture a latent image. The cassette is taken to a CR reader, where a laser scanning system stimulates the plate, causing it to release light. A photodetector converts this light into a digital signal. The plate is then erased and ready for reuse.
Direct Radiography (DR) eliminates the reader step by using flat-panel detectors. These detectors work in one of two ways:
- Indirect conversion uses a scintillator to convert X-rays into light, which is then converted into an electrical charge and digitized.
- Direct conversion detectors convert X-ray photons directly into an electrical charge, which is then digitized.
The main advantage of DR is immediate image display, which dramatically improves workflow in busy departments. To learn more about these systems, our course Radiography in the Digital Age 3rd Ed covers these principles in detail.
Mastering Image Quality and Radiation Safety
Digital radiography’s flexibility is a great asset, but it requires vigilance to maintain image quality and protect patients from unnecessary radiation. Upholding the ALARA principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) is the ethical foundation of our profession. Every exposure must achieve a diagnostic image with the minimum necessary dose. This involves preventing artifacts, implementing quality control, and ensuring both patient and staff safety.
Managing Radiation Dose: Exposure Indicators and Dose Creep
Unlike film, which provides immediate visual feedback on exposure, digital systems rely on Exposure Indicators (EI). These are numerical values (e.g., Fuji’s S-number, Carestream’s exposure index) that report the amount of radiation that reached the receptor. It is critical to understand your facility’s target EI ranges to ensure appropriate dosage. For more information, see resources like Watch Exposure Indicators.
This reliance on numerical indicators is necessary because digital systems can lead to dose creep—the gradual, unintentional increase in radiation exposure over time. Digital detectors have a wide exposure latitude and can produce acceptable-looking images even when significantly overexposed. With film, overexposure created a dark, unusable image. With digital, post-processing can mask the error, but the patient still receives an unnecessarily high dose.
This risk grows when technologists use higher techniques “just to be safe.” Without diligent monitoring of EIs, patient doses can become three to five times higher than necessary. Preventing dose creep requires discipline: review EIs for every image, adhere to technique charts, and take digital radiography ce that reinforces these best practices. Our Radiographic Imaging and Exposure 5th Ed Ebook Test digs deep into exposure management.
The Critical Role of Collimation and Artifact Management
Physical collimation—restricting the X-ray beam to the area of interest—is a fundamental skill with a powerful impact. Proper collimation reduces patient dose and improves image quality by minimizing scatter radiation, which degrades contrast and detail.
It is crucial not to confuse this with electronic masking (or shuttering). This post-processing tool digitally crops an image to make it look properly collimated, but it does nothing to reduce the patient’s radiation dose or prevent the scatter that already occurred. Real collimation happens before the exposure. For examples, see Collimate to improve image quality.
Technologists must also be able to identify image artifacts. Common digital artifacts include:
- Plate reader artifacts (CR): Caused by dirt, laser issues, or transport problems.
- Dead pixels (DR): Non-functioning detector elements that appear as dots.
- Image noise: A grainy appearance, often from low mAs (quantum mottle) or electronic interference.
- Uberschwinger: A halo effect around metal implants from excessive edge improvement.
- Lag or ghost images: Residual signals from previous exposures.
Understanding these artifacts is essential for troubleshooting. Quality digital radiography ce courses like Radiographic Image Analysis help you develop the critical eye needed to spot and correct these issues.
Navigating Your Digital Radiography CE Requirements
Keeping your credentials current means navigating a maze of CE requirements from national and state boards. While it can seem complex, quality digital radiography ce courses are often designed to satisfy these overlapping demands with Category A credits.
ARRT and State-Specific Digital Radiography CE Mandates
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) sets the baseline, requiring 24 Category A CE credits every two years (a biennium). However, state licensing boards often add their own specific mandates.
California is a key example. The Radiologic Health Branch (RHB) requires Certified Radiologic Technologists (CRTs) to complete 24 approved CE credits every two years, with a crucial stipulation: at least 4 of those 24 credits must specifically cover digital radiography. This rule also applies to Limited Permit X-Ray Technicians (XTs) with digital authorization. You can verify this on the California Department of Public Health – Radiologic Health Branch (RHB) Continuing Education Requirements page.
Other states like Florida and Texas have their own distinct requirements. Always check with your specific state licensing authority to confirm their expectations. Our guide on How Many X-Ray CE Credits Do I Need for Radiography? can help break down these variations.
Finding Approved Digital Radiography CE Courses
To ensure your courses count, look for proper accreditation. ASRT approval is the gold standard, as these courses are accepted by the ARRT for Category A credit and by most state boards.
Beyond accreditation, choose courses that cover the material you need for both professional development and state mandates. The best digital radiography ce programs address these core areas:
- Fundamentals of CR/DR Systems
- Radiation Safety and Dose Reduction
- Digital Image Processing and Artifacts
- PACS and Healthcare Informatics
These topics form the foundation of competent digital practice and will typically satisfy state-specific content requirements. We know finding time for CE is challenging, which is why our Continuing Education Courses for X-Ray Technologists are ASRT-approved, self-paced, and designed to meet both ARRT and state-specific mandates like California’s.
The Future of Digital Radiography and Lifelong Learning
Digital radiography is constantly evolving, which is why lifelong learning is so critical. Digital radiography ce is not just about licensure; it’s about staying relevant in a rapidly changing profession.
The biggest game-changer on the horizon is Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI is already entering imaging suites through machine learning algorithms that can recognize patterns in images that the human eye might miss.
Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) systems are a prime example. These AI tools can flag potential abnormalities and highlight areas for a radiologist’s attention. They are not here to replace us, but to augment our skills. AI is also being used to optimize exposure parameters in real-time and analyze patient positioning to reduce repeats.
This technological shift will evolve our roles. We will need to understand how AI systems work, their limitations, and the ethical considerations surrounding their use in healthcare, such as data privacy and algorithmic bias.
Future digital radiography ce will need to cover AI fundamentals, CAD tool integration, and how to interpret their outputs. The technologists who thrive will be those who accept continuous learning and see these advancements as an opportunity to provide better, safer patient care.
Staying ahead is about being the best possible advocate for our patients. Understanding the latest technologies ensures they are used safely and effectively. As we stand on the edge of radiology’s next great change, The Importance of Continuing Education (CE) for X-Ray Technologists has never been more apparent.
Frequently Asked Questions about Digital Radiography CE
Navigating continuing education requirements can be confusing. Here are clear answers to the most common questions we hear from technologists.
How many digital radiography CE credits do I need?
This depends on your credentials and where you work. The ARRT requires 24 Category A CE credits every two years to maintain your registration. However, many states add their own rules. For example, California requires that at least 4 of those 24 credits be specifically in digital radiography. This applies to both CRTs and XTs with digital authorization. Always check with your specific state licensing board to confirm their requirements. Our guide on What You Need to Know About X-Ray Continuing Education Requirements can help clarify state-by-state rules.
What is ‘dose creep’ and why is it a concern in digital radiography?
Dose creep is the gradual, unintentional increase in radiation exposure to patients over time. It happens because digital detectors have a very wide exposure latitude, meaning they can produce a perfect-looking image even when significantly overexposed. Unlike film, there are no immediate visual cues of overexposure. This creates a risk of patients receiving much higher doses than necessary. The only way to prevent dose creep is by diligently monitoring Exposure Indicators (EI) on every image. Organizations like Image Wisely promote awareness of this critical safety issue.
Can I use the same CE course for my ARRT and state license renewal?
In most cases, yes. A digital radiography ce course that is ASRT-approved for Category A credit will typically be accepted by both the ARRT and your state licensing board. This allows you to satisfy multiple requirements with a single course.
However, you must verify that the course content meets any specific state mandates. For example, a general radiation safety course will count for your ARRT credits, but it may not fulfill California’s mandatory 4-credit requirement for digital radiography content. Always read course descriptions carefully to ensure they align with your state’s rules. Our courses are designed for broad acceptance, including Accepted Everywhere, Guaranteed for ARRT Category A credit, but a final check with your state board is always a good idea.
Conclusion
Digital radiography ce is more than a requirement—it’s a commitment to professional excellence and patient safety. Digital technology has given us incredible tools, but it also brings responsibilities. The same systems that improve efficiency can mask issues like dose creep, where patients receive excessive radiation without any visual warning. Mastering exposure indicators, collimation, and artifact recognition are essential skills for modern practice.
CE requirements, like the ARRT’s 24 credits or California’s 4-credit digital mandate, exist to keep us sharp and engaged with new developments, from PACS integration to emerging AI. Quality continuing education bridges the gap between compliance and professional growth, providing practical knowledge that improves your daily work and patient outcomes.
At ScrubsCE, we build our courses with this in mind. We offer ASRT-approved, state-compliant courses that are self-paced, convenient, and filled with useful content. You get practical skills for your next shift and an instant certificate upon completion.
Whether you’re preparing for the future of AI-assisted imaging or ensuring you meet today’s state requirements, we are here to support your career journey. Continuing education is how we not only keep up but move forward, providing the safest, highest-quality care possible.
Ready to tackle your CE requirements with courses that matter? Browse our full catalog of Radiology CE courses and find what you need to keep your license current and your skills sharp.
California Fluoroscopy CME Survival Guide
Why California Fluoroscopy CME Requirements Matter for Your License
California fluoroscopy CME is the mandatory continuing education you need to renew your fluoroscopy permit or certificate in California every two years. The specific requirements depend on your professional role, but all fluoroscopy permit holders must complete credits in radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy.
Quick Reference: California Fluoroscopy CE Requirements
| Professional Role | Total CE Credits (2 years) | Radiation Safety Credits |
|---|---|---|
| Physicians, Podiatrists, Chiropractors (with Supervisor & Operator Permit) | 10 | 4 |
| Physician Assistants (with Fluoroscopy Permit) | 10 | 4 |
| Physician Assistants (with RTF Permit) | 24 | 4 |
| Certified Radiologic Technologists (with Fluoroscopy Permit) | 24 | 4 (plus 4 in digital radiography) |
If you operate fluoroscopy equipment in California, you’re working with powerful X-ray technology that requires specialized knowledge. The state takes radiation safety seriously—and for good reason. One interventional cardiologist who completed their fluoroscopy CME noted it was “valuable as a refresher with new updates,” even after years of practice.
The California Radiologic Health Branch oversees these requirements to protect both patients and healthcare workers from unnecessary radiation exposure. Missing your renewal deadline means you can’t legally operate fluoroscopy equipment until you’re compliant.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know. We’ll cover your specific requirements based on your role, how to find approved courses, and how to submit your renewal without stress.
The good news? Meeting these requirements doesn’t have to be complicated or expensive. With online courses and instant certificates, you can complete your California fluoroscopy CME on your schedule.
Understanding Your Specific California Fluoroscopy CE Requirements
Let’s get straight to what you need to know about your California fluoroscopy CME requirements. The California Radiologic Health Branch (RHB) oversees all fluoroscopy permits and certificates in the state, and they’ve set clear rules about continuing education that every permit holder needs to follow.
Here’s the foundation: all your CE content must relate directly to the application of X-ray to the human body. This isn’t just a guideline—it’s written into law under 17 CCR 30400(a)(4). That means your courses need to be about actual radiologic procedures, not general medical topics.
The renewal cycle runs on a two-year schedule. During those two years, you’ll need to complete a specific number of CE credits, and a certain portion must focus on radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy. This requirement exists for good reason—it keeps everyone current on best practices and patient safety in a field that’s constantly advancing.
Your exact requirements depend on your professional license and the type of fluoroscopy permit you hold. Let’s walk through what each credential requires.
For Physicians, Podiatrists, and Chiropractors (Licentiates of the Healing Arts)
If you’re a physician, osteopath, podiatrist, or chiropractor with a Fluoroscopy Supervisor and Operator Permit, you need 10 approved CE credits every two years. Simple enough, right?
Here’s where it matters: at least 4 of those 10 credits must be in radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy. These 4 credits aren’t optional—they’re your core requirement for keeping patients and staff safe from unnecessary radiation exposure. The state takes this seriously, and it’s all spelled out in the California Code of Regulations [17 CCR 30403(b)].
The remaining 6 credits can cover other approved topics related to fluoroscopy and radiologic procedures. Just remember that everything needs to relate to X-ray applications in clinical practice.
For general information about maintaining your medical license, the Medical Board of California is your go-to resource.
For Physician Assistants (PAs)
Physician Assistants have two possible paths when it comes to fluoroscopy permits, and your CE requirements depend on which permit you hold.
If you have a standard Fluoroscopy Permit, you need 10 CE credits every two years, with 4 credits in radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy. This matches the requirements for physicians and other healing arts licentiates.
But if you hold a Radiologic Technology Fluoroscopy (RTF) Permit, your requirements jump to 24 CE credits every two years. You’ll still need 4 credits in radiation safety specifically, but the higher total reflects the expanded scope of practice that comes with an RTF Permit.
Make sure you know which permit you hold—it makes a big difference in your CE planning. You can review all the details in the PA fluoroscopy permit regulations.
For Certified Radiologic Technologists (CRTs)
Certified Radiologic Technologists face the most comprehensive CE requirements in California. Every CRT must complete 24 approved CE credits every two years, regardless of specialty.
Within those 24 credits, California requires 4 credits in digital radiography. This applies to every single CRT in the state—not just those working in CT or advanced imaging. It’s a universal requirement that recognizes how digital technology has transformed the field.
If you also hold a Fluoroscopy Permit, you need an additional 4 credits in radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy. These can count toward your total 24 credits, so you’re not adding extra courses—you’re just making sure those credits cover the right topics.
Think of it this way: as a CRT with a fluoroscopy permit, you need 24 total credits that include 4 in digital radiography and 4 in fluoroscopy radiation safety. The remaining 16 credits can cover other approved radiologic topics.
Understanding why these radiation safety credits matter can help you choose better courses. Check out Why You Should Take Your Fluoroscopy Radiation Safety CEs for California for more context on this critical requirement.
Finding and Verifying Compliant California Fluoroscopy CME Courses
Now that you understand your specific requirements, it’s time to find courses that actually count. This is where many healthcare professionals hit a roadblock—not all continuing education is created equal, and the California Radiologic Health Branch has clear standards about what they’ll accept.
The good news? Once you know what to look for, choosing the right courses becomes straightforward. Let’s walk through what makes a course compliant and how to verify you’re investing your time and money wisely.
Mandatory Topics for your California Fluoroscopy CME
Here’s the golden rule: all your California fluoroscopy CME credits must relate to the application of X-ray to the human body. The RHB takes this seriously because fluoroscopy is fundamentally about using radiation safely and effectively.
This means your courses should cover topics like radiation physics, equipment operation, dose optimization, patient positioning, image quality, or quality assurance. Radiology administration and management courses count too, as long as they connect back to X-ray applications. For fluoroscopy permit holders specifically, at least 4 of your credits must focus on radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy—this isn’t negotiable. And if you’re a CRT, 4 credits in digital radiography are required regardless of your specialty.
But here’s what won’t count: CPR, MRI techniques, nuclear medicine, ultrasound, billing and coding, stress management, or general wellness topics. These subjects might be valuable for your career or your general medical license, but they won’t help you renew your fluoroscopy permit. Think of it this way—if you can’t see an X-ray machine in the course description, it probably won’t qualify.
The RHB explicitly lists unacceptable topics in their regulations, so there’s no gray area here. A course on “Advanced Cardiac Life Support” might be critical for your job, but it won’t satisfy your fluoroscopy renewal requirements. One technologist we spoke with learned this the hard way when 8 credits of their submitted CE were rejected during an audit—all because they assumed any medical education would count.
Understanding patient safety is central to radiation work. If you’re looking to deepen your knowledge in this area, Patient Safety in Fluoroscopy Procedures: Guidelines for the Radiologic Imaging Team offers valuable insights that align perfectly with RHB requirements.
How to Ensure Your Course is RHB-Approved
Here’s something that surprises many professionals: the RHB doesn’t directly approve individual courses. Instead, they recognize certain credentialing bodies whose approval stamps make courses acceptable for your renewal.
If your course is approved by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (particularly through their RCEEMs—Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanisms), you’re in good shape. The Medical Board of California, Osteopathic Medical Board of California, California Board of Chiropractic Examiners, Board of Podiatric Medicine, and California Physician Assistant Board all provide recognized approval as well.
For physicians and podiatrists, courses designated as AMA PRA Category 1 CME™ credit are widely accepted. Technologists should look for ASRT Category A credit or courses approved through an ARRT®-recognized third-party mechanism. These designations tell you that the course has been vetted by a credible organization that understands California’s standards.
Before you enroll, check the course provider’s website for clear statements about their approval status. Reputable providers will prominently display which credentialing bodies have approved their courses. Your certificate should also clearly state the type of credit you’re receiving—this documentation matters if you’re ever audited.
When in doubt, the Official RHB CE Renewal PDF provides detailed guidance on acceptable credentialing organizations. The responsibility to verify course acceptability ultimately falls on you as the permit holder. It’s worth taking five minutes to confirm before you commit.
The Rise of Online Learning for California Fluoroscopy CME
Let’s be honest—finding time for continuing education between shifts, patient care, and everything else in your life isn’t easy. That’s exactly why online learning has become the go-to solution for so many California healthcare professionals.
Online courses let you learn on your schedule, whether that’s during a quiet Sunday morning or in 30-minute chunks between appointments. There’s no commuting to a conference center, no hotel expenses, and no taking precious time off work. You can pause when you need to and pick up right where you left off.
The cost savings are real too. Traditional in-person seminars often come with registration fees, travel costs, and lost income from days away from practice. Online courses typically cost a fraction of that amount, making it much easier to Satisfy California Fluoroscopy CME Requirements on a Budget without compromising on quality.
One of the biggest advantages? Instant certificates. When you complete a course with a provider like Scrubs CE, you get immediate access to your certificate of completion. No waiting for mail delivery or following up weeks later. This is especially helpful when your renewal deadline is approaching and you need documentation fast.
Online learning also means you can review challenging material multiple times. If radiation physics isn’t your strong suit, you can replay that section until it clicks. You’re in control of your learning pace, which often leads to better retention and understanding.
At Scrubs CE, we’ve designed our Fluoroscopy CE Courses specifically with busy healthcare professionals in mind. Our courses are self-paced, affordable, and fully compliant with California RHB requirements. We understand that your time is valuable, and we’ve built our platform to make meeting your California fluoroscopy CME requirements as painless as possible.
The shift to online education isn’t just about convenience—it’s about making quality continuing education accessible to everyone, regardless of location or schedule constraints. And in a state as large as California, that accessibility matters.
The Renewal Process: From Exam Prep to Final Submission
You’ve worked hard to complete your California fluoroscopy CME credits—congratulations! But before you can truly relax, there are a few more steps to tackle. Think of this phase as crossing the finish line: you need to prepare for any required exams, organize your documentation, and submit everything correctly to the California Radiologic Health Branch. Getting these practical details right means your permit stays active and you can keep doing what you do best without interruption.
Preparing for the Fluoroscopy Supervisor and Operator Exam
If you’re pursuing a Fluoroscopy Supervisor and Operator Permit for the first time, you’ll need to pass a state examination before you can get started. This isn’t just a formality—it’s a comprehensive test that covers radiation physics, safety protocols, equipment operation, and the clinical applications of fluoroscopy. The exam ensures you have the knowledge to safely supervise and operate fluoroscopic equipment, protecting both patients and staff.
The good news? Your CE courses can double as excellent study materials. Many of the topics you’ll cover in radiation safety and technical courses align directly with what’s on the exam. Key topics include radiation physics fundamentals, dose reduction techniques, equipment specifications, and patient safety protocols. Combining quality CE courses with a thorough review of the exam content specification gives you a solid foundation.
You’ll need to apply for and be admitted to the California fluoroscopy permit examination independently. Make sure you verify your eligibility and understand all the requirements before scheduling. Our courses can help you prepare, but always refer to the official RHB resources for the most current exam information.
Documenting Your Credits and Submitting Your Renewal
Every two years, renewal time rolls around. The California RHB keeps the process straightforward, though it does require some attention to detail. You’ll need to submit your renewal application, renewal fee, and evidence of your completed continuing education credits via U.S. mail. Yes, actual mail—it’s refreshingly old-school in our digital age!
You should receive renewal billing notices about 90 days before your permit expires. If you don’t receive one or it gets lost in the shuffle, you can use a special renewal application. When you submit your renewal, you’ll provide specific information about each course you completed, including the provider, course title, dates, and credit hours.
Here’s the part you absolutely can’t forget: retain your original course certificates for four years following the dates you earned them. Why four years? Because the RHB conducts random audits, and if your name comes up, you’ll need to produce those certificates as proof. Keep them organized in a safe place—a folder, a file cabinet, or even a digital backup system. Think of it as your professional insurance policy. Without those certificates, you could face serious headaches during an audit.
What Happens If You Miss the Deadline?
Let’s talk about something nobody wants to experience: missing your renewal deadline. Unfortunately, this isn’t just a minor inconvenience—it has real consequences for your ability to practice.
If you don’t earn the required credits and submit your renewal application with the proper documentation and fees on time, your permit will expire. Once that happens, you cannot legally operate fluoroscopy equipment. Period. Continuing to work with an expired permit is a direct violation of California regulations, and it can lead to fines, disciplinary action, and potentially serious professional repercussions.
The reinstatement process exists, but it’s not fun. It typically involves additional fees, extra paperwork, and a frustrating period where you’re unable to perform procedures that require fluoroscopy. Some facilities may not allow you to work in certain capacities until your permit is reinstated, which can affect your income and career momentum.
The simple truth? Staying on top of your California fluoroscopy CME requirements and submitting your renewal well before the deadline saves you stress, money, and potential career disruptions. Set reminders, mark your calendar, or tie a string around your finger—whatever it takes to avoid letting that deadline slip past you. A little planning now prevents a lot of headaches later.
Frequently Asked Questions about California Fluoroscopy CME
Navigating continuing education requirements can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re juggling your daily clinical responsibilities with renewal deadlines. We hear your questions every day, and we want to make sure you have clear, straightforward answers. Here are the most common questions we get about California fluoroscopy CME, answered with the practical insights you need.
How do fluoroscopy CE requirements compare to general medical license CE?
If you’re a physician renewing both your medical license and your fluoroscopy permit, you might wonder how these two sets of requirements interact. The short answer is they’re different, but there’s often significant overlap.
Your general California Medical License requires 50 CME credits every two years. These credits can cover a broad spectrum of medical topics—everything from clinical updates and patient care to medical ethics and even practice management. It’s a wide-open field designed to keep you current across your entire scope of practice. You can find all the details on the Medical Board of California’s continuing education page.
In contrast, California fluoroscopy CME is much more focused. For your Fluoroscopy Supervisor and Operator Permit, you need 10 CE credits every two years, with at least 4 credits specifically in radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy. These credits must relate directly to the application of X-ray to the human body. So while your general medical license CE can cover almost anything medically relevant, your fluoroscopy CE has to stay in its lane—X-rays and radiation safety.
Here’s the good news: many fluoroscopy CE courses, particularly those approved for AMA PRA Category 1 CME™ credit, can count toward both requirements simultaneously. That means when you complete your 10 fluoroscopy CE credits, they can also chip away at your 50-credit general medical license requirement. It’s about working smarter, not harder. With a little strategic planning, you can satisfy multiple requirements with the same educational investment.
Can I use the same course for my ARRT biennium and my California renewal?
This question comes up constantly, and for good reason—who doesn’t want to maximize efficiency? The answer is usually yes, but timing is everything.
If a course is approved by both the ARRT (typically as Category A credit) and meets California’s content requirements for X-ray application to the human body, you can indeed use it for both renewals. That’s the easy part.
The tricky part is the timing. California requires that your CE credits be completed within the 24 months immediately before your permit expiration date. The ARRT has its own biennium cycle, which may or may not line up with your California permit dates. If you complete a course early in your ARRT biennium—say, 28 months before your California permit expires—it won’t count for your California renewal, even though it’s perfectly valid for ARRT.
So while dual-purpose courses are fantastic for efficiency, you need to pay close attention to when you complete them. Check both your ARRT biennium dates and your California permit expiration date, and make sure your course completion falls within the acceptable window for both. A little calendar work upfront can save you from having to retake courses later.
Do I need digital radiography credits if I don’t perform CT?
Yes, you do—and this surprises a lot of people. If you’re a Certified Radiologic Technologist (CRT) in California, you must complete 4 CE credits in digital radiography as part of your 24-credit biennial requirement. This applies to every CRT, regardless of your specialty or daily practice.
You might be thinking, “But I never touch CT equipment—why do I need digital radiography credits?” The regulation isn’t limited to CT technologists. It reflects how thoroughly digital imaging has transformed the entire field of radiography. Whether you’re working in general radiography, fluoroscopy, or another specialty, digital technology is woven into almost every aspect of modern imaging.
California wants to ensure that all CRTs have a solid foundational understanding of digital imaging principles, quality control, and safety considerations. Even if you’re not performing CT scans, understanding digital radiography helps you work more effectively with the technology you encounter every day.
If you’re looking for courses that cover digital radiography along with other essential topics for your renewal, our Radiology CE Courses offer a range of options designed specifically to meet California’s requirements while fitting into your busy schedule.
Conclusion: Stay Compliant and Confident in Your Practice
You’ve made it through the maze of California fluoroscopy CME requirements, and now you have a clear roadmap ahead. What might have seemed overwhelming at first—the different credit requirements, the specific radiation safety mandates, the documentation process—is actually quite manageable when you break it down into clear steps.
Think of your fluoroscopy CE journey as a three-part process: first, know exactly what your profession requires (those 10 or 24 credits with their specific radiation safety and digital radiography components). Second, choose courses from accredited providers that the California RHB will actually accept. And third, keep those certificates organized and ready for at least four years, because audits do happen.
But here’s the thing: meeting these requirements isn’t just about checking boxes to keep your permit active. Yes, compliance matters—you can’t legally operate fluoroscopy equipment without it. But the real value goes deeper. Every course you complete strengthens your understanding of radiation safety, updates your knowledge of current best practices, and ultimately makes you better at what you do. Your patients benefit. Your colleagues benefit. And you grow as a professional.
The landscape of medical imaging is constantly evolving. New safety protocols emerge. Equipment becomes more sophisticated. Dose optimization techniques improve. By engaging with quality continuing education every two years, you’re not just maintaining your license—you’re staying at the forefront of your field.
We built Scrubs CE specifically to make this process easier for busy healthcare professionals like you. No traveling to conferences. No rigid schedules. No waiting weeks for certificates to arrive in the mail. Just high-quality, California-approved courses you can complete on your own time, with instant certificates ready the moment you finish. We get it—you have enough on your plate without CE becoming a source of stress.
Your next renewal deadline might be months away, or it might be approaching faster than you’d like. Either way, taking action now means you won’t be scrambling at the last minute. Explore our California-approved course bundles and knock out your California fluoroscopy CME requirements with confidence. Your future self will thank you.
X Things Every Sonographer Needs to Know About CE Courses
Why Continuing Education Matters for Your Sonography Career
CE for sonographers is a mandatory requirement to maintain your professional credentials and licensure. Understanding how continuing education works can save you time, money, and stress throughout your career.
Here’s what you need to know:
- ARDMS requires 30 CME credits every three years for credentials like RDMS, RDCS, and RVT
- ARRT requires 24 CE credits every two years, with 16 being ultrasound-specific
- Credits must be earned from approved providers (AIUM, SDMS, SVU, ASRT, or other recognized RCEEMs)
- Documentation must be kept for 4-5 years in case of an audit
- Specialty credentials (breast, vascular, musculoskeletal) may have additional requirements
The requirements vary based on which credentials you hold and which credentialing body you’re registered with. ARDMS uses a three-year cycle, while ARRT uses a two-year biennium tied to your birth month. Both organizations accept credits from specific approved providers, and both conduct random audits to verify compliance.
Failing to meet CE requirements can result in probation status or even permanent revocation of your credentials. That’s why understanding the rules, finding quality courses, and maintaining proper documentation is essential for every practicing sonographer.
I’m Zita Ewert, and I’ve spent years helping imaging professionals steer the complexities of CE for sonographers and other radiologic credentials through SCRUBS Continuing Education®. My goal is to make continuing education straightforward, accessible, and affordable so you can focus on what matters most—delivering excellent patient care.
The “What” and “Why” of Continuing Education
Let’s talk about why CE for sonographers matters so much. It’s not just another box to check off—it’s what keeps us sharp, current, and confident in our work. Think about how much has changed in ultrasound technology just in the past five years. New imaging techniques, updated protocols, and advanced equipment mean that without continuing education, we’d be left behind pretty quickly.
Understanding CE for Sonographers
So what is continuing education? At its core, CE for sonographers involves educational activities that develop, maintain, and expand your knowledge and skills. This includes conferences, online courses, webinars, or even peer-reviewed journal articles about new imaging techniques.
Earning these credits is about more than just maintaining your credentials. While required to keep your certification active, the real purpose is to uphold high standards of patient care and professional competency. Each credit represents new knowledge you can apply directly to your patients.
These requirements reflect a commitment to lifelong learning in our field. For sonographers, this means staying on top of evolving ultrasound technology, new diagnostic approaches, and improved scanning techniques that can make a real difference in patient outcomes.
The Importance of Staying Current
The medical field doesn’t stand still, and neither can we. What was state-of-the-art when you first got certified might be outdated now. New ultrasound equipment comes with advanced features, diagnostic criteria get refined, and protocols change to reflect better practices.
Staying current through continuing education helps you adapt to medical advancements as they happen. That new 3D imaging technique? You’ll learn it through CE. Updated guidelines for fetal measurements? You’ll find out through your coursework. These topics are essential for providing accurate, safe care.
Staying up to date directly improves patient outcomes. A sonographer familiar with the latest techniques can spot findings previously missed, use more comfortable exam protocols, and improve diagnostic accuracy by applying the most current standards.
Healthcare facilities expect staff to be competent with modern equipment and best practices. Meeting employer expectations makes you a more valuable team member and can open doors for career advancement.
Continuing education also keeps you aligned with professional standards and ethics. Many CE courses include updates on regulatory changes, ethical guidelines, and legal considerations, helping you practice responsibly and protect both your patients and your career.
As credentialing bodies make clear, CE credits are essential for maintaining your certifications and licensure. But beyond compliance, it’s about being the best sonographer you can be—for yourself, your patients, and your profession.
Want to explore more about why this commitment to learning makes such a difference? Check out our detailed look at 5 Reasons to Pursue Ultrasound Continuing Education.
Navigating Your CE Requirements
Let’s be honest—figuring out your specific CE for sonographers requirements can feel like trying to read a map in the dark. Different credentialing bodies, varying cycles, specialty-specific rules… it’s enough to make your head spin. But here’s the good news: once you understand the basics of your particular situation, it becomes much more manageable.
The key is knowing which credentialing body (or bodies) you’re registered with, because that determines everything—your reporting period, how many credits you need, and what types of activities actually count.
Typical CE Requirements for Sonographers
Most sonographers are credentialed through either ARDMS or ARRT, and while both organizations are committed to maintaining professional standards, they have different approaches.
If you hold credentials through ARDMS (like RDMS, RDCS, or RVT), you’re working on a three-year cycle. You’ll need to earn 30 ARDMS/APCA-accepted CME credits during that three-year period. Now, if you have specialty credentials like RMSK (musculoskeletal) or RPVI (vascular) in addition to your primary credential, things get a bit more specific. For example, holding RMSK plus another ARDMS credential means you’ll need 10 CMEs specifically in musculoskeletal ultrasound and 20 in any specialty—still 30 total, but with targeted requirements.
For ARRT-credentialed sonographers, the cycle is shorter but the requirements are different. You’ll need 24 CE credits every two years, and here’s the important part: 16 of those credits must be ultrasound-specific. Your two-year cycle (called a biennium) is tied to your birth month, so everyone’s deadline is personalized. It’s like having your own professional birthday celebration—except instead of cake, you get CE credits!
Here’s a quick comparison to help you see the differences at a glance:
| Credentialing Body | Reporting Cycle | Total Credits | Sonography-Specific Credits |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARDMS | 3 years | 30 | Varies by specialty |
| ARRT | 2 years | 24 | 16 |
Both organizations conduct audits to verify compliance, so keeping detailed records isn’t optional—it’s essential. ARDMS does an annual audit where they randomly select registrants, while ARRT conducts audits throughout the year. Think of it as a pop quiz you want to be prepared for.
Of course, these are general guidelines. Your specific situation might have additional nuances, especially if you hold multiple credentials or specialty certifications. That’s why it’s always smart to check your credentialing body’s official website for the most current requirements that apply to your unique combination of credentials.
Understanding Your Credentialing Body’s Rules
Once you know the basic numbers, it’s time to understand the fine print. And trust me, the details matter here.
First, let’s talk about timing. ARRT uses a two-year biennium cycle, while ARDMS works on a three-year CME period. It’s not just about different lengths of time—these cycles can start on different dates depending on when you were certified or when your birthday falls. Missing your deadline isn’t like forgetting to return a library book; the consequences can include probation or even losing your credentials.
Then there’s the matter of specialty-specific requirements. If you’re ARDMS-certified with specialty credentials like RMSK or RPVI, a certain portion of your CMEs must relate directly to that specialty area. For ARRT sonographers, 16 of your 24 credits must be sonography-specific. The good news? Most courses with “Ultrasound” or “Sonography” in the title will meet ARRT’s sonography-specific criteria. It’s usually pretty straightforward to identify which courses count.
For ARRT registrants, you’ll also want to understand Category A and A+ credits. These are the types of CE activities ARRT accepts, and they’re generally approved by what’s called a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM or RCEEM+). When you’re choosing courses, look for this designation—it tells you the credit will be accepted.
Here’s something that catches some sonographers off guard: if you were certified by ARRT on or after January 1, 2011, you’re also subject to Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR) every 10 years. This involves completing a professional profile, taking a Structured Self-Assessment to identify any knowledge gaps, and completing prescribed CE if needed. The silver lining? Any prescribed CE activities for your CQR can also count toward your regular biennial CE requirements. ARRT designed it this way so you’re not doubling up on work.
If you’re maintaining ARRT credentials, their official Guide to Maintaining Your ARRT Credential is an invaluable resource. It walks you through everything in detail, and it’s worth bookmarking.
The bottom line? Understanding your specific requirements upfront saves you from scrambling at the last minute. Take an hour to review your credentialing body’s rules, mark your renewal date on your calendar, and you’ll sleep better knowing exactly what you need to do and when you need to do it.
How to Find, Earn, and Document Your Credits
So you know what credits you need—now let’s talk about actually getting them done. The good news? Earning your CE for sonographers credits has never been easier, especially with online learning. No more sitting through day-long conferences when you’d rather be home (though those still have their place!). Today, you can knock out credits during your lunch break or while your favorite show buffers.
Finding Approved CE Providers
Here’s the thing about CE credits: they’re only valuable if your credentialing body actually accepts them. Not all courses are created equal, and choosing the wrong provider means wasted time and money. That’s why picking an approved provider is step one.
For sonographers, you’ll want to look for courses approved by recognized organizations. These typically include the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM), the Society of Diagnostic Medical Sonography (SDMS), the Society for Vascular Ultrasound (SVU), or the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT). These organizations are often designated as Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanisms (RCEEMs) by ARRT, which is exactly what you need.
Look for providers that offer automatic credit transfer—this is a game-changer. Some organizations can submit your CME transcripts directly to ARDMS, ARRT, and CCI, saving you from manual entry and potential headaches during audit season. It’s like having someone else do your paperwork while you focus on learning.
Professional membership benefits can also make a difference. Many professional organizations offer exclusive discounts on CE activities to their members. If you’re part of a professional society, it’s worth checking to see what educational benefits are included with your membership.
Of course, convenience and affordability matter too. Let’s be real: you’re juggling shifts, patients, maybe a family at home. The last thing you need is complicated course registration or courses that cost more than your grocery budget. That’s why platforms like Scrubs CE focus on making continuing education straightforward—high-quality, self-paced online courses with instant certificates, so you can meet your requirements without the stress. Check out our Ultrasound CE Courses to see what fits your schedule and specialty.
The bottom line? Always verify that courses are accepted by your specific credentialing body before you enroll. A quick check now prevents disappointment later.
Documenting Your Credits for Audits
Think of your CE certificates as your professional insurance policy. You probably won’t need them until suddenly you do—and then you really, really need them. Both ARDMS and ARRT conduct random audits, and if your number comes up, you’ll have to prove you actually completed those credits you reported.
Your documentation needs to be precise. Your full name and ID number should appear on every certificate (these can often be handwritten). The date of the course must be pre-printed in MM/DD/YYYY format—handwritten dates typically won’t cut it. Same goes for the provider name, sponsoring organization, and course title—all must be pre-printed on the certificate. The only thing you can usually get away with handwriting is the number of credit hours awarded.
Why so picky? Because during an audit, your credentialing body needs to verify that you took legitimate courses from approved providers on specific dates. Handwritten information is too easy to alter, so they require pre-printed details. It’s not about doubting your honesty—it’s about maintaining professional standards across the board.
Keep your certificates for at least four to five years. ARDMS requires four years minimum, while ARRT recommends five. Create a folder (physical or digital) and stash every certificate the moment you earn it. Trust me, trying to track down a certificate from three years ago when you’re selected for an audit is not fun.
Using your credentialing body’s online portal makes life easier. Platforms like MY ARDMS or the AIUM CME Tracker help you organize everything in one place. Some even allow direct submission of transcripts, which means less manual work for you. For specific details on what makes documentation acceptable, check out the CME Documentation Requirements outlined by ARDMS and SDMS.
The key takeaway? Stay organized from day one. It’s much easier to file certificates as you go than to scramble when audit season rolls around.
Specialty and Financial Considerations
As sonographers, our roles can be incredibly specialized, and so too can our CE for sonographers requirements. Beyond the general credits, some areas of practice demand very specific educational updates. And, of course, there’s the question of cost – because professional development shouldn’t break the bank!
Special Considerations for Sonography Specialties
If you’ve chosen to specialize in a particular area of sonography, you’ll likely face some extra requirements on top of the standard credits. This isn’t bureaucratic red tape for its own sake – it’s about making sure you have the most current, relevant knowledge for your specific field of practice.
Take breast ultrasound, for example. The American College of Radiology (ACR) sets specific minimum criteria for sonographers performing breast ultrasound examinations. When you’re first qualifying, you might need 5 CEUs specific to breast ultrasound. After that, if you’re a registered technologist, you’ll need to comply with your certifying organization’s standard CE requirements, but your credits should be pertinent to your ACR-accredited clinical practice. For unregistered or state-licensed technologists, the requirements might be 24 hours of CE every two years, focused on imaging, radiologic sciences, and patient care. Your facility will need to keep documentation of your qualifications on file for accreditation purposes. For all the specifics, the ACR’s Sonographer/Technologist: Breast Ultrasound guidelines are your go-to resource.
Vascular ultrasound has its own set of expectations. If you work at a facility seeking Vascular Ultrasound Accreditation, the ACR requires that at least one technologist with specific vascular credentials (like ARDMS’s RVT, ARRT’s RT(VS), or CCI’s RVS) must be on-site during vascular examinations. This underscores why maintaining your specialty-specific credentials and related CE is so important.
For those of you with the ARDMS RMSK (musculoskeletal) credential, your 30-credit CME period includes a requirement for a specific number of credits in musculoskeletal ultrasound. For instance, if you hold RMSK plus RDMS, RDCS, or RVT, you’ll need 10 ARDMS/APCA-accepted CMEs in musculoskeletal ultrasound and 20 in any specialty, totaling 30.
These specialty requirements ensure that sonographers aren’t just generally competent – they’re true experts in their chosen fields. And that expertise directly translates to better patient care.
The Costs Associated with Earning CE Credits
Let’s talk money. Budgeting for professional development is a real concern for most of us, and the costs associated with earning CE credits can vary wildly.
Course fees can range from free modules to thousands of dollars for multi-day conferences or extensive online programs. The good news is that membership discounts can help. Many professional organizations offer discounts on CE activities as a benefit of membership. If you belong to such an organization, the annual fee may be offset by savings on education.
Don’t overlook free CE opportunities, either. Webinars, sponsored content, and introductory courses can sometimes offer free credits – you just need to keep your eyes open for them. And here’s something many sonographers don’t take advantage of: employer reimbursement. Some employers offer financial assistance or reimbursement for CE, recognizing the value it brings to their practice. It never hurts to check with your HR department!
While some options can certainly be pricey, there are many affordable ways to earn your required credits. At Scrubs CE, we’re committed to providing convenient and affordable online courses that help you meet your requirements without stretching your budget. Think of CE as an investment in your career and your patients – one that pays dividends in skill, confidence, and continued employability. And with the right provider, that investment doesn’t have to cost a fortune.
Frequently Asked Questions about CE for Sonographers
We know you might have more questions, so let’s tackle some of the most common ones we hear about CE for sonographers. These are the real-world concerns that keep many sonographers up at night, so let’s clear them up.
What happens if I get audited by my credentialing body?
Getting that audit notification in the mail can make your heart skip a beat, but here’s the thing: audits are completely routine. Both ARDMS and ARRT randomly select registrants each year to verify compliance. It’s not personal, and it’s not because they suspect anything—it’s just part of maintaining the integrity of our profession.
If you’re selected for an ARDMS audit in March, you’ll typically have one month (until April 30) to submit all your required documentation. ARRT operates similarly, with specific deadlines once you receive your notification. This is exactly why keeping those certificates organized and accessible is so crucial. ARDMS requires you to maintain your documentation for a minimum of four years, while ARRT recommends hanging onto them for five years.
Missing the deadline isn’t the end of the world, but it does complicate things. ARDMS may offer a CME Reinstatement option by August 1, though this involves additional paperwork and stress you’d probably rather avoid. For ARRT, failing to meet CE requirements can land you in “CE Probation” status, where you’ll need to complete the missing credits and pay a fee within six months.
The most serious consequence? Failure to comply with audit requests or meet probation requirements can lead to permanent revocation of your credentials. That’s why accurate record-keeping isn’t just a suggestion—it’s essential protection for your career.
Can I use the same CE credits for multiple credentials?
Yes, and this is genuinely good news if you’re juggling multiple credentials! Many sonographers hold certifications from both ARDMS and ARRT, and the overlap can actually work in your favor.
When you complete a Category A course or an ARDMS/APCA-accepted course from a provider recognized by both organizations, those credits can often count toward both sets of requirements. For example, if you’re an ARRT-certified sonographer, the 16 sonography-specific credits you earn will simultaneously count toward your overall 24 biennial credits. Similarly, if you take a musculoskeletal ultrasound course that fulfills your ARDMS specialty requirement, those credits also count toward your total 30.
The key is making sure the CE provider is accepted by all the credentialing bodies you need to satisfy. Many CE providers, especially those recognized by major professional societies, offer credits that are accepted by both ARDMS and ARRT, which simplifies your planning considerably.
That said, always cross-reference the specific requirements of each credentialing body. If you hold an ARDMS specialty credential requiring a certain number of credits in that specific area, you’ll need to ensure your chosen courses meet that particular criterion. The general credits can overlap beautifully, but specialty-specific requirements need special attention.
How are CE requirements for sonographers different from other medical professionals?
While continuing education is a universal thread throughout healthcare, our requirements as sonographers have some unique characteristics that set us apart.
The most noticeable difference is our specialty-specific credit mandates. While a nurse might have broader CE requirements covering general nursing topics, sonographers need credits directly related to sonography or particular sub-specialties. Those 16 sonography-specific credits for ARRT or specialty CMEs for ARDMS credentials like RMSK or RPVI? That’s uniquely ours.
Our CE content also digs deeply into ultrasound physics, instrumentation, image optimization, and advanced scanning techniques—subjects that wouldn’t be relevant for a physical therapist or even a radiographer working in a different modality. We’re constantly learning about transducer technology, Doppler principles, and artifact recognition in ways specific to our field.
We also interact with different credentialing bodies than most other medical professionals. While physicians deal with state medical boards and nurses with nursing boards, sonographers primarily work with ARDMS, ARRT, and CCI. Each organization has its own rules, reporting cycles, and audit processes that we need to master.
Then there’s ARRT’s Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR), with its Structured Self-Assessment every 10 years. This in-depth process is specifically designed for radiologic technologists, including sonographers, to proactively identify and address knowledge gaps. It’s not just about earning credits—it’s about proving ongoing competency in a structured, measurable way.
These differences highlight just how specialized our profession really is and underscore our commitment to maintaining expertise in a field that’s constantly evolving with new technology and techniques.
Conclusion
You made it! We’ve covered a lot of ground together, from understanding what CE for sonographers actually means to navigating the specific requirements of different credentialing bodies. Whether you’re tracking ARRT’s two-year biennium or ARDMS’s three-year CME period, the path forward is clearer now. You know what you need, where to find it, and how to keep those all-important records safe for audits.
Here’s the thing: continuing education isn’t just another box to check off on your professional to-do list. It’s your commitment to lifelong learning, to staying on top of the latest ultrasound techniques and technologies, and to giving your patients the absolute best care possible. Every credit you earn represents another step forward in your career, another skill sharpened, and another way you’re contributing to the high standards of our profession.
The beauty of today’s CE landscape is that it doesn’t have to be stressful or expensive. With online learning, you can fit professional development into your life on your schedule. Whether you’re squeezing in a course during lunch breaks or dedicating a weekend to knock out several credits at once, you’re in control. And when you choose quality, affordable options, you’re making a smart investment in yourself without breaking the bank.
Being proactive about managing your credits means you’ll never face that last-minute scramble before a deadline. It means you’ll be ready if you’re selected for an audit. Most importantly, it means you’re continuously growing as a sonographer, keeping pace with our changing field.
At Scrubs CE, we understand the challenges you face. That’s why we’ve built a platform that makes earning your CE for sonographers credits straightforward, accessible, and affordable. We’re here to support your journey every step of the way, with high-quality courses, instant certificates, and a hassle-free experience that respects your time and budget.
So take that next step. Take control of your professional development and invest in your future. Your patients, your employers, and your career will thank you.
Ready to easily earn your required credits? Explore our comprehensive Ultrasound Continuing Education courses at Scrubs CE – where convenience, affordability, and quality come together to support your career journey.
5 Ridiculously Awesome Ways to Find Radiologic Technologist CE
Why Radiologic Technologist CE Matters for Your Career
Radiologic technologist CE (continuing education) is required to maintain your ARRT certification and registration. Most radiologic technologists need 24 approved CE credits every two years (a biennium), while Registered Radiologist Assistants need 50 credits per biennium.
Quick Answer: How to Find Radiologic Technologist CE
- Online CE Providers – Self-paced courses with instant certificates.
- Professional Organizations – Membership often includes CE credits and access to course libraries.
- Unlimited Subscription Services – A flat annual fee for access to a large library of credits.
- Academic Courses – University courses that convert to a high number of credits.
- Conferences & Seminars – In-person events for networking and hands-on learning.
Your biennium starts on the first day of your birth month and you must report your CE credits by the last day of your birth month at the end of the two-year cycle.
Juggling patient care, new technology, and CE deadlines is a familiar challenge. The good news is that finding quality CE has never been easier. Gone are the days of mandatory travel for conferences; today’s technologists have flexible online courses, professional resources, and subscription services that fit any schedule.
With so many options, it’s important to find the right CE for your needs. Whether you’re maintaining certification, pursuing advanced credentials, or meeting state requirements, understanding your options is key. CE isn’t just about checking a box—it’s about maintaining competence, demonstrating accountability, and ensuring the best care for your patients.
Let’s explore the five most effective ways to earn your radiologic technologist CE credits without breaking your budget or schedule.
First, Understand Your Core CE Requirements
Before searching for courses, it’s crucial to understand your specific requirements from the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT). Knowing these rules prevents last-minute panic as your deadline approaches.
The foundation is straightforward: Most radiologic technologists need 24 approved CE credits every two years. This two-year period is called a “biennium.” For Registered Radiologist Assistants (R.R.A.s), the requirement is 50 credits per biennium.
Your biennium cycle is tied to your birth month. It begins on the first day of your birth month, runs for two years, and ends on the last day of that same month two years later. You report your completed CE during your annual renewal, which opens about two months before your birth month.
Crucially, the ARRT does not track your past CE activities. You are responsible for maintaining all CE documentation for at least four years. These certificates are your proof of compliance if any questions arise.
The ARRT offers a guide to maintaining your ARRT credential that details these requirements. For more on why this matters, see the importance of continuing education for X-ray technologists. You can also request to change your biennium year if the cycle doesn’t fit your schedule, offering helpful flexibility.
What Types of CE Activities Are Accepted?
Not all educational activities count toward your radiologic technologist CE requirements. The ARRT specifies what qualifies, so understanding these categories saves you time and money.
- Category A or A+ Activities: These are the gold standard, approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM). Most state boards also require Category A credits.
- Academic Courses: Courses from an accredited college or university are a great option. You earn 16 CE credits per semester credit or 12 CE credits per quarter credit for relevant coursework.
- Advanced CPR: Certifications like ACLS, PALS, or ATLS can earn you up to six credits per biennium. Basic BLS does not count.
- Authoring Articles: Writing a peer-reviewed article for an approved journal can earn you CE credit.
- Applications Training: Training on new equipment from a manufacturer may count if it meets ARRT clinical application criteria.
Activities that don’t count include basic CPR, clinical instruction (with some exceptions), and earning a new credential itself (though the required education often does). For full details, consult the ARRT’s Education Requirements for Obtaining and Maintaining Certification and Registration.
The Evolution of CE: Online vs. In-Person
The way technologists earn radiologic technologist CE has changed dramatically. The choice between online and in-person learning offers different advantages.
Online learning offers best flexibility. You can complete self-paced courses anytime, anywhere, fitting education around your work and life schedule. The variety of topics is vast, and costs are typically much lower than in-person events.
However, in-person conferences and seminars provide unique benefits. They are excellent for networking with colleagues, meeting mentors, and finding job opportunities. Hands-on workshops allow you to practice new techniques on modern equipment, and live Q&A sessions provide direct access to experts.
Many technologists find a blend of both approaches works best. Use affordable online courses for core requirements and attend an occasional in-person event for networking and specialized, hands-on training. To see what’s next in CE, check out these 5 Trends Transforming Radiology Continuing Education You Need to Know.
The 5 Best Ways to Earn Your Radiologic Technologist CE Credits
Now that you understand the requirements for radiologic technologist CE, let’s explore how to earn your credits. We have more convenient and affordable options than ever, so there’s no need to dread your biennium deadline.
Whether you prefer learning from home or networking at a conference, there’s a path that fits your lifestyle, budget, and professional goals. You can even mix and match these approaches to create a personalized CE strategy.
Let’s explore the five most effective ways to earn your credits without the stress.
1. Online CE Providers & Course Marketplaces
Online CE providers have transformed how radiologic technologists meet their radiologic technologist CE requirements. The primary benefit is flexibility—you can complete courses on your schedule, whether on a lunch break or late at night.
Here at Scrubs CE, we’ve been helping healthcare professionals since 2001. We design courses specifically for your profession that speak your language and address your daily challenges. When you finish a course, you get your certificate instantly, with no waiting.
The variety of online topics is another advantage, from radiation safety to advanced modalities. For even greater value, our radiology CE course combos bundle related courses at a better price point.
We know your time is valuable, so our enrollment process is fast and simple. You can enroll in X-ray CE in minutes and start learning immediately. Our courses are ARRT-approved and accepted by most state boards, offering an affordable and convenient way to stay compliant and in control of your professional development.
2. Membership in Professional Organizations
Joining a professional organization is a smart investment in your career. Beyond networking and advocacy, many organizations bundle substantial radiologic technologist CE benefits directly into the membership fee, offering a great return on investment.
Upon joining, members often receive a block of CE credits that can satisfy a large portion of their biennial requirement. This immediate benefit makes membership an efficient way to get a head start on your CE.
In addition, membership frequently includes access to an extensive online CE library. These libraries contain a wide selection of courses covering various modalities, from radiography and CT to mammography and radiation therapy. This allows you to explore different topics and stay current without extra cost.
Learning formats are also diverse. Many organizations offer credits for reading and reviewing professional journal articles or watching recorded webcasts from industry experts. These activities typically count as Category A credits, accepted by the ARRT and most state boards.
Beyond CE, membership provides access to job boards, salary surveys, and advocacy efforts that support the profession. It’s an investment that contributes to both your immediate CE needs and long-term career growth.
3. Unlimited Access Subscription Services
Imagine a streaming service model for your radiologic technologist CE credits. That’s what unlimited access subscription services offer, and they can be a game-changer.
These platforms operate on a simple premise: pay one flat annual fee for access to their entire library. No per-course fees or worrying about the cost of an extra credit. Many services offer access to hundreds of CE credits for a low yearly price, typically approved by the ASRT for ARRT certification.
This model is ideal if you have high-volume credit needs, such as R.R.A.s who need 50 credits or technologists with multiple certifications. It’s also perfect for those who simply love to learn and want to go beyond the minimum requirements.
Another key benefit is the ability to explore new modalities without financial risk. If you’re curious about CT or MRI, you can take introductory courses to test the waters while still meeting your current CE requirements. These platforms keep their content fresh, ensuring you’re learning about the latest advancements.
The budget-friendly nature of these subscriptions is a major advantage over buying individual courses. For more insight on getting the most value, see why a combo e-course is a good fit for your radiology CE. The peace of mind from having unlimited learning potential at your fingertips is invaluable.
4. Academic Courses and Advanced Certifications
For those looking to advance their careers, academic courses and advanced certifications provide a powerful way to earn radiologic technologist CE while opening new professional doors.
Many technologists don’t realize that university or college courses can be worth significant CE credits. Each academic semester credit converts to 16 CE credits, and each quarter credit converts to 12 CE credits, as long as the coursework relates to radiologic science. A single three-credit course could fulfill half of your biennium requirement.
This approach is ideal for those who thrive in a structured learning environment and want to make serious progress on their CE.
Furthermore, if you plan to earn a new post-primary credential in a modality like CT, MRI, or Mammography, the required structured education often counts toward your biennial CE. Structured education is the ARRT’s comprehensive training pathway for entering a new specialty. By pursuing a new credential, you are essentially earning your CE while building a new skill set and advancing your career.
This pathway to explore other modalities can transform your career trajectory. Every hour spent serves double duty—fulfilling CE obligations and making you a more valuable and marketable professional. To learn more, read about what you need to know about ARRT’s structured education solutions and requirements.
5. In-Person Conferences, Seminars, and Lectures
While online courses offer incredible convenience for earning radiologic technologist CE, in-person events still hold a unique value in professional development.
Attending a live event, like a state society conference or a specialized seminar, offers more than just credits. The networking opportunities can be career-changing, connecting you with colleagues, mentors, and potential employers. These professional relationships often last long after the event ends.
From an educational standpoint, in-person events feature hands-on workshops where you can practice new techniques on actual equipment. Live Q&A sessions allow you to get immediate, specific answers from experts. For some, the structure of a conference is a great way to focus and earn many credits in just a few days.
The trade-off is the cost of registration, travel, and time away from work. However, many technologists find a hybrid approach—combining affordable online courses with an occasional in-person event—provides the best of both worlds. These events remind us we are part of a larger professional community dedicated to patient care. For more on this, see the 5 benefits of continuing radiology education.
Navigating Specific and State-Level CE Requirements
Meeting your ARRT requirements is the baseline, but you may have additional radiologic technologist CE rules to follow. Your state licensing board and specific modality can have their own requirements that go beyond the ARRT’s.
These rules exist because different states have unique regulations and imaging specialties have specific competency concerns. It’s crucial to be compliant with both ARRT and state-level requirements to avoid issues with your license renewal.
Modality-Specific Radiologic Technologist CE
Specialized modalities often require focused continuing education to ensure expertise and patient safety.
- Mammography: Under the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA), technologists need 10 of their 24 biennial credits to be specific to mammography. You can find more on mammography continuing education requirements.
- Fluoroscopy: If you hold a fluoroscopy permit, four of your 24 CE credits must focus on radiation safety for fluoroscopy. This is particularly relevant in states like California. Learn why you should take your fluoroscopy radiation safety CE’s for California.
- Sonography: Sonographers must earn 16 of their biennial CE credits directly related to their discipline.
- CT and MRI: While not always mandated by ARRT, many states and employers require modality-specific CE to stay current with these advanced technologies. Understanding what is involved in MRI training can guide your CE choices.
State-Specific and Other Radiologic Technologist CE Rules
Many state licensing boards have their own radiologic technologist CE requirements in addition to ARRT’s.
California, for example, requires 24 Category A or A+ credits every two years, with four of those credits focused on digital radiography—a requirement unique to the state. You can find a guide on how to maintain your X-ray license in California and official details from the California Department of Public Health – Radiologic Health Branch (RHB).
Other states like Florida and Texas have their own acceptance criteria and approval processes. Limited Permit X-Ray Technicians (XTs) also have specific CE requirements, including 24 approved credits every two years, with four in digital radiography if they have that authorization.
The bottom line is to always check your state’s specific guidelines. We offer courses accepted in many states, including California, Florida, and Texas, to help you meet these varied requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions about Radiologic Technologist CE
Navigating radiologic technologist CE can bring up questions. Here are clear answers to the most common ones.
How many CE credits do I need and how often?
Most radiologic technologists must complete 24 approved CE credits every two years (your biennium). This cycle is tied to your birth month, starting on the first day and ending on the last day two years later. Registered Radiologist Assistants (R.R.A.s) have a higher requirement of 50 approved CE credits each biennium. Always check your personal ARRT account to confirm your specific requirements and deadlines.
What is the difference between Category A credits and Structured Education?
This is a common point of confusion. Category A credits are for maintaining your current certification. These are the 24 biennial credits most technologists need, covering topics relevant to daily practice. Structured Education, on the other hand, is required when you want to earn a new credential in a different modality, like CT or MRI. It’s a comprehensive, modality-specific curriculum you must complete before taking the certification exam. The good news is that credits earned through structured education often count toward your biennial CE requirement. Learn more about ARRT’s structured education solutions and requirements.
What happens if I don’t complete my CE on time?
Missing your CE deadline has serious consequences. The ARRT will likely place you on CE probation, requiring you to complete the overdue credits within a set timeframe and pay additional fees. Your certification remains active during probation, but it’s a formal warning. If you fail to resolve the probation, you risk losing your ARRT certification and registration entirely. Reinstatement is a complex and expensive process with no guarantee of success. Planning ahead and using flexible online options can help you avoid this stressful situation. The official consequences are detailed in the ARRT Rules and Regulations.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you now feel more confident about managing your radiologic technologist CE requirements. Continuing education is more than a mandate; it’s a commitment to lifelong learning, professional growth, and ultimately, better patient care. The medical imaging field evolves quickly, and CE keeps you sharp, adaptable, and marketable.
As we’ve explored, there are many ways radiology CE can benefit you as a radiologic technologist. The best part is that you have flexible and affordable options. Whether you prefer online courses, professional memberships, subscription services, academic study, or in-person conferences, there is a path that works for you.
Take control of your professional development. Don’t wait until your biennium deadline is near. Start exploring courses that interest you and make learning a rewarding part of your career.
Ready to begin? Explore our extensive library of Radiology CE Courses to make your next biennium a breeze!
A – Z Guide to X-Ray Tech CE Credit Requirements
Why X-Ray Tech CE Credits Matter for Your Career
X ray tech ce credits are mandatory continuing education requirements that X-ray technologists must complete to maintain their ARRT certification and state licensure. Here’s what you need to know:
Quick Answer:
- Standard Requirement: 24 CE credits every 2 years (biennium) for most radiologic technologists
- Credit Types: Category A or A+ credits from ARRT-approved providers
- Reporting Deadline: By the last day of your birth month at the end of your biennium
- Specialty Requirements: Additional credits may be required for mammography, CT, or state-specific licenses
- Consequences: Failure to complete requirements can result in certification probation or discontinuation
The field of medical imaging evolves rapidly. Continuing education is your pathway to providing the best possible patient care while protecting your professional credentials.
As one technologist noted after finding an affordable CE provider: “For the price, the CE credits and tracking alone are worth the membership. Best value for the money, especially for techs that need CE credits in a hurry.”
Understanding the CE landscape can feel overwhelming, with different requirements for ARRT certification, state licenses, and specialty modalities. Finding time and budget for courses adds to the stress.
The good news is that maintaining your credits is straightforward once you understand the framework. This guide breaks down everything you need to know—from decoding your biennium dates to finding affordable courses that fit your schedule.
Understanding Your Core CE Requirements
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) sets the primary standards for continuing education, based on a two-year cycle known as a biennium. Understanding this cycle is the first step to staying compliant and stress-free.
The ARRT sets the national benchmark for professional excellence, ensuring certified radiologic technologists (R.T.s) continuously engage in professional development. Understanding these requirements helps you plan ahead and avoid a last-minute scramble. For a comprehensive overview, check out our guide on What You Need to Know About X-Ray Continuing Education Requirements.
How many x ray tech ce credits are required per biennium?
Most R.T.s need 24 approved x ray tech ce credits per two-year biennium. However, requirements vary based on your credentials:
- Registered Radiologist Assistant (R.R.A.): 50 approved CE credits per biennium.
- Sonography Credentials: 16 of the biennial CE credits must be sonography-related.
The ARRT has hinted that similar discipline-specific requirements might be introduced for other modalities in the future, so it’s smart to stay informed.
Earning additional credentials doesn’t typically change your primary CE credit count, unless you move to a higher-level credential like an R.R.A. For a more detailed breakdown custom to your specific credentials, check out How Many X-Ray CE Credits Do I Need for Radiography?.
What are the deadlines for completing and reporting CE?
Your biennium—the two-year period for completing your x ray tech ce credits—is tied to your birth month and the year you first passed an ARRT exam. It begins on the first day of your birth month and ends two years later on the last day of the month before your birth month.
After your biennium ends, you have until the last day of your birth month to report your completed credits during your annual renewal. This is a grace period for reporting, not for completing credits. You must complete all CE activities within your biennium. Missing the reporting deadline has serious consequences for your certification.
While your CE reporting dates remain consistent, the ARRT does offer some flexibility. In certain circumstances, you can request to change the year of your CE biennium if needed.
The bottom line is to mark your calendar and set reminders. Your future self will thank you for being proactive rather than panicking as the deadline approaches.
Navigating Accepted CE Activities and Credit Types
The ARRT has specific guidelines on acceptable x ray tech ce credits, including the activity type and provider. Understanding these rules ensures your efforts are recognized and you don’t waste valuable time. For more detailed information, Review ARRT’s Education Requirements for Obtaining and Maintaining Certification. Our courses, like Radiography Essentials for Limited Practice 6th ed. Ebook Test, are designed to meet these standards.
What is the difference between Category A and Category A+ CE credits?
When looking for x ray tech ce credits, you’ll encounter two main categories:
- Category A Credits: Approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM), these are the standard for most technologists, including those in X-ray, mammography, nuclear medicine, radiation therapy, and CT.
- Category A+ Credits: Required for Registered Radiologist Assistants (R.R.A.s) and evaluated by a RCEEM+. They are accepted for other certifications but not required.
Always verify that an activity is approved by the appropriate ARRT-recognized RCEEM to ensure it counts towards your requirements.
What types of CE activities are accepted?
The ARRT accepts a variety of activities, offering flexibility in how you earn your x ray tech ce credits. Accepted activities include:
- Online and Homestudy Courses: Offer flexibility to learn at your own pace.
- Live Lectures and Conferences: Provide direct interaction and networking opportunities.
- Academic Courses: College or university courses count, with one semester credit typically equaling 16 CE credits and a quarter credit equaling 12.
- Advanced CPR Certification: Certifications like ACLS or PALS from ARRT-recognized providers can earn you up to six CE credits per biennium.
- Authoring Published Articles: Writing for ARRT-accepted peer-reviewed medical journals can earn significant CE credits.
- State Licensing CE: In some states (Florida, Kentucky, Massachusetts, or Oregon), activities for state licensure may also count toward ARRT requirements.
Activities that are not accepted include:
- Clinical instructorships
- Earning a new credential itself (though the coursework may count)
- Basic Life Support (BLS) certification
- Non-clinical topics (e.g., billing, stress management) or modalities outside your certification.
Our Part 1 Radiation Protection for X-Ray Procedures E-Course Test is an example of an accepted online course designed to meet these rigorous standards.
Finding and Completing Your X-Ray Tech CE Credits
Once you know the requirements, the next step is finding approved courses that fit your schedule and budget. The rise of online CE has been a game-changer for busy professionals, offering the flexibility to complete credits anytime, anywhere.
As one technologist shared, “I can pick any CE article, take the quiz, and have my CE done anywhere, anytime. It’s definitely worth the price!” This convenience means learning fits into your life, not the other way around. You can explore more about these advantages in our article on the Benefits of Taking X-Ray Continuing Education Courses.
Where can X-ray technologists find approved CE courses?
Finding approved x ray tech ce credits is straightforward if you know where to look.
- ARRT Biennial CE Search Tool: This is the best place to search for and verify approved Category A and A+ activities.
- Professional Organizations: These groups often offer comprehensive CE libraries as part of their membership benefits. Their courses are vetted and reliable.
- Dedicated Online CE Providers: Companies like Scrubs CE specialize in accessible and straightforward education. Our platform at Scrubs CE X-Ray CEU Courses offers a wide range of self-paced, ARRT-approved activities with instant certificate delivery. You can also browse our complete selection at Continuing Education Courses for X-Ray Technologists.
- State Licensing Board Websites: Check your state board’s website for lists of approved providers, especially if you have state-specific requirements.
When evaluating a provider, look for clear accreditation information and testimonials from other technologists. Need to get started quickly? We’ve put together a guide on How to Enroll in X-Ray CE Fast.
What are the costs and are there affordable options?
The cost of x ray tech ce credits varies, but budget-friendly options are available.
- Per-Credit Pricing: This model allows you to pay for individual courses, but costs can add up quickly when you need 24 credits.
- Annual Memberships: Often the most cost-effective solution, memberships offer unlimited access to a CE library for a flat yearly fee. This provides exceptional value, allowing you to complete your requirements for a low annual cost.
- Group Rates: This is a great option for departments or imaging centers to secure discounted pricing for their staff.
At Scrubs CE, we focus on providing affordable, high-quality education. Our platform is designed to be convenient and stress-free, helping you invest in your career without financial burden.
Specialty and State-Specific CE Requirements
Beyond the ARRT’s national standards for x ray tech ce credits, many states and specialty areas have their own unique CE requirements. It’s essential to understand all layers of requirements that apply to you to ensure you maintain expertise in your specific modality. Pursuing specialty-specific CE can also help you explore other modalities and advance your career.
| Credential/State | CE Credits Required | Specific Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Radiography (ARRT) | 24 credits per biennium | Category A credits from RCEEM-approved providers |
| Mammography | 15 credits every 3 years | Must meet MQSA requirements; includes 8 hours in specific mammography topics |
| CT/MRI New Credentials | Varies | Structured education programs; credits may count toward biennial CE |
| California CRT | 24 CECs per biennium | Must include 4 credits in digital radiography and 4 credits in fluoroscopy safety (if holding fluoroscopy permit) |
| Sonography | 16 discipline-specific credits | Out of the standard 24 biennial credits, 16 must be sonography-related |
| Registered Radiologist Assistant | 50 credits per biennium | Category A+ credits from RCEEM+ approved providers |
How do requirements differ for specialties like Mammography or CT?
Specialized modalities require specific continuing education beyond your standard x ray tech ce credits.
- Mammography: Under the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA), technologists must complete 15 CME units every three years, with at least eight hours on mammography-specific topics.
- CT or MRI: Structured education programs required for new credentials in these areas can often count toward your biennial CE requirements.
- Sonography: 16 of your 24 biennial credits must be directly related to sonography.
- Fluoroscopy: Many states mandate specific CE in radiation safety for fluoroscopy due to the higher doses involved.
Our courses, like The Top X-Ray Continuing Education Courses That Pay Off in the Long Run, are designed to help you meet both general and specialty-specific requirements efficiently.
How do I meet specific state requirements like California or Florida?
State licensing boards often have rules that differ from the ARRT. Always verify a course is accepted by your state board before you invest time and money.
- California has very specific rules: CRTs need 24 CECs every two years, including 4 credits in digital radiography. If you have a fluoroscopy permit, you need an additional 4 credits in fluoroscopy safety. Check the California Department of Public Health rules for full details.
- Florida and Texas also have their own state-specific requirements managed by their respective state boards.
The key is to always verify state acceptance. At Scrubs CE, we offer courses that meet many state-specific requirements, including California’s. Our course Radiography in the Digital Age 3rd ed. Test Only Emailed is designed with these varied requirements in mind.
Introduction
Staying current in the evolving field of medical imaging is a requirement. For X-ray technologists, continuing education (CE) credits are essential for maintaining certification and state licensure. This guide covers everything you need to know about x ray tech ce credits, from understanding the requirements to finding and reporting your courses.
The Importance of Continuing Education (CE) for X-Ray Technologists; Certification maintenance; State licensure; Career advancement; Patient safety.
Understanding Your Core CE Requirements
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) sets the CE standards on a two-year cycle called a biennium. Knowing your dates and totals prevents last-minute stress. You can dive deeper with our guide on What You Need to Know About X-Ray Continuing Education Requirements.
How many x ray tech ce credits are required per biennium?
Most R.T.s need 24 approved x ray tech ce credits per biennium. Exceptions include: R.R.A.s (50 credits) and those with a Sonography credential, where 16 of the 24 must be sonography-specific. Adding credentials typically doesn’t change your 24-credit total unless you move to a higher-level role like R.R.A. For details, see How Many X-Ray CE Credits Do I Need for Radiography?.
What are the deadlines for completing and reporting CE?
Your biennium starts on the first day of your birth month and ends two years later on the last day of the month before your birth month. You then have until the last day of your birth month to report during renewal. Complete all credits within the biennium; the extra time is for reporting only. In limited cases, you can request to change the year of your CE biennium.
Navigating Accepted CE Activities and Credit Types
The ARRT defines what counts toward your x ray tech ce credits. Always verify activities against ARRT rules: Review ARRT’s Education Requirements for Obtaining and Maintaining Certification. Many of our courses, like Radiography Essentials for Limited Practice 6th ed. Ebook Test, meet these standards.
What is the difference between Category A and Category A+ CE credits?
- Category A: Approved by a RCEEM; standard for most technologists.
- Category A+: Evaluated by a RCEEM+; required for R.R.A.s (accepted for others but not required).
What types of CE activities are accepted?
Accepted examples:
- Online and homestudy courses
- Live lectures, conferences, and academic courses (1 semester credit = 16 CE; 1 quarter credit = 12)
- Advanced CPR like ACLS/PALS from ARRT-recognized providers (up to 6 per biennium)
- Authoring peer-reviewed publications
- Certain state licensing CE (varies by state)
Not accepted:
- Clinical instructorships
- Earning the new credential itself
- Basic Life Support (BLS)
- Non-clinical topics or modalities outside your certification
A good fit: our Part 1 Radiation Protection for X-Ray Procedures E-Course Test.
Finding and Completing Your X-Ray Tech CE Credits
Online CE makes meeting your requirements flexible and fast. As many techs note, being able to learn anywhere, anytime is a game-changer. Learn more about the benefits here: Benefits of Taking X-Ray Continuing Education Courses.
Where can X-ray technologists find approved CE courses?
- ARRT Biennial CE Search Tool: Verify Category A/A+ activities.
- Professional organizations: Reliable libraries vetted for quality.
- Dedicated online CE providers: Scrubs CE offers self-paced, ARRT-approved courses with instant certificates: Scrubs CE X-Ray CEU Courses and our full catalog Continuing Education Courses for X-Ray Technologists.
- State-approved lists: Check your board for any additional requirements.
What are the costs and are there affordable options?
- Per-credit pricing: Pay as you go; costs can add up to 24 credits.
- Annual memberships: Typically the best value. Scrubs CE offers access to 240+ credits for around $55/year.
- Group rates: Cost-effective for departments.
Ready to start quickly? See How to Enroll in X-Ray CE Fast.
Specialty and State-Specific CE Requirements
In addition to ARRT standards, specialties and states may add requirements for x ray tech ce credits. Exploring these can support career growth: X-Ray Continuing Education Offers a Pathway to Explore Other Modalities.
How do requirements differ for specialties like Mammography or CT?
- Mammography (MQSA): Specific CE on breast anatomy, pathology, positioning, and QC—beyond general ARRT credits.
- CT/MRI: ARRT “structured education” for new credentials; these hours can often count toward biennial CE.
- Sonography: 16 of 24 credits must be sonography-specific.
- Fluoroscopy: Many states require radiation safety-focused CE.
Courses like Radiography in the Digital Age 3rd ed. Test Only Emailed and The Top X-Ray Continuing Education Courses That Pay Off in the Long Run can help.
How do I meet specific state requirements like California or Florida?
- California (CDPH-RHB): 24 CECs every two years for CRTs, including 4 in digital radiography; +4 fluoroscopy safety CECs if you hold the permit. Mammography certificate holders need mammography-specific CECs. Details: California Department of Public Health rules.
- Florida/Texas: State boards set additional rules—confirm acceptance before enrolling.
Key takeaway: ARRT approval doesn’t guarantee state approval. Verify both.
Reporting Credits, CQR, and Consequences of Non-Compliance
Completing your x ray tech ce credits is only half the battle; you must also report them correctly and on time. This diligence is critical for protecting your certification, as detailed in Radiologic Technologists Jobs: The Importance of X-Ray Continuing Education.
How should I report my completed x ray tech ce credits?
You report CE activities to the ARRT during your online annual renewal, which starts two months before your birth month. You will enter the details for each completed course.
You must keep copies of your completion certificates. The ARRT conducts random CE audits, and if selected, you must provide proof of completion for all reported credits.
State board reporting processes vary; some allow electronic submission by providers, but for most, you are responsible for manual entry. Ensure all information is correct before submitting your renewal.
What are the consequences of not meeting CE requirements?
Failing to meet CE requirements on time can have significant professional repercussions.
- CE Probation: If you miss the deadline, your certification is placed on probation, giving you a six-month extension to complete the credits.
- Discontinued Certification: Failure to correct the deficiency during probation can lead to your ARRT certification being discontinued.
- Impact on State License and Employment: A discontinued ARRT certification will likely affect your state license and ability to work legally.
- Reinstatement Process: Reinstating a discontinued certification is a complex and costly process.
The bottom line is to stay on top of your CE requirements. Proactive planning and utilizing convenient online resources can help you avoid these stressful and career-damaging situations.
Conclusion
Navigating x ray tech ce credits is a manageable and rewarding part of your professional journey. A little regular attention keeps your career running smoothly.
This guide covered the essentials: most R.T.s need 24 CE credits every two years during a biennium tied to their birth month. You must complete credits within the biennium and report them by the deadline.
We clarified that most technologists need Category A credits and that accepted activities range from online courses to advanced CPR, while things like basic BLS or non-clinical topics do not count.
Finding approved courses is easy with the ARRT’s search tool, professional organizations, and dedicated online providers like Scrubs CE. Affordable options like annual memberships offer great value and peace of mind.
For specialties like mammography or in states like California, specific requirements often apply. Always verify that your chosen courses meet both ARRT and your state board’s unique criteria—ARRT approval doesn’t automatically equal state acceptance.
Finally, remember to keep your certificates for potential audits. Failing to meet CE requirements can lead to probation or discontinued certification, which is far more stressful and expensive than staying compliant in the first place.
Your commitment to lifelong learning through x ray tech ce credits does more than check a regulatory box. It keeps your skills sharp, ensures you’re providing the best possible patient care, and opens doors to career advancement.
Ready to make your CE journey seamless and stress-free? Scrubs CE offers a wide range of ASRT-approved online courses designed specifically for busy professionals like you. With our self-paced learning, instant certificates, and affordable pricing, meeting your licensure requirements has never been easier.
Explore all X-Ray CEU courses and take the next step in your professional development today.
7 of the Best X-ray CE Credits for Radiographers
Your Guide to X-Ray Continuing Education
X ray ce credits are continuing education units required for radiologic technologists to maintain their ARRT certification and state licensure. If you’re a radiographer, you need to understand these requirements to stay compliant and keep practicing.
Quick Answer: X-Ray CE Credit Requirements
- ARRT Requirement: 24 Category A credits every two years (biennium)
- Biennium Cycle: Based on your birth month and the year you passed your ARRT exam
- Deadline: Last day of the month before your birth month
- Approval: Courses must be approved by ASRT or another RCEEM (Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism)
- State Requirements: May vary; some states like California require specific credits in digital radiography and fluoroscopy
As one radiologic technologist shared: “For the price, the CE credits and tracking alone are worth the membership. Not to mention the great courses!”
Meeting your CE requirements doesn’t have to be stressful or expensive. With over 140 X-ray CE courses available online, you can complete your credits on your own schedule. Whether you’re working full-time, managing family responsibilities, or juggling multiple commitments, online CE courses offer the flexibility you need.
Why CE Credits Matter
Your CE credits aren’t just a bureaucratic checkbox. They help you:
- Stay current with evolving imaging technology
- Maintain patient safety standards
- Advance your career opportunities
- Keep your ARRT certification and state license active
The ARRT doesn’t keep records of your CE credits—you’re responsible for maintaining your own documentation. If you’re selected for an audit, you’ll need to provide original certificates of completion. That’s why choosing a reputable CE provider that offers instant certificates and record-keeping is essential.
Most states follow ARRT guidelines, but some have additional requirements. California mandates specific credits in digital radiography and fluoroscopy. Texas requires ethics and human trafficking courses. Florida requires courses from DOH-BRC approved providers.
Understanding these requirements helps you plan ahead and avoid the stress of last-minute credit hunting. In this guide, we’ll walk you through seven essential topic areas for your next X-ray CE credits, explain how to steer ARRT and state requirements, and help you choose the best online courses for your needs.
Understanding the Essentials of X-Ray CE Credits
Think of continuing education as your professional fuel tank. Just as you wouldn’t let your car run on empty, you shouldn’t let your knowledge and skills stagnate. For radiologic technologists, earning x ray ce credits keeps you current with the latest imaging technology, safety protocols, and best practices that directly impact patient care.
Here’s the reality: medical imaging technology evolves rapidly. The equipment you trained on five years ago might already be outdated. New radiation safety guidelines emerge. Digital systems get upgraded. Without ongoing education, you’d fall behind—and in healthcare, staying current isn’t optional. It’s essential for patient safety and quality care.
Beyond keeping your patients safe, x ray ce credits are non-negotiable for maintaining your ARRT certification and state licensure. Miss your CE requirements, and you could lose your ability to practice. But here’s the good news: when you approach CE strategically, it becomes more than just a checkbox exercise. The right courses can open doors to specializations, leadership positions, and career advancement opportunities you might not have considered.
The ARRT requires 24 credits every two years—a period called a biennium. These must be Category A credits, which we’ll explain shortly. Most state licensing boards follow similar requirements, though some add their own specific mandates.
Not all courses count toward your x ray ce credits. Generally, courses must relate directly to applying X-ray technology to the human body. That means CPR certifications, medical billing, stress management workshops, and general workplace training typically don’t qualify. Similarly, courses for other modalities like MRI, nuclear medicine, or ultrasound won’t count unless you hold certification in those areas or your state specifically requires them.
When in doubt about whether a course qualifies, check with your certifying body or state board before investing your time and money. For a comprehensive look at what makes continuing education valuable for radiologic technologists, read our Guide to Continuing Education for X-Ray Technologists.
What are the general requirements for earning X-ray CE credits?
The basic requirement is simple: 24 credits within your two-year biennium period. Your personal biennium starts on the first day of your birth month in the year after you earned your ARRT certification. It ends two years later, on the last day of the month before your birth month.
Let’s say you were born in June and certified in 2022. Your biennium would run from June 1, 2023, to May 31, 2025. You’d need all 24 credits completed by that May 31st deadline. Miss it, and you’re looking at consequences like probation, fines, or even license suspension.
Here’s something critical to remember: the ARRT doesn’t track your CE credits for you. That responsibility is entirely yours. Keep every certificate of completion in a safe place—digital copies work great, but make sure they’re backed up. If the ARRT selects you for an audit (and they do conduct random audits), you’ll need to produce original certificates proving you completed the required credits.
Your state licensure renewal date might not align with your ARRT biennium, so you may need to track two separate deadlines. It sounds complicated, but a simple spreadsheet or calendar reminder system keeps everything manageable.
For everything you need to know about meeting these requirements, check out What You Need to Know About X-Ray Continuing Education Requirements.
What is the difference between Category A and Category A+ credits?
You’ll encounter two types of credits: Category A and Category A+. For most radiologic technologists, this distinction is straightforward.
Category A credits are your standard credits, and they’re what nearly everyone needs. These courses are approved by a recognized continuing education evaluation mechanism (RCEEM)—organizations like the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT) or the American Healthcare Radiology Administrators (AHRA). When a course is ASRT-approved (like all our courses at Scrubs CE), it meets ARRT requirements and is accepted by all 50 states and North American registries.
Category A+ credits are advanced-level credits designed for specific specialties. Unless you’re a Registered Radiologist Assistant (R.R.A.) or hold another advanced certification that explicitly requires A+ credits, you don’t need them. Think of Category A+ as the honors version—nice to have if required, but standard Category A credits fulfill most technologists’ needs perfectly.
If you earn Category A+ credits and don’t need them, they’ll still count toward your requirement. But don’t stress about seeking them out unless your specific certification demands it. Focus your energy on quality Category A courses that genuinely interest you and advance your career goals.
Curious about how many credits you need based on your specific situation? Read our guide on How Many X-Ray CE Credits Do I Need for Radiography?
7 Key Areas for Your Next X-ray CE Credits
When it’s time to earn your x ray ce credits, you’re not just checking a box—you’re choosing where to grow as a professional. The field of radiologic technology is constantly evolving, and the courses you select can sharpen your existing skills, introduce you to emerging technologies, or even open doors to entirely new career paths.
The beauty of continuing education is that you get to decide where to focus your energy. Maybe you want to stay current with the digital systems you use every day, or perhaps you’re curious about branching into a specialized modality like CT or MRI. Either way, there are seven key areas where you can earn valuable x ray ce credits while expanding your expertise and staying at the top of your game.
Here are the seven key areas to consider:
- Digital Radiography and PACS
- Fluoroscopy and Radiation Safety
- Mammography (MQSA)
- Computed Tomography (CT)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Specialized & Interventional Radiography
- Patient Care and Professionalism
1. Digital Radiography and PACS
Remember the days of film processing? If you started your career recently, probably not—and that’s exactly the point. The shift from film to digital has completely transformed how we capture, process, and store images. Understanding digital imaging principles isn’t optional anymore; it’s the foundation of modern radiography.
Courses in this area cover everything from how pixels translate into diagnostic images to the nuances of spatial resolution and dose efficiency in digital systems. You’ll learn about image acquisition, processing techniques, and how to optimize image quality while keeping patient exposure as low as possible. And let’s not forget about PACS administration—the system that stores and manages all those digital images. Knowing how to troubleshoot PACS issues and maintain quality control can make you an invaluable team member.
If you’re working in a state like California, you’ll need specific credits in digital radiography to maintain your permit. These courses ensure you’re not just using the technology, but truly understanding it.
Check out our offerings like Digital Radiography in Practice Test Only Emailed and Radiography in the Digital Age Test Only Mailed to deepen your digital expertise.
2. Fluoroscopy and Radiation Safety
Fluoroscopy is fascinating—it gives us real-time, dynamic images that are crucial for so many procedures. But with that power comes responsibility. Because fluoroscopy involves continuous radiation exposure, understanding how to minimize patient dose and protect yourself and your colleagues is absolutely critical.
Courses in this area focus heavily on the ALARA principle—As Low As Reasonably Achievable. You’ll learn about dose metrics, collimation techniques, pulsed fluoroscopy, and proper use of protective shielding. It’s about making smart choices with equipment operation that keep everyone safe without compromising image quality.
Some states, particularly California, take fluoroscopy safety so seriously that they require specific CE credits in this area. California mandates 4 CE credits focused on radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy for permit holders. These aren’t just regulations—they’re about creating a culture of safety in every imaging suite.
Deepen your knowledge with our Fluoroscopy Radiation Safety E-Course Test. And if you’re working in California, you’ll definitely want to read Why You Should Take Your Fluoroscopy Radiation Safety CEs for California to understand why these credits are so important.
3. Mammography (MQSA)
Mammography is one of the most specialized areas in radiologic technology, and for good reason. Early detection of breast cancer saves lives, and the quality of mammography services directly impacts patient outcomes. That’s why the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) exists—to ensure that every mammography facility meets rigorous standards.
If you’re certified in mammography, you already know that specialized CE is mandatory. Courses in this area cover everything from conventional mammography to digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), which creates three-dimensional images of the breast. You’ll also learn about breast ultrasound and how different imaging techniques complement each other in detecting abnormalities.
California technologists with mammography certificates need to earn 10 of their 24 general CE credits specifically in mammography. It’s a significant commitment, but it reflects how specialized and important this work is.
Stay current with the latest in breast imaging by reviewing Mammography Continuing Education Requirements and exploring our comprehensive Mammography CE Courses.
4. Computed Tomography (CT)
CT imaging has become indispensable in modern diagnostics. Those detailed cross-sectional images can reveal what conventional X-rays simply can’t, making CT an incredibly powerful tool for diagnosing everything from trauma to cancer.
Courses in CT cover the fundamental principles of CT imaging, including how the scanner acquires data and reconstructs it into images. You’ll study cross-sectional anatomy in depth—because understanding what you’re looking at is just as important as knowing how to capture it. Protocol optimization is another key topic, teaching you how to adjust scanning parameters for different clinical indications while managing radiation dose effectively.
With CT being such a high-demand modality, earning x ray ce credits in this area can significantly expand your career opportunities. Many facilities actively seek technologists with CT expertise, and these courses give you the knowledge to step confidently into that role.
Improve your CT skills with Computed Tomography for Technologists Test Only Emailed and explore our general CT/MRI CE options.
5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is fascinating because it creates incredibly detailed images without using any ionizing radiation at all. Instead, it relies on powerful magnetic fields and radio waves. But those strong magnets also create unique safety considerations that make MRI one of the most safety-conscious modalities in medical imaging.
MRI safety is always the top priority in CE courses for this modality. You’ll learn about magnetic field strength, projectile risks, implant compatibility, and patient screening protocols. Beyond safety, courses cover the complex physics and instrumentation behind MRI—how those magnetic fields interact with hydrogen atoms in the body to create images. Advanced applications like functional MRI (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) show just how far this technology has come.
If you’re curious about expanding into MRI, these courses provide both foundational knowledge and advanced techniques that can prepare you for this specialized field.
Find why continuous learning matters at Why MRI Programs for Continuing Education Are Important and ensure you’re up-to-date on safety protocols with Essentials of MRI Safety Test Only Mailed.
6. Specialized & Interventional Radiography
Some of the most exciting work in radiography happens in specialized and interventional settings. Whether it’s assisting with cardiac catheterization, supporting vascular procedures, or focusing on musculoskeletal imaging, these areas require a deeper understanding of specific anatomical regions and complex techniques.
Courses in this category prepare you to work effectively in cardiology, interventional radiology, or orthopedic settings. You’ll learn about the specialized equipment used in these procedures, how to position patients for optimal imaging, and how to assist physicians during complex interventions. It’s hands-on, work that requires both technical skill and the ability to think quickly.
If you’re considering a career in cardiac interventional radiography, start with How to Get Certified in Cardiac Interventional Radiography. For those interested in vascular procedures, our Vascular and Interventional Radiology The Requisites Ebook Test is an excellent resource.
7. Patient Care and Professionalism
Here’s something that doesn’t show up on an X-ray: the human connection. All the technical skill in the world doesn’t matter much if you can’t communicate effectively with patients, put them at ease, or work collaboratively with your team. That’s why patient care and professionalism are essential areas for continuing education.
Courses in this area address the soft skills that make you not just a good technologist, but a great one. You’ll explore effective communication techniques, learn about patient assessment beyond just positioning, and develop cultural competence to serve diverse patient populations. Ethics courses help you steer complex situations with integrity, reminding you that every decision you make impacts real people.
These courses reinforce something we all know but sometimes forget in the rush of a busy day: empathy, clear communication, and professional conduct are just as vital as technical proficiency. They’re what turn a good image into great patient care.
Strengthen your patient care skills with Radiologic Imaging Sciences & Patient Care(7th Ed) Ebook Test and explore the broader benefits of continuing education in 7 Ways Radiology CE Can Benefit You as a Radiologic Technologist.
Navigating ARRT, State, and CQR Requirements
Staying compliant with your x ray ce credits involves understanding a multi-layered system of requirements from national certifying bodies like the ARRT, state licensing boards, and even specific professional programs like CQR. It can feel like a maze, but we’re here to help you steer it with confidence.
The ARRT sets the national benchmark, requiring 24 Category A credits every two years. When it’s time to renew your certification, you’ll submit a CE Report Form along with your renewal application. Here’s something important to know: the ARRT doesn’t keep records of your CE credits. They may audit your CE reporting at any time, which is why keeping your original certificates of participation is absolutely crucial. If you’re selected for an audit, you’ll need to provide these documents to verify your credits.
This is where choosing the right CE provider makes all the difference. Look for courses approved by recognized continuing education evaluation mechanisms, or RCEEMs. The ASRT (American Society of Radiologic Technologists) and AHRA (American Healthcare Radiology Administrators) are two of the most widely accepted organizations that approve x ray ce credits. All of our courses, for instance, are ASRT approved for Category A credit, which means they meet ARRT certification and registration requirements without any hassle.
Many quality providers automatically transfer your completed CE credits to the ARRT and other registries. This automation removes the stress of manual reporting and helps ensure nothing falls through the cracks. For more guidance on finding reputable courses, check out CE Credits for Radiology: How Can I Get Them?
How do state-specific CE requirements differ?
While the ARRT sets a general standard of 24 x ray ce credits every two years, many states have additional or unique requirements that you must fulfill to maintain your license. It’s not uncommon for state agencies to mirror ARRT guidelines, but the details can vary significantly. Think of ARRT requirements as the foundation, and state requirements as the extra touches that make each location unique.
Here’s a quick look at how requirements can differ for some of the most populated states:
| Requirement | ARRT General | California | Texas | Florida |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Credits | 24 Category A every 2 years | 24 every 2 years | 24 every 2 years | 24 every 2 years |
| Special Topics | None required | 4 in digital radiography; 4 in fluoroscopy radiation safety (if applicable) | 1 in ethics; 1 in human trafficking | Must be from DOH-BRC approved providers |
| Mammography | N/A | 10 of 24 must be mammography-specific (for certificate holders) | N/A | N/A |
California has some of the most specific requirements in the nation. If you hold a general X-ray permit in California, you need 4 CE credits specific to digital radiography and may need 4 credits in fluoroscopy radiation safety if you perform fluoroscopic procedures. For mammography certificate holders, 10 of your 24 general CE credits must be specific to mammography. The California Department of Public Health maintains detailed information about these requirements on their official website. To understand how to stay compliant in the Golden State, read our guide on How to Maintain Your X-Ray License in California.
Texas takes a different approach, requiring 1 credit in ethics and 1 credit in human trafficking prevention. These requirements reflect the state’s commitment to professional conduct and awareness of vulnerable populations. For more on how continuing education benefits Texas technologists, explore the Benefits of Texas Medical Radiologic Technologist Continuing Education.
Florida requires that your CE credits come from providers approved by the Florida Department of Health Bureau of Radiation Control (DOH-BRC). This means you need to verify that your course provider is on Florida’s approved list before taking any courses. We provide detailed information to help Florida technologists with FL Continuing Education Self-Submission Information.
The key takeaway? Always check both your ARRT requirements and your specific state board requirements. Don’t assume that meeting ARRT standards automatically covers your state license. A few minutes of research can save you from compliance headaches down the road.
How do CQR and Structured Education fit in?
Beyond standard CE requirements, the ARRT introduced Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR) to ensure that certified professionals maintain current knowledge throughout their careers. CQR applies to certain ARRT-certified individuals and includes additional components beyond the traditional 24 x ray ce credits.
CQR consists of two main components: a self-assessment and prescribed CE. The self-assessment is a non-graded evaluation that helps you identify knowledge gaps in your practice area. Based on your assessment results, you’ll then complete prescribed CE activities that target those specific areas where you could strengthen your knowledge. This personalized approach ensures that your continuing education is directly relevant to your current practice.
There’s also something called Structured Education (SE), which serves as an alternative pathway for obtaining post-primary certification. Instead of taking a traditional certification exam, you can complete a structured series of educational activities. This option is particularly valuable for experienced technologists who want to expand into new modalities but prefer a different learning approach than exam-based certification.
Understanding how CQR and Structured Education work can open new doors in your career. For a comprehensive overview of these programs and how they might benefit you, read What You Need to Know About ARRT’s Structured Education Solutions and Requirements.
Whether you’re navigating standard CE requirements, state-specific mandates, or exploring CQR and Structured Education, staying informed is your best strategy. These requirements exist to ensure you remain a competent, current professional who provides the highest quality patient care.
Detailed Guide to Radiography CE Credits
Why Radiography CE Credits Matter for Your Certification
Radiography CE credits are continuing education credits that radiologic technologists must earn to maintain their ARRT (American Registry of Radiologic Technologists) certification and state licensure. These credits ensure you stay current with evolving technologies, safety protocols, and best practices in medical imaging.
Quick Answer: What You Need to Know
- Standard Requirement: Most R.T.s need 24 approved CE credits every two years (a biennium).
- R.R.A. Requirement: Registered Radiologist Assistants need 50 credits per biennium.
- Specialty Requirements: Some credentials like Sonography require discipline-specific credits.
- Reporting Deadline: Credits are reported during your annual renewal in your birth month.
- Where to Get Them: Courses must be approved by a RCEEM (Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism) like ASRT or AHRA.
As one technologist shared: “Best value for the money, especially for techs that need CE credits in a hurry!!” This reflects the reality for many busy imaging professionals.
This requirement isn’t just red tape; it exists to ensure patient safety and quality care. Medical imaging technology evolves rapidly with new digital radiography, MRI sequences, and updated radiation safety protocols. Without ongoing education, technologists would fall behind, potentially compromising patient outcomes.
Your CE credits also represent professional growth, opening doors to new specializations and demonstrating a commitment to excellence. Whether you’re in a hospital, imaging center, or mobile unit, staying current through CE is essential.
The system of state, ARRT, and specialization rules can feel overwhelming. However, once you understand the framework, managing your CE becomes straightforward.
Understanding ARRT and State Board CE Requirements
Managing radiography CE credits seems complicated, but it’s manageable once you understand the framework. You’ll need to meet requirements for both your national ARRT certification and your individual state license.
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) sets national certification standards. To maintain certification, you must complete continuing education (CE) during a two-year period called a “biennium.” Your reporting dates are tied to your birth month, making them easy to remember and consistent throughout your career. For official details, refer to the ARRT Education Requirements for Obtaining and Maintaining Certification and Registration.
Additionally, your state licensing board has its own requirements, which can differ from ARRT standards in credit hours or specific topics. Understanding both is crucial to practice without interruption.
The ARRT Biennium: How Many Radiography CE Credits Do You Need?
Most Registered Technologists (R.T.s) need 24 approved radiography CE credits every two years. Registered Radiologist Assistants (R.R.A.s) need 50 credits per biennium, reflecting their expanded scope of practice.
Your biennium period is tied to your birth month. Your first biennium may be shorter to align with your birth month, standardizing your schedule going forward. Once established, your biennium dates generally stay the same, even if you add credentials. All credits must be earned within your specific two-year window; credits earned before or after don’t count for that biennium. We’ve created resources to help you satisfy radiology continuing education requirements for the biennium without stress.
What are Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR)?
Beyond the basic 24 credits, the ARRT’s Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR) ensure your CE addresses knowledge areas specific to your practice. The CQR process begins with a self-assessment. Based on the results, the ARRT may prescribe CE activities to address knowledge gaps, offering personalized learning.
These prescribed activities count toward your total CE, making your learning more strategic. The ARRT also requires 16 hours of structured education per biennium—courses with clear objectives and assessments. Your radiography CE credits fulfill CQR requirements when you choose approved courses that meet the structured education criteria. Most online CE from recognized providers already meets these standards. For a deeper dive, visit what you need to know about x-ray continuing education requirements.
State-Specific Licensing Requirements: CA, FL, & TX
While ARRT certification is national, your state license allows you to practice in a specific state, and each has its own rules.
California has detailed requirements via the California Department of Public Health. Technologists need 24 CECs related to applying X-rays to the human body. Of these, four must cover digital radiography. Fluoroscopy permit holders need four credits in radiation safety for fluoroscopy, and mammography certificate holders need ten credits in mammography. Credits for topics like MRI or ultrasound are not accepted for the radiography license. All credits must be earned within 24 months of permit expiration. We offer guidance on how to maintain your x-ray license in California and provide California combos that bundle required courses.
Florida requires 12 CE credits every two years, including a mandatory medical errors course. Technologists must self-submit credits to the state board. For details, see our FL continuing education self submission information.
Texas requirements are set by the Texas Medical Board and vary by license type. Always verify current rules directly with the state.
The takeaway is that meeting ARRT requirements doesn’t automatically satisfy your state’s; you must check both.
Finding and Selecting Approved Radiography CE Credits
Once you know the requirements, you must find courses that count. Earning unrecognized credits is a waste of time and effort.
To find accepted radiography CE credits, look for courses approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM). These organizations, like the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT) and the American Healthcare Radiology Administrators (AHRA), act as quality gatekeepers. Courses with their approval will count toward your ARRT certification.
At Scrubs CE, we offer courses accepted for Category A and A+ credits for ARRT® certification. Every course in our catalog meets the rigorous standards of accrediting bodies, so there’s no guesswork at renewal time.
Types of Accepted CE Activities and Formats
You can earn your radiography CE credits in various formats to fit your learning style and schedule.
Category A and A+ credits both count toward ARRT requirements. Academic courses from accredited institutions can also earn CE credits (16 per semester credit, 12 per quarter credit), a bonus if you’re pursuing a degree.
Traditional options include lectures, conferences, directed readings, and home study. In-person events offer networking but require travel, while home study provides flexibility.
Online courses are the most popular format, offering maximum convenience. Our catalog is built for this flexibility, with interactive content and instant certificates. Live webcasts are another option, combining live learning with at-home convenience.
For a comprehensive look, explore the top x-ray radiology ce credits you can earn online and our full selection of continuing education courses for x-ray technologists.
Where to Find Approved CE Courses
You can find approved radiography CE credits through several reliable sources.
Many employer-sponsored training programs offer CE opportunities, sometimes at no cost. It’s always worth asking your supervisor what’s available. Our course catalog at Scrubs CE is designed for busy technologists, with ASRT® and AHRA® approved courses on topics like Radiation Safety, Patient Care, Image Production, and Digital Imaging. All courses include free online testing and instant certificates.
The ARRT also provides a helpful biennial CE search tool that lets you verify whether specific activities are approved. When evaluating courses, always check for that approval number—it’s your guarantee the credits will count.
Costs and Budget-Friendly Options
CE costs vary, with options like per-credit pricing or unlimited subscriptions. At Scrubs CE, affordability is a cornerstone. We offer low-cost, high-quality options with free online testing and instant certificates. Our radiology ce course combos provide even greater savings by bundling credits.
We also provide free CE options, perfect for earning credits without cost. Don’t forget to check if your employer offers reimbursement or funding for CE. Many facilities invest in their staff’s professional growth, so it’s worth asking HR about education benefits.
CE Requirements for Radiography Specializations
Specializing in an imaging modality is an exciting career step, but it comes with specific radiography CE credits requirements.
Pursuing a post-primary certification requires maintaining expertise in that area. The ARRT typically requires 16 hours of structured education for a new credential to ensure you have a solid foundation. If you hold multiple credentials, you must earn credits to satisfy each one. While some credits may apply to multiple certifications, others must be discipline-specific. Careful planning makes this manageable.
CE for CT, MRI, and Mammography Technologists
As a dynamic field, Computed Tomography (CT) requires radiography CE credits that keep pace with evolving protocols, dose optimization, and new scanning techniques. Our Computed Tomography for Technologists course addresses these needs.
MRI technologists need CE focused on complex physics, unique safety protocols, and new pulse sequences. Our Magnetic Resonance Imaging course covers these essential areas and is accepted by ARMRIT for credential maintenance.
Mammography has some of the most stringent CE requirements, largely due to federal MQSA regulations. For example, California requires 10 of 24 CECs to be mammography-specific. These credits cover breast imaging techniques, quality assurance, and screening guidelines. We’ve created comprehensive resources on mammography continuing education requirements and offer mammography ce courses to meet these needs.
CE for Sonography, Fluoroscopy, and Nuclear Medicine
Sonography technologists must earn 16 discipline-specific ultrasound credits each biennium. We offer a variety of ultrasound ce courses that meet these requirements, and many are accepted by ARDMS.
For fluoroscopy, CE focuses on radiation safety due to higher potential exposure. California, for instance, requires four CECs in radiation safety for fluoroscopy permit holders. Our fluoroscopy ce courses emphasize these critical safety aspects.
Nuclear medicine technologists must meet NMTCB requirements, staying current on radiotracer protocols, imaging procedures, and radiation safety. We’ve developed nuclear medicine continuing education courses for these specialized topics.
The common thread is that your radiography CE credits are about maintaining expertise, not just checking boxes. The key is finding quality education that respects your time and genuinely advances your knowledge.
Best Practices for Managing Your CE and Renewal
Managing your radiography CE credits is a marathon, not a sprint. To avoid a last-minute rush, start early, stay organized, and spread your CE activities throughout your two-year cycle. The ARRT does not track your CE activities; the responsibility is yours. A simple system for managing CE is key to a smooth renewal process.
One tech shared this wisdom: “I block out one Saturday morning every quarter to knock out a few credits. By the time my renewal comes around, I’m already done and can focus on my actual job.” That’s the mindset that keeps your certification secure and your stress levels low.
How to Verify and Track Your Radiography CE Credits
Properly tracking your radiography CE credits provides peace of mind. Before starting a course, use the ARRT’s biennial CE search tool to verify its approval and avoid wasting time. Every legitimate CE course has an approval number from an RCEEM (like ASRT or AHRA) on the certificate, which is essential for ARRT recognition.
Our platform at Scrubs CE includes built-in tracking tools. You get an instant certificate upon completion, and your course history is always accessible in your account. We also recommend creating your own dedicated CE folder, digital or physical, for all your records. The golden rule is to save every certificate of completion. These are your proof, so back them up.
The Reporting and Audit Process
At renewal, you’ll attest to completing your required radiography CE credits. For most, the process ends there. However, the ARRT randomly audits a percentage of renewals. If audited, you must provide documentation for the credits you claimed. This is a standard quality control measure.
If audited, you’ll submit copies of your CE certificates. This is why meticulous record-keeping is vital. The standard recommendation is to keep all CE documentation for at least one full biennium after you renew (e.g., keep 2022-2024 certificates until at least 2026). Being prepared for an audit is professional practice. With organized records, an audit is a minor inconvenience, not a career crisis.
Frequently Asked Questions about Radiography CE Credits
Let’s tackle the most common questions about radiography CE credits to help you manage your requirements with confidence.
Can I use the same CE credits for my ARRT certification and my state license?
Usually, yes. Radiography CE credits that meet ARRT requirements (Category A/A+) often count toward state licensure, allowing you to satisfy both without doubling your work. However, you must verify your state’s specific rules, as some have unique requirements.
For example, California requires specific course designations and rejects topics not directly related to applying X-rays to the human body, even if ARRT accepts them. The bottom line: always check with your state board. ARRT-approved credits may not cover all state-specific requirements. We have resources like how to maintain your radiologic technology license in the state of colorado that can help.
What happens if I don’t complete my CE credits on time?
Failing to complete your radiography CE credits on time can derail your career. The ARRT will place your certification on CE probation, giving you a limited time to complete the credits. Failure to do so can result in the loss of your certification and registration.
Losing your certification means you cannot legally practice. The reinstatement process is costly, time-consuming, and requires you to prove competency again. This is a nightmare scenario. Proactive planning and timely completion are crucial to avoid it. It’s always easier to stay on track than to fix a missed deadline.
Can I carry over extra CE credits to my next biennium?
No. The ARRT does not allow you to carry over extra radiography CE credits. All credits must be earned within your specific two-year biennium. If you earn 30 credits when only 24 are required, the extra 6 credits do not roll over. It’s a “use it or lose it” system.
Being proactive is smart, but don’t stockpile credits for the next cycle. Meet your current requirements, and then you’ll start fresh at zero for the next biennium. This helps you pace yourself and explore topics that genuinely interest you rather than just checking boxes.
Conclusion: Investing in Your Radiography Career
Radiography CE credits are more than a requirement; they are your ticket to staying relevant, competent, and confident in an evolving field.
Medical imaging technology changes rapidly. Without CE, you risk falling behind on new equipment, safety protocols, and patient care techniques. This isn’t fair to you or your patients.
CE is also about career advancement. It’s your path to specializing in areas like CT or MRI, making you more valuable to employers and more competitive in the job market. We’ve outlined 8 ways x-ray continuing education can help you with x-ray tech jobs because the benefits extend far beyond compliance.
Each course adds to your toolkit, making you the go-to expert on the latest strategies and equipment. Investing in your education helps you excel, not just maintain certification.
We know finding time for CE is tough. That’s why Scrubs CE offers high-quality, self-paced courses with instant certificates that fit your schedule. It’s straightforward, affordable education designed for busy professionals.
Your career deserves this investment. Your patients deserve a technologist who stays current. And you deserve the satisfaction that comes from being excellent at what you do.
Ready to knock out those radiography CE credits and keep your career moving forward? We’re here to make it easy.
Fulfill your ARRT biennium requirements with our radiology continuing education courses.
Beyond the Degree: Unpacking Professional Development in Healthcare
Why Professional Development Healthcare Matters More Than Ever
Professional development healthcare is the continuous learning healthcare professionals engage in throughout their careers, extending far beyond an initial degree or license. It includes:
- Clinical Skills Updates – Staying current with evidence-based practices.
- Soft Skills Training – Improving communication, conflict resolution, and patient interaction.
- Leadership Development – Building team management and decision-making skills.
- Technology Proficiency – Mastering AI, telehealth, and electronic health records.
- Regulatory Compliance – Meeting continuing education (CE) requirements.
In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, skills become outdated quickly. It takes an average of 14-17 years for new medical evidence to be broadly implemented—a gap professional development aims to close.
The stakes are high, with an estimated 33% of new nurses leaving the profession in their first year. This workforce crisis makes continuous learning and career satisfaction more critical than ever.
Professional development isn’t just about maintaining a license; it’s about advancing your career, improving patient outcomes, and finding fulfillment. As Jimmy Chung, Chief Medical Officer at Advantus Health Partners, notes: “All healthcare careers now require a level of proficiency in health IT.” Fortunately, opportunities from flexible online courses to hands-on workshops are more accessible than ever.
What is Professional Development in Healthcare?
Think of professional development healthcare as a personal commitment to continuous growth. As technology, treatments, and patient expectations evolve, professional development is how you keep pace. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) defines continuing professional development as activities integrated into daily work life that enable professional growth.
Unlike initial training, professional development is learner-driven. You set your goals and choose your path on a career-long journey that adapts to your needs and the changing healthcare landscape.
Defining the Scope: More Than Just Clinical Updates
Successful professional development goes beyond clinical procedures. It involves building soft skills like communication and leadership to handle difficult conversations and guide teams. It also includes Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) training for culturally sensitive care and a focus on physician wellness and burnout management. This is about upskilling for the real world—gaining new competencies and leadership qualities to be a proactive, well-rounded caregiver.
Professional Development vs. Continuing Medical Education (CME)
While often used interchangeably, these terms have different meanings. Continuing Medical Education (CME)—or Continuing Education (CE)—focuses on the clinical knowledge required to maintain licensure and meet regulatory requirements (e.g., 12 annual credits for a physician in Alabama, 5-15 contact hours for a nurse).
Professional Development (PD) is the bigger picture. It includes CME but also encompasses non-clinical skills like leadership, conflict management, and career planning. In short, CME is often about what you need to know, while PD is about how you apply it and who you become as a professional.
| Feature | Continuing Medical Education (CME)/CE | Professional Development (PD) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Narrower, often clinical or technical | Broader, encompasses clinical, non-clinical, and personal growth |
| Focus | Maintaining competence, updating knowledge | Enhancing overall capabilities, career advancement, holistic growth |
| Driver | Often regulatory/licensure requirements | Learner-driven, career goals, organizational needs, passion for growth |
| Outcome | Compliance, updated clinical skills | Improved performance, leadership, job satisfaction, career progression |
Many courses, like those at Scrubs CE, fulfill CE requirements while contributing to your broader professional growth. See how CE fits into your career in our Guide to Continuing Education for X-Ray Technologists.
The Transformative Benefits of Lifelong Learning
Professional development healthcare is transformative for you, your patients, and your entire healthcare system. Investing in your learning creates a positive chain reaction: you become more confident, patients receive better care, and your workplace grows stronger. It’s a win-win-win. For a deeper look at this in radiology, see our article: 5 Benefits of Continuing Radiology Education.
For the Professional: Career Growth and Satisfaction
Continuous learning makes work more engaging. By mastering new skills or developing leadership qualities, you keep the spark alive in your career. Professional development also creates valuable networking opportunities at conferences or in online forums, building a professional support system. The impact on job satisfaction is significant. Feeling challenged and valued leads to increased employee retention and reduced turnover, which is crucial in a field where burnout is high. We’ve written about this for radiologic technologists here: 7 Ways Radiology CE Can Benefit You.
For the Patient: Enhancing Safety and Quality of Care
Your professional development improves patient safety and quality of care. Research shows it takes 14 to 17 years for new medical evidence to be widely used in practice. Professional development closes that gap, ensuring patients benefit from the latest research. The landmark 1999 IOM report “To Err is Human” highlighted the problem of preventable medical errors, an issue that ongoing education directly addresses by keeping professionals current on best practices. Furthermore, training in health equity and cultural sensitivities ensures all patients receive respectful, appropriate care that honors their individual backgrounds.
For the Health System: Building a Resilient Workforce
High turnover is a painful reality for healthcare organizations. With 33% of new nurses leaving in their first year, the costs of recruitment and lost knowledge are immense. Professional development is a powerful tool for reducing staff turnover. When employees feel invested in, they are more likely to stay, seeing a future for themselves in the organization. A continuously learning workforce is also more adaptable to new technologies and protocols, which improves system performance. While training requires an upfront investment, it generates significant cost savings compared to the expense of constant staff replacement. Our article on The Importance of Continuing Education (CE) for X-Ray Technologists explores how this strengthens entire teams.
Navigating Your Growth: Types of Professional Development Training
Finding the right professional development healthcare opportunity is easier than ever, with a variety of formats to fit your schedule and learning style. The modern toolkit includes everything from online courses and hands-on workshops to conferences, mentorship programs, and clinical simulations. The key is to find what fits your career aspirations.
Flexible and Accessible: Online Learning and E-Courses
For busy professionals, online learning is a game-changer. On-demand, self-paced study means you control when and where you learn, without the pressure of a fixed schedule. You can pause, rewind, and review material as needed. Virtual webinars bring experts to your screen, and many are recorded for later viewing. Online platforms are also highly cost-effective, eliminating travel and lodging expenses. This accessibility breaks down geographical barriers, bringing specialized training to everyone. At Scrubs CE, our platform is built on this principle—providing high-quality, affordable courses that fit into your real life. For a look at your options, check out The Top X-Ray Radiology CE Credits You Can Earn Online.
Hands-On and Collaborative: Workshops, Conferences, and Mentorship
While online learning offers flexibility, in-person and collaborative formats provide unique benefits. In-person conferences expose you to cutting-edge research and valuable networking opportunities. Hands-on workshops and clinical simulations allow you to practice new skills in a supportive, low-risk environment—like a flight simulator for healthcare. Mentorship programs offer personalized guidance from experienced professionals, accelerating your growth with hard-won wisdom. Finally, peer-to-peer learning in journal clubs or study groups builds a community of practice. As a report from the National Academies Press on Continuing Professional Development: Building and Sustaining a Quality Workforce highlights, a blend of these diverse methods creates a well-rounded, resilient workforce.
The Evolving Landscape of Professional Development Healthcare
The journey of professional development healthcare is one of constant evolution, shaped by technology and our growing understanding of excellent patient care. Understanding this evolution helps us prepare for the future.
From Past to Present: A Brief History and Current Trends
The idea that healthcare professionals should never stop learning has deep historical roots, from Florence Nightingale’s advocacy in the 1800s to the post-WWII boom in formal continuing medical education. Early frameworks like the 1910 Flexner Report laid the groundwork for today’s evidence-based standards.
Today, the landscape is being transformed by several key trends. Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing diagnostics and treatment, while the expansion of telehealth demands new skills in remote care. Data analytics has become essential for quality improvement, and interprofessional education is gaining ground to improve team-based care. This has led to a shift toward personalized learning custom to individual needs. To learn more, see our article on 5 Trends Transforming Radiology Continuing Education You Need to Know.
Overcoming Barriers to Effective Professional Development in Healthcare
Despite its importance, pursuing professional development healthcare has its challenges. Common barriers include time constraints due to demanding schedules, the cost of courses and conferences, and a lack of organizational support. Many also feel overwhelmed by information overload.
Fortunately, solutions are emerging. Integrated learning embeds education into daily workflows, while microlearning delivers content in short, manageable bursts. Organizational support, such as protected learning time and financial assistance, is crucial. For individuals, flexible online platforms like Scrubs CE offer an affordable, self-paced solution. We’ve even streamlined the process, as explained in our guide: How to Enroll in X-Ray CE Fast.
The Future of Professional Development in Healthcare
The future of professional development healthcare is exciting. Personalized learning paths, powered by AI, will tailor content to your specific needs and goals. Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) will offer immersive, risk-free training for complex procedures. Gamification will make learning more engaging and effective. Crucially, there is a growing focus on workforce well-being, with programs increasingly including training on resilience and burnout prevention. This all points toward a true lifelong learning culture, where growth is an integral part of professional identity and excellent patient care.
Fostering a Culture of Growth: The Role of Organizations and Regulators
A thriving environment for professional development healthcare requires a partnership between motivated individuals, supportive organizations, and clear regulatory bodies. When these three elements work together, continuous learning becomes a cornerstone of quality care.
How Healthcare Organizations Can Champion Staff Development
Organizations have the power to foster a culture of growth. The most effective strategies include:
- Providing Resources: This means not just funding for training but also offering protected learning time so staff can develop skills without being overwhelmed.
- Implementing Mentorship Programs: Connecting experienced professionals with those earlier in their careers transfers invaluable knowledge and provides guidance.
- Encouraging Personal Development Plans (PDPs): These plans help align individual career aspirations with organizational goals, creating a clear path for growth.
- Fostering a Learning Culture: Beyond formal programs, leaders must create an environment where curiosity is celebrated, knowledge-sharing is routine, and learning from mistakes is encouraged.
The Influence of Regulatory and Professional Bodies
Regulatory and professional bodies set the standards for professional development healthcare. State licensing boards establish mandatory continuing education (CE) requirements, which can vary significantly by state and profession. (For example, we help professionals steer these rules in our guide, How Many X-Ray CE Credits Do I Need for Radiography?).
Accreditation councils like the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) ensure that CE courses meet rigorous quality standards. Finally, professional organizations such as the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) and the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) advocate for lifelong learning policies and define best practices, bridging the gap between regulatory mandates and the needs of working professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions about Professional Development
Here are answers to some common questions about professional development healthcare.
How is professional development different from the training I received in school?
Your initial schooling provided the foundation. Professional development healthcare is the lifelong process of upgrading and expanding on that foundation. Healthcare evolves rapidly with new research, technologies, and standards of care that differ from what you learned in school. Professional development keeps you current, allows you to specialize, and helps you translate knowledge into the practical skills needed for evidence-based patient care.
How do I find the right professional development opportunities for my career goals?
Start with a self-assessment of your strengths, weaknesses, and long-term goals. A personal development plan (PDP) can help map out the skills you need. Consult your professional association for recommended courses and career pathways. Explore online platforms like Scrubs CE for a wide range of accredited, self-paced courses. Finally, network with peers and mentors for valuable insights and recommendations. For more on this, see our guide: How to Use Continuing Education to Advance to a Different Modality Within Radiology.
Can I get CE credits for professional development activities?
Yes, many professional development activities offer CE credits. The key is to ensure the activity is accredited by a body recognized by your profession’s licensing board (e.g., ACCME for physicians, ASRT for radiologic technologists). Always verify that the credit type is accepted by your board and be sure to document your learning by keeping all certificates for renewal. At Scrubs CE, our courses provide the necessary accreditation to help you confidently earn your required credits. Learn more here: CE Credits for Radiology: How Can I Get Them?.
Take the Next Step in Your Healthcare Career
Healthcare never stands still. Every day brings new research, new technologies, and new challenges that shape how we care for our patients. In this dynamic environment, professional development healthcare isn’t just about checking boxes or maintaining your license—it’s about embracing growth as a core part of who you are as a professional.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored how continuous learning transforms careers, lifts patient care, and strengthens entire healthcare systems. We’ve seen how it bridges the gap between new evidence and everyday practice, how it combats burnout and turnover, and how it opens doors you might not have known existed.
The truth is, taking ownership of your professional growth is one of the most empowering decisions you can make. When you commit to lifelong learning, you’re not just adapting to change—you’re staying ahead of it. You’re positioning yourself to thrive in new roles, master emerging technologies, and find renewed purpose in your work. You’re becoming the kind of professional who doesn’t just react to the healthcare landscape, but actively shapes it.
We know your time is precious and your schedule is demanding. That’s why we created Scrubs CE—to make high-quality continuing education accessible, affordable, and convenient for busy healthcare professionals like you. Our self-paced online courses fit around your life, not the other way around. You get instant certificates, clear credit tracking, and the knowledge you need to not only meet licensure requirements but genuinely advance your career.
Whether you’re looking to fulfill your CE requirements, explore a new specialty, or simply stay at the top of your game, we’re here to support your journey every step of the way.
Ready to invest in yourself? Explore our full range of radiology CE courses and take the next step in your healthcare career today.
The Ultimate Guide to Continuing Education for Limited Scope X-Ray Techs
Why Limited Scope X-Ray Techs Need to Understand CE Requirements
Limited license radiology CE is the continuing education required to maintain your limited scope x-ray technologist license. For Limited X-Ray Operators and Limited Medical Radiologic Technologists (LMRTs), CE isn’t optional—it’s mandatory for keeping your license active.
Key CE Requirements for Limited License Radiology:
- Credit Hours: Typically 12-24 hours every 1-2 years (varies by state)
- Radiation Safety: Many states require a minimum number of hours in this area.
- Approval: Look for ARRT Category A credits or state-specific approvals.
- Format: Online, self-paced courses are widely accepted.
- Cost: Expect $90-$165 per course or bundle.
The main challenge is that every state has different rules. For example, Mississippi requires 12 hours biennially with at least 6 in radiation safety, while Texas mandates 18 hours per biennium. California, Florida, and others have their own unique requirements.
Feeling overwhelmed by the different rules, costs, and course approvals is common. The good news is that understanding your state’s specific requirements and knowing where to find approved courses makes the process much simpler. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about limited scope CE, from credit types to finding affordable courses that meet your exact state requirements.
Introduction: Who is a Limited Scope X-Ray Technologist?
If you’re reading this, you’re likely working as or considering becoming a limited scope x-ray tech. Let’s start with the basics.
A Limited Scope X-Ray Technologist goes by several names, including Limited X-Ray Operator or Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist (LMRT). Whatever the title, the role is the same: you’re trained to perform a specific set of radiographic procedures, unlike a full Radiologic Technologist (RT) who performs a wider range.
Your role is specialized and essential to the healthcare settings where you work, such as urgent care clinics and orthopedic offices.
Defining the Role and Responsibilities
Your scope of practice is defined by state regulations and focuses on specific body areas. Most limited scope techs are authorized to perform chest x-rays and extremity imaging (hands, wrists, feet, ankles). Some states also permit limited spine imaging. These procedures are the bread and butter of urgent care clinics and orthopedic offices.
Your daily work involves positioning patients, operating equipment safely, acquiring quality images, and ensuring proper patient care and radiation protection. You typically work under the supervision of a physician or a fully certified radiographer, providing timely diagnostic imaging in settings where a full-time RT may not be necessary.
The Path to Becoming a Limited Tech
Becoming a limited tech is often more accessible than becoming a full RT. Most people complete shorter, focused initial training programs. Afterward, requirements vary by state. Some states require passing a state licensure exam, while others accept certification from recognized bodies like the ARRT through its ARRT Limited Scope Exam.
Certification paths can be flexible, sometimes accepting related coursework, military training, or work experience. However, clinical experience is always required to develop hands-on skills.
Getting your initial license or certification is just the beginning. Maintaining it requires ongoing education. That’s where limited license radiology ce comes in, and it’s the focus of this guide. Understanding your CE requirements is about maintaining your professional standing and providing the best patient care.
The “Why” Behind CE: Maintaining Your License and Skills
Continuing education can feel like just another requirement, but limited license radiology CE is vital for keeping your career active and your patients safe.
Medical technology and safety protocols are constantly evolving. Without CE, you risk falling behind. License renewal is the most immediate reason for CE; failing to complete the required hours means your license expires, and you can no longer legally work. For example, some certifications require 5 CE credits annually to remain current.
Beyond paperwork, patient safety is paramount. CE courses on radiation protection teach you how to minimize exposure, while updates on image quality reduce the need for repeat x-rays. Every credit earned translates to safer care.
CE also improves your skills and can lead to career advancement. Learning new positioning techniques or quality control procedures makes you a more valuable employee. It shows a commitment to professional growth that can open doors to supervisory roles and ensures you’re prepared for new technology, like an upgraded digital imaging system.
The Importance of ARRT Approval and CQR
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) sets the standard for quality in our field. The ARRT requires its certified technologists to complete 24 CE credits every two years (a biennium). These must be “Category A” or “A-plus” credits, meaning they are approved by an ARRT-recognized body, ensuring the course content meets professional standards.
ARRT also has Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR), a 10-year cycle where technologists complete a Structured Self-Assessment (SSA) to identify and fill knowledge gaps. While CQR primarily applies to certain credentials, its principle is valuable for all techs: regularly assess your knowledge and actively seek education to improve.
Joining professional organizations like the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT) can simplify the CE process by providing access to a large library of approved courses.
Understanding CE Credit Types: Category A vs. Others
Not all CE credits are equal. Category A credits are the gold standard, as they are approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM) and trusted by the ARRT. These credits are widely accepted by state licensing boards. Many of our courses at Scrubs CE are ASRT-approved, qualifying them as Category A.
CE topics can be directly related (e.g., radiation physics, positioning, image analysis) or indirectly related (e.g., patient care, medical ethics). States may also have rules about how many credits can be earned through self-study versus live formats.
Because of these variations, choosing Category A courses is your safest bet, as they have the broadest acceptance. Always verify what your specific licensing board accepts before enrolling in a course to ensure your time and money are well spent.
Navigating State-Specific Limited License Radiology CE Requirements
The biggest challenge for limited license X-ray technologists is that CE requirements vary dramatically from state to state. Unlike the more standardized national requirements for full radiologic technologists, there is no single blueprint for limited license radiology CE. Your requirements depend entirely on where you practice.
Each state sets its own rules on renewal frequency, credit hours (typically 6 to 24 per cycle), and mandatory topics, with most requiring a certain number of hours in radiation safety. This patchwork of regulations means a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work.
A Closer Look at Key States
Let’s examine a few states to see how diverse the regulations are. Remember to always verify these with your state’s official board, as rules can change.
| State | Total CE Hours | Renewal Cycle | Required Topics & Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | 24 hours | 2 years | For Limited Permit X-ray Technicians. Must include 4 hours in digital radiography. |
| Texas | 18 hours | 2 years | For LMRTs. At least 9 hours must be directly related to ionizing radiation. A human trafficking prevention course is also required. See the Texas Medical Board for details. |
| Florida | 12 hours | 2 years | For Basic X-Ray Machine Operators (BXMO). |
Other states have different rules. For example, Mississippi requires 12 hours biennially (6 in radiation safety), and Arkansas requires 6 hours annually (3 in radiologic sciences). This diversity highlights why checking your own state’s rules is critical.
Finding and Completing Your CE Courses
Once you know your state’s requirements, the next step is finding and taking the courses. Thanks to online education, completing your limited license radiology ce has never been more convenient.
Most techs now use online courses for their flexibility. You can learn at your own pace, whether late at night or during a lunch break, without the need for travel. Platforms like Scrubs CE provide everything you need in one place: materials, quizzes, and instant certificates. You can explore options on our Continuing Education Courses for X-Ray Technologists page.
What to Look for in a Limited License Radiology CE Course
To ensure you’re investing your time and money wisely, look for courses with these key features.
First, verify accreditation and approval. ARRT Category A credits are the gold standard and widely accepted. If a course isn’t Category A, double-check that your state board accepts it for limited license renewal.
Next, evaluate the content. The course should cover topics relevant to your daily work. Key subjects include:
- Radiation Protection: Principles like time, distance, shielding, and radiation biology.
- Radiographic Image Analysis: Evaluating image quality and identifying artifacts or pathology.
- Patient Positioning: Techniques for projections within your scope of practice.
- Digital Radiography Principles: How CR and DR systems work, image processing, and dose effects.
- Medical Ethics: Patient safety, infection control, and professionalism.
Some comprehensive courses may require a specific textbook. For example, our Radiography Essentials for Limited Practice course uses a textbook, which we offer as an e-book and test bundle: Radiography Essentials for Limited Practice 6th ed.
Finding Affordable and Convenient CE Options
Continuing education doesn’t have to be expensive or complicated. Online providers are often the most affordable option, eliminating travel and lodging costs. At Scrubs CE, we focus on making limited license radiology ce accessible and convenient.
Look for course bundles or memberships to save money if you need multiple credits. Another key feature is instant certificates, which allow you to submit proof of completion to your state board without delay.
Before enrolling, check reviews from other technologists to gauge course quality. At Scrubs CE, we offer ASRT-approved Category A courses that are convenient and affordable. You can browse our full catalog on our All Courses page or check out our Radiography Prep course.
Frequently Asked Questions about Limited Scope Radiology CE
Navigating CE requirements can be confusing. Here are answers to the most common questions we hear from limited scope X-ray technologists.
What are the typical CE requirements for limited license radiology ce?
Typically, you’ll need 12 to 24 credit hours over a one-to-two-year renewal cycle (biennium). However, the exact number is determined by your state. For example, Texas requires 18 hours every 24 months, while Arkansas requires 6 hours annually.
Most states also mandate a specific number of hours in radiation safety (often 6 or more per cycle). Some states may also limit the number of credits you can earn through self-study. The key takeaway is to always check your specific state’s requirements.
How do I know if a CE course is approved for my limited license?
This is a critical step. To ensure a course will count toward your renewal, follow these steps:
- Look for ARRT Category A approval. This is the gold standard in radiologic technology. Courses approved by the ASRT, like those at Scrubs CE, qualify as Category A.
- Verify with your state licensing board. ARRT approval doesn’t automatically guarantee state acceptance for a limited license. Some states have their own approval systems. Always check your board’s website or contact them directly.
- Check the content. Ensure the course topics, such as radiation protection, positioning, and image analysis, are relevant to your limited scope of practice.
Reputable providers will be transparent about their accreditations. This is a good sign that the credits will be recognized.
Can I use the same CE credits for my ARRT renewal and my state license?
Yes, in many cases, you can. This is a huge time-saver. If your state accepts ARRT Category A credits, then a single ASRT-approved course can often satisfy both your ARRT biennial requirement and your state license renewal.
However, exceptions exist. Some states have unique requirements that must be met separately. For example, Texas requires a specific human trafficking prevention course for state licensure that does not count toward ARRT CE. Similarly, if you participate in ARRT’s Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR), the CE you complete for that process can often be applied to your biennial requirements.
Always double-check with both your state board and ARRT (if applicable) to confirm that your chosen credits will work for both. Keep detailed records of your completion certificates for documentation.
Conclusion: Invest in Your Career with Quality CE
We’ve covered the essentials of limited license radiology ce, from understanding your role to navigating state-specific requirements. We hope this guide has made the process feel more manageable.
Continuing education is an investment in your skills, confidence, and ability to provide excellent patient care. Every course you take makes you a better, more knowledgeable professional, which matters for your career and for every patient you serve.
While requirements vary and tracking credits can seem complex, you’re not alone. With the right resources, staying current can become a seamless part of your professional life.
At Scrubs CE, we understand the demands on your time and budget. We’ve built our platform to provide convenient, ASRT-approved Category A online courses that you can complete at your own pace. With instant certificates and clear guidance, we make meeting your CE requirements straightforward.
Your commitment to lifelong learning is what sets you apart. When you’re ready to take the next step, we’re here to help.
Ready to knock out your CE requirements with confidence? Explore our comprehensive Radiography Essentials course for limited practice and see how simple staying current can be.
Florida Radiology License: The Sunshine State’s Path to Certification
Getting Started with Your Radiology License in Florida
If you’re looking to obtain a radiology license Florida, you must get certified through the Department of Health to administer ionizing radiation to humans. You can achieve this through two pathways: by examination for new applicants or by endorsement for out-of-state practitioners with equivalent credentials. All applicants must be at least 18, have a good moral character, hold a high school diploma or GED, and pay the required fees.
Florida’s radiology field offers strong career prospects, with an average salary of $56,650 and top earners reaching $85,000 annually. The Florida Department of Health oversees over 27,000 professionals across several certification categories. The process involves meeting educational and background screening requirements and passing the ARRT exam or demonstrating equivalent credentials. Once certified, you must renew your license every two years by completing 12 hours of continuing education.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about obtaining and maintaining your Florida radiology license, from choosing a certification to meeting renewal requirements.
Understanding Florida’s Radiologic Technology Certifications
To work in medical imaging in Florida, you must have the correct radiology license Florida requires for your role. The Florida Department of Health (DOH) certifies all professionals who use ionizing radiation. With over 27,000 certified professionals in the state, you’ll be joining a large community. For more details on your options, you can find more info about certification options here.
The state offers five primary certification categories and three specialty certifications.
Main Certification Categories
Florida offers five primary pathways into radiologic technology, each serving different roles in patient care and medical imaging.
Basic X-Ray Machine Operator (BMO) is an entry-level certification for operating X-ray machines for basic procedures. Florida doesn’t require a formal educational program, but you must demonstrate competency and pass an examination.
General Radiographer is the most common certification, covering a wide range of diagnostic imaging. It requires completing a two-year accredited Radiologic Technology Program for comprehensive training in patient positioning, radiation safety, and image quality.
Nuclear Medicine Technologist (NMT) is a specialty using radiopharmaceuticals for diagnosis and treatment. This path requires a two-year accredited Nuclear Medicine Technology program.
Radiation Therapy Technologist (RTT) is a certification for those who want to work in cancer treatment, administering radiation doses under oncologist supervision. This role requires completing a two-year accredited Radiation Therapy program.
Radiologist Assistant (RA) is an advanced practice role. RAs work under radiologist supervision to assist with procedures and patient management, but they do not interpret or diagnose from medical images.
Specialty Certification Categories
Once established, you can pursue specialty certifications to expand your career opportunities.
Computed Tomography (CT) qualifies you to operate CT scanners, which create detailed cross-sectional images and is a high-demand specialty.
Mammography certification focuses on breast imaging, a critical role in early breast cancer detection.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) combines nuclear medicine with advanced imaging to visualize how tissues and organs are functioning.
Modalities like Ultrasound and MRI are not certified by the Florida DOH because they do not use ionizing radiation, though employers often require national registry credentials for these roles. For your radiology license Florida, you’ll focus on certifications for radiation-based imaging.
How to Get Your Radiology License Florida: Exam vs. Endorsement
Florida offers two pathways to get your radiology license Florida: certification by examination for new graduates and certification by endorsement for those licensed in another state. The Florida Department of Health (DOH) oversees the process, and their Florida DOH Licensing Page is an essential resource. The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) administers the exam required for most certifications.
General Requirements for a Radiology License in Florida
All applicants must meet these baseline requirements:
- Age: Be at least 18 years old.
- Moral Character: Possess good moral character. A criminal history requires detailed disclosure and documentation for DOH review.
- Education: Hold a high school diploma or GED.
- Application Fees: Fees are non-refundable and vary by pathway. Examination applications are $50 plus exam fees ($150-$200), while endorsement applications are $45.
- Background Screening: You must disclose any criminal convictions or professional disciplinary actions. Certain crimes prohibit licensure under s. 435.03 F.S. criminal history statute. Be prepared to provide extensive documentation if you have a criminal history.
Path 1: Certification by Examination
This is the standard path for new graduates.
- Complete Educational Requirements: General Radiographers, NMTs, and RTTs must complete a two-year accredited program. Florida does not require a formal program for Basic X-Ray Machine Operators (BMOs), though study guides are available. For this limited license, see our guide on how to become a limited license radiologic tech.
- Submit Application: Send your completed application and fees to the Florida DOH.
- Receive Eligibility: Once approved, the DOH will send you an eligibility letter to schedule your exam.
- Register for ARRT Exam: Register at www.arrt.org. You have 90 days from receiving your eligibility letter to take the exam. Missing this window requires reapplication and paying all fees again.
- Take the Exam: Ensure the name on your government-issued photo ID exactly matches your Candidate Status Report. Discrepancies can prevent you from testing. Bring two forms of ID.
- Passing/Failing: You have up to five attempts to pass. After five failures, a refresher course is required before you can re-test.
- Temporary License: New graduates can apply for a temporary license before graduation, allowing them to work while awaiting their exam. It converts to a permanent license upon passing.
Path 2: Certification by Endorsement
This pathway is for technologists already licensed in another state.
- Hold a Current License: You must have an active license in good standing from another jurisdiction.
- Meet Equivalent Standards: Florida must verify that your original state’s requirements meet or exceed its own. Holding a current ARRT (or NMTCB for Nuclear Medicine) certification generally satisfies this. The governing statute is s. 468.3065, F.S. endorsement statute.
- Submit Application: Complete the endorsement application, pay the $45 fee, and provide verification of your current license. The DOH will review your credentials and issue your Florida license upon approval.
Maintaining and Verifying Your Florida License
Earning your radiology license Florida is the first step; maintaining it requires ongoing effort. Your license must be renewed every two years, which involves completing continuing education (CE) and tracking your credentials.
Continuing Education for Your Radiology License in Florida
The field of radiologic technology is always evolving, and CE keeps your skills current.
- Requirement: Florida requires 12 hours of continuing education during each two-year license period. Your first renewal cycle may be shorter to align your expiration date with your birth month.
- Approved Providers: Courses must be from a DOH-approved provider. You can Find Approved CE Providers on the DOH website.
- Course Rules: CE courses must be earned within your current renewal cycle, and you cannot repeat the same course for credit in the same biennium. Relevant college courses also count.
- Post-Primary Exam Credit: Passing a post-primary ARRT or NMTCB exam (e.g., CT, PET, Mammography) during your renewal cycle grants you all 12 required CE hours.
- HIV/AIDS Course: This course is a condition for renewal of your radiology license Florida.
- Submitting CE: You can submit certificates via fax, email (MQAOnlineService@flhealth.gov), upload with your online renewal at www.flhealthsource.gov, or mail.
- Tracking CE: Track your completed hours at www.flhealthsource.gov by using the “Verify A License” feature.
- Reactivation: An expired license can be reactivated for up to 10 years by submitting a form, paying fees, and providing proof of CE (12 hours from the last 24 months, plus 3 hours for every six months the license was inactive).
At Scrubs CE, we offer convenient, affordable online courses to help you meet Florida’s CE requirements. Our self-paced courses provide instant certificates upon completion. We even conducted a Florida continuing education survey to better serve Florida technologists.
How to Verify a License (For Techs and Employers)
License verification is crucial for patient safety and compliance.
- State License Verification: Use the Florida DOH MQA License Verification portal to check a licensee’s status, expiration date, and disciplinary history. You can Verify a Florida License directly on the MQA site.
- ARRT Certification Verification: The ARRT maintains its own online directory, which updates daily. Important: The ARRT does not issue paper credential cards; always use the official online directory for verification.
- Requesting Verification: If an individual is not in the public ARRT directory, you can request official verification on ARRT letterhead by calling 651-687-0048. You will need to provide two identifiers (SSN, DOB, or ARRT ID).
Regularly checking your own license status is a good professional practice to ensure you remain in compliance.
The Professional Landscape: Salary and Regulations
Understanding the professional landscape, including salary expectations and regulations, is key to a successful career with your radiology license Florida.
Radiologic Technologist Salary in Florida
Florida offers competitive compensation for radiologic technologists. The average salary is approximately $56,650 per year. With experience and specialization, your earning potential can grow significantly, with the top 20% of technologists earning up to $85,000 annually. Additional certifications in areas like CT, mammography, or nuclear medicine can lead to higher-paying positions.
Penalties for Unlicensed Practice
Florida’s regulations exist to protect patients from the dangers of ionizing radiation. Practicing without proper credentials is illegal and has severe consequences.
According to Section 468.302, F.S., only a licensed practitioner or a certificate holder may administer ionizing radiation to humans. Violating this law can result in:
- Substantial monetary fines
- Court-issued injunctions to cease practice
- Misdemeanor or felony criminal charges
Beyond legal penalties, unlicensed practice leads to permanent damage to your professional reputation. The Florida DOH actively enforces these rules through facility inspections. If you encounter someone practicing without a license, you can file a complaint through the Florida Health Care Complaint Portal or by calling 1-888-419-3456 or 850-245-4339. These standards protect patients, professionals, and the integrity of the healthcare system.
Frequently Asked Questions about Florida Radiology Licenses
Here are answers to common questions about obtaining and maintaining your radiology license Florida.
What is the role of the ARRT in Florida?
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) develops and administers the national certification exam that Florida requires for most radiologic technology licenses. The Florida Department of Health (DOH) uses a passing ARRT score as a primary requirement for issuing a license by examination.
How do I contact the Florida Department of Health’s Radiologic Technology office?
You can reach the DOH Customer Contact Center at (850) 488-0595 (Monday-Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. EST). For email, use mqa.rad-tech@flhealth.gov. Mail general correspondence to: Department of Health | Radiologic Technology Certification, 4052 Bald Cypress Way, Bin C-85, Tallahassee, FL 32399-3285.
How long is my Florida radiologic technology certificate valid?
Your certificate is valid for a two-year period (a biennium). Your first renewal period may be shorter to align the expiration date with your birth month. To maintain an active license, you must complete 12 hours of continuing education and renew before it expires.
What are the continuing education requirements for radiologic technologists in Florida?
You must complete 12 hours of continuing education (CE) every two years. The hours must be from DOH-approved providers and earned within your current renewal cycle. A HIV/AIDS course is also required as a condition for renewal. Passing a post-primary ARRT or NMTCB exam during your renewal period fulfills the entire 12-hour requirement.
Where can I find approved continuing education providers for radiologic technologists in Florida?
The Florida DOH provides an official list of approved providers on its website. You can access the approved CE providers listing to ensure your courses will count toward renewal. We’ve also created a Florida continuing education survey to help us understand what radiologic technologists need most from their CE experience.
How can employers verify the certification and registration status of radiologic technologists?
For state licensure, use the Florida DOH Medical Quality Assurance (MQA) portal to verify a Florida license. For national certification, use the ARRT’s official online directory. The ARRT does not issue paper cards, so employers must use the online directory or request official verification by calling the ARRT at 651-687-0048.
What are the penalties for practicing radiologic technology without a license in Florida?
Practicing without a license is illegal under Florida Statute 468.302. Penalties are severe and can include large fines, court injunctions, and misdemeanor or felony criminal charges. It also results in irreversible damage to one’s professional reputation. Report suspected unlicensed activity via the Florida Health Care Complaint Portal or by calling 1-888-419-3456 or 850-245-4339.
What is the average salary for a radiologic technologist in Florida?
The average salary for a radiologic technologist in Florida is approximately $56,650 per year. Top earners with experience and advanced certifications can make up to $85,000 annually, making it a financially stable and rewarding career path.
Conclusion
You now have a clear roadmap for how to obtain and maintain your radiology license Florida. Whether you are starting your career or relocating to the Sunshine State, the path to certification is straightforward and rewarding.
The Florida Department of Health’s process ensures that all technologists meet high standards of competency and patient safety. Earning your license is the starting point of a fulfilling career in a dynamic healthcare market, with an average salary of $56,650 and top earners reaching $85,000. You’ll join a community of over 27,000 professionals dedicated to patient care.
Staying compliant means completing 12 hours of continuing education every two years to keep your skills sharp. At Scrubs CE, we make this process simple. Our courses are convenient, affordable, and designed for your practice, offering self-paced learning and instant certificates. When you’re ready to meet your renewal requirements, explore our ASRT-approved radiology CE courses to fulfill your Florida renewal requirements and keep your career on track.
Here’s to your success in Florida’s radiologic technology field—welcome to a career where your expertise truly matters!
Keep Your Texas License Current: A Radiologist’s CE Handbook
Understanding Your Texas Radiology CE Obligations
Texas medical board radiology ce requirements vary by license type, but all radiologic professionals in Texas must complete continuing education every 24 months to maintain their licenses. Whether you’re a Medical Radiologic Technologist, a Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist, or a Non-Certified Technician, understanding these requirements is essential to keeping your license current and your career on track.
Quick Answer: Texas Radiology CE Requirements by License Type
| License Type | Total CE Hours (24 months) | Minimum Category A/A+ Hours | Human Trafficking Training |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Radiologic Technologist (MRT) | 24 hours | 12 hours | Required |
| Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist (LMRT) | 18 hours | 9 hours | Required |
| Non-Certified Technician (NCT) | 12 hours | 6 hours | Required |
Key Requirements for All License Types:
- At least 50% of CE hours must be directly related to ionizing radiation use in diagnostic imaging or treatment
- Human trafficking prevention training (HHSC-approved) is mandatory for every renewal
- No live or in-person courses required—all hours can be completed online
- CE credits can roll over to the next renewal period (up to 2x your requirement)
The Texas Medical Board has partnered with CE Broker to help licensees track and report their continuing education more easily. This means you need a reliable system to document your completed courses and ensure you’re meeting all the specific requirements for your license type.
As one radiology professional noted, “Completing CE credits often becomes a pain point for RTs struggling to find high-quality, genuine, and affordable online CE courses.” This guide will break down exactly what you need to know about Texas radiology CE requirements, so you can focus on your patients instead of worrying about compliance.
CE Requirements by Texas Radiology License Type
The Texas Medical Board recognizes three distinct types of radiologic professionals, and each one has its own set of continuing education requirements. If you’re reading this, you probably already know which category you fall into—but it’s worth double-checking because getting this wrong could mean scrambling to complete extra hours before your renewal deadline.
All Texas medical board radiology ce requirements follow a 24-month (biennial) cycle, which means you have two full years to complete your hours. That might sound like plenty of time, but we’ve all been there—suddenly it’s month 23 and you’re realizing you still need half your credits!
Here’s how the requirements break down:
| License Type | Total CE Hours (24 months) | Minimum ‘Directly Related’ / Category A Hours | Maximum Rollover Credits (excluding human trafficking) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Radiologic Technologist (MRT) | 24 hours | 12 hours (Category A or A+) | 48 hours |
| Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist (LMRT) | 18 hours | 9 hours (Category A or A+) | 24 hours |
| Non-Certified Technician (NCT) | 12 hours | 6 hours (Category A or A+) | 12 hours |
General Medical Radiologic Technologists (MRTs)
As a General Medical Radiologic Technologist, you’re looking at 24 CE hours every 24 months. That’s the most of any license type, which makes sense given the broader scope of your practice. Here’s the thing though—not just any 24 hours will do. At least 12 of those hours must be Category A or A+ credits, which means they need to be approved by an ARRT-recognized RCEEM or RCEEM+ provider.
The good news? You can roll over up to 48 extra credits to your next renewal period (not counting your human trafficking training, which we’ll talk about later). So if you’re someone who loves learning and tends to complete more than the minimum, those extra hours won’t go to waste.
Looking for courses that fit the bill? Check out our Radiology CE Courses designed specifically to meet these requirements.
Limited Medical Radiologic Technologists (LMRTs)
If you hold an LMRT license, your requirement is 18 CE hours over 24 months. At least 9 of those hours need to be Category A or A+ credits that focus on radiation health and safety or topics directly related to your specific limited certificate category.
The nice thing about being an LMRT is that while your requirements are slightly lower than full MRTs, you still get meaningful rollover benefits. You can carry over up to 24 extra CE credits to your next renewal period. This flexibility recognizes that professional development doesn’t always fit neatly into two-year blocks.
Non-Certified Technicians (NCTs)
Non-Certified Technicians have the most streamlined requirements: 12 CE hours every 24 months, with at least 6 hours being Category A or A+ credits. Just because the number is lower doesn’t mean the quality matters any less—these hours ensure you’re maintaining the foundational knowledge and skills that keep patients safe.
NCTs can roll over up to 12 extra credits to the next renewal period. It’s worth noting that even though your total hours are fewer, the same quality standards apply. Your Category A or A+ hours need to meet the same rigorous approval standards as those for MRTs and LMRTs.
Need courses custom to X-ray work? We’ve got you covered with our Continuing Education Courses for X-Ray Technologists.
No matter which license type you hold, understanding your specific requirements is crucial. The Texas Medical Board takes compliance seriously, and meeting these standards isn’t just about checking boxes—it’s about ensuring you’re equipped to provide the best possible care to your patients.
Understanding the Texas Medical Board Radiology CE Requirements
Once you know how many hours you need, the next step is understanding what actually counts toward your texas medical board radiology ce requirements. The Texas Medical Board isn’t just looking at quantity—they care deeply about the quality and relevance of your continuing education. After all, these requirements exist to ensure you’re providing the safest, most up-to-date care to your patients.
‘Directly Related’ vs. ‘Indirectly Related’ CE
Here’s where things get specific. The TMB divides continuing education into two categories: directly related and indirectly related. Understanding this distinction is essential for staying compliant.
The golden rule is simple: at least 50% of your total CE hours must be directly related to ionizing radiation. This means the courses need to focus on how you actually use radiation in diagnostic imaging or medical treatment. Think radiation safety, patient positioning, exposure techniques, or emerging imaging technologies. These are the bread and butter of what you do every day.
What qualifies as directly related? Courses covering radiation safety, biology, and physics are the obvious ones. But it also includes anatomical positioning and radiographic exposure technique, emerging imaging modality studies, and patient care directly associated with radiologic procedures. If you’re working with contrast media, radiopharmaceutics, or specialized applications like mammography, nuclear medicine, or radiation therapy—those all count too. Even computer function and application in radiology falls into this category since modern imaging is so technology-dependent.
On the flip side, indirectly related courses are still valuable for your professional development, but they’re not tied directly to ionizing radiation. These might include general patient communication skills, computer literacy, management and administration topics, or professional ethics. While these subjects make you a better healthcare professional overall, they can’t make up more than 50% of your CE hours.
Think of it this way: the TMB wants to make sure you’re staying sharp on the technical skills that keep patients safe from unnecessary radiation exposure, while also recognizing that soft skills and broader healthcare knowledge matter too.
If you want to dive into the technical details, the Official TMB rules on CE content spell everything out. We know regulatory language can be dense, so we’ve tried to break it down in plain English here.
Mandatory Human Trafficking Prevention Training
This one’s non-negotiable: every Texas radiology professional providing direct patient care must complete human trafficking prevention training before every renewal. Yes, that means every two years, not just once.
Why is this so important? Healthcare workers are often the first people who might encounter trafficking victims. Knowing the signs and understanding how to help can literally save lives. The training must be approved by the Texas Health and Human Services Commission (HHSC), and fortunately, many approved courses are free and available online.
The good news is this training counts toward your total CE hours. It often qualifies as medical ethics or professional responsibility CE, so you’re not adding extra hours on top of your existing requirements—you’re just making sure one of those hours addresses this critical topic.
You can find approved courses on the HHSC Training page. Most take just an hour or two to complete, and they provide valuable information that could make a real difference in someone’s life.
Using Acceptable Credits and Online Course Flexibility
Let’s talk about the flexibility you have in meeting your CE requirements—because honestly, this is where things get easier than you might think.
You can complete 100% of your CE hours online. There’s no requirement for live seminars, in-person workshops, or conference attendance. Whether you’re learning at 6 AM before your shift or at midnight after the kids go to bed, online courses give you the freedom to learn on your schedule. This is especially helpful if you work irregular hours or live far from major cities where in-person training might be offered.
If you hold a current ARRT® certification, there’s even better news. The CE credits you complete for your ARRT® renewal typically satisfy your Texas state requirements too, as long as they meet or exceed the Texas hour requirements and were completed during your biennial renewal period. Just remember that the human trafficking prevention course is a Texas-specific requirement, so you’ll still need to complete that separately even if your ARRT® credits otherwise cover everything.
Hold another Texas health profession license? CE activities completed for that license can count toward your radiology requirements, provided they meet the TMB’s criteria for radiology professionals. It’s worth checking if any of your existing CE can do double duty.
For those hours beyond your required Category A or A+ credits, you can even use self-study activities—things like reading professional journals, audio programs, or watching educational videos—as long as you can verify that you completed them. Just keep good records, because if you’re audited, you’ll need to show proof.
At Scrubs CE, we’ve designed our courses specifically to meet both Texas TMB and ARRT® requirements, so you can check both boxes at once. Our Radiology CE Course Combos bundle everything you need for a complete renewal cycle, including courses that qualify as directly related to ionizing radiation. You get instant certificates, so there’s no waiting around wondering if you’re compliant.
Your Texas Radiology License Renewal Guide
You’ve put in the work to complete your CE hours—now it’s time to make it official. Renewing your Texas radiology license is actually pretty straightforward once you know the steps. Let’s walk through the process together, so you can check this box with confidence and get back to what matters most: caring for your patients.
Navigating the Texas medical board radiology ce requirements for renewal
The good news? The Texas Medical Board has made renewal mostly a digital experience. No more mailing forms or waiting weeks for processing. Here’s how it works:
Your renewal journey starts about 60 days before your license expires. The TMB will send you a friendly postcard reminder—though we always recommend marking your calendar independently, just in case that postcard takes a detour through the mail system!
When you’re ready to renew, head to the TMB online renewal portal. Have your license number and the last four digits of your Social Security Number handy. Once you log in, you’ll see your current information displayed. Take a moment to review everything carefully—your name, address, and contact details. If anything’s changed since your last renewal, now’s the time to update it.
Here’s where those texas medical board radiology ce requirements come into play: you’ll be asked to attest that you’ve completed all your required continuing education hours, including that mandatory human trafficking prevention training we discussed earlier. Notice we said “attest”—you won’t actually upload your certificates during the renewal process itself. You’re essentially giving your professional word that you’ve done the work. (But keep reading, because those certificates are definitely important!)
After confirming your information and CE completion, you’ll move to the payment section, which is handled through Texas.gov. Choose your payment method—credit card or electronic check—and submit your renewal. Most online renewals process within two business days, which means you’ll have peace of mind almost immediately.
If you hit any snags with the online system, the TMB’s helpdesk is available at registrations@tmb.state.tx.us. They’re there to help, so don’t hesitate to reach out.
Renewal Fees and Record Keeping
Let’s talk about the financial side first. Medical Radiologic Technologists (MRTs) and Limited Medical Radiologic Technologists (LMRTs) pay $66 to renew their licenses. Non-Certified Technicians (NCTs) pay $56 for registry renewal. These are the base fees set by the Texas Medical Board. Texas.gov may tack on a small processing fee depending on whether you pay by credit card or electronic check—usually just a few dollars, but it’s good to know ahead of time.
Now, here’s the part that really deserves your attention: keeping records of your completed CE courses. We can’t stress this enough! While you don’t submit your certificates during the online renewal, the Texas Medical Board conducts random audits. If your name comes up, you’ll need to provide documentation proving you completed every single CE hour you claimed.
Think of your CE certificates as your professional insurance policy. We recommend keeping them organized and accessible for at least five years. Your records should clearly show the course name, the provider who offered it, when you completed it, how many credit hours you earned, and what category it falls under (Category A/A+, directly related, indirectly related, etc.).
The TMB has partnered with CE Broker to help licensees track and report their continuing education more easily. This platform can be a helpful tool for staying organized. That said, we always recommend maintaining your own backup copies of certificates. Technology is wonderful until it isn’t, and having your own files means you’re never caught off guard.
When you complete courses through Scrubs CE, you’ll receive instant certificates that include all the documentation details you need. Save them in a dedicated folder—whether that’s a physical binder or a digital file on your computer—and you’ll be ready for anything the TMB throws your way. It’s one of those small organizational habits that can save you from major headaches down the road.
Frequently Asked Questions about Texas Radiology CE
We know that navigating continuing education requirements can sometimes feel overwhelming, especially when your career depends on getting it right. Let’s tackle some of the most common questions we hear from radiologic professionals across Texas, so you can approach your CE with confidence.
What happens if I fail to meet the CE requirements?
Let’s be honest—this is the question that keeps many professionals up at night. Failing to meet your Texas medical board radiology ce requirements isn’t something to take lightly, as the consequences can significantly impact your career.
The most immediate consequence is that the Texas Medical Board will deny your license renewal. Without the required CE completed, you simply won’t be able to renew, which means you can’t legally practice until you resolve the issue. This isn’t just a formality—it’s a legal requirement that protects patients and maintains professional standards.
Beyond renewal denial, the TMB can take disciplinary action against your license. This might include suspension or, in severe cases of repeated non-compliance, even revocation. These actions become part of your professional record and can affect future employment opportunities, insurance coverage, and your professional reputation.
If you find yourself in this situation, the reinstatement process can be both lengthy and costly. You’ll need to complete all outstanding CE requirements, potentially pay penalty fees, and possibly appear before the Board to explain your non-compliance. Some licensees are also required to complete additional education beyond their standard requirements.
We understand that life happens—unexpected circumstances can derail even the best-laid plans. If you’re approaching your renewal deadline and haven’t completed your CE, don’t wait until the last minute. Reach out to the TMB early to discuss your options, and consider using online courses that offer instant certificates so you can complete your requirements quickly. At Scrubs CE, we’ve helped countless professionals get back on track with flexible, self-paced courses that fit even the busiest schedules.
Are there specific CE requirements for modalities like MRI or Mammography?
This is a great question, especially as radiology becomes increasingly specialized. The good news is that the general TMB rules apply across all modalities, but there are some important nuances to understand.
For MRI technologists, while the TMB’s standard requirements still apply, many employers and credentialing bodies recommend (or require) at least 16 hours of MRI-specific education every four years, with at least 8 of those hours focused on clinical applications. If you’re ARRT® certified in MRI, you’ll want to ensure your CE meets both the TMB’s “directly related” criteria and ARRT®’s specialty requirements. Fortunately, MRI courses focusing on safety, physics, and imaging protocols clearly count as “directly related” to ionizing radiation use when they cover the full scope of your practice.
For mammography professionals, courses focusing on mammography applications definitely count as “directly related” CE under Texas law, since they involve ionizing radiation for diagnostic imaging. If you hold an ARRT® Mammography (M) certification, you’ll need to ensure your CE is relevant to that specialty for both your state and national requirements.
The key is to remember that national certifying bodies like ARRT® often have more specific requirements for maintaining specialty credentials than the TMB’s general rules. You’ll want to check both sets of requirements and choose CE that satisfies all your obligations. We always recommend selecting courses that align with your actual day-to-day practice—not only does this help you stay compliant, but it also makes the education more relevant and engaging.
How do I prove I completed my CE hours?
This might be the most practical question of all, because having completed your CE is only half the battle—you need to be able to prove it when the TMB comes knocking.
Your primary proof is your certificates of completion. Every time you finish a CE course, download and save that certificate immediately. We recommend keeping both digital copies (in a dedicated folder on your computer or cloud storage) and physical copies in a binder. Think of it as your professional insurance policy—you hope you never need it for an audit, but you’ll be incredibly grateful if you do.
When you renew your license online, you’ll attest that you’ve completed all required CE, including the mandatory human trafficking prevention training. While you don’t submit certificates during the renewal process itself, you’re making a legal declaration of compliance. This attestation is your official statement to the TMB that you’ve met all requirements.
Here’s where it gets real: the TMB conducts random audits of licensees. If your name is selected, you’ll receive a notice requesting copies of your CE certificates, typically within a specified timeframe. This isn’t a sign that something’s wrong—it’s just their quality assurance process. But if you can’t produce the documentation, you could face serious consequences, even if you actually completed the courses.
Using a CE tracker makes this whole process much easier. The TMB has partnered with CE Broker to help licensees track and report their continuing education, which can automatically compile your records. At Scrubs CE, we also provide a personal dashboard where you can access and download all your completed course certificates anytime, anywhere. Many of our customers tell us this feature alone saves them hours of searching through old emails or files when renewal time comes around.
The bottom line? Keep meticulous records from day one of your renewal period. Set up a simple filing system, whether digital or physical, and add each certificate as soon as you earn it. Your future self will thank you, especially if you’re one of the lucky ones selected for a random audit!
Conclusion
You’ve made it to the end of this guide, and hopefully, you’re feeling a lot more confident about tackling your Texas medical board radiology ce requirements! Whether you’re an MRT needing 24 hours, an LMRT working toward 18, or an NCT completing your 12 hours, you now have a clear roadmap for staying compliant with the Texas Medical Board.
Meeting these requirements isn’t just about checking boxes or avoiding penalties—though those are certainly important! It’s really about something bigger. Every course you complete, every new technique you learn, and every safety protocol you review makes you a better radiologic professional. Your patients benefit from your updated knowledge. Your colleagues benefit from your expertise. And honestly, you benefit too, by keeping your skills sharp and your career moving forward.
We understand that juggling work schedules, family commitments, and continuing education can feel overwhelming. That’s exactly why we’ve built our course library to fit your life. You can learn at midnight in your pajamas or during your lunch break—whatever works for you. No driving to seminars, no rigid schedules, just high-quality education when and where you need it.
From understanding the difference between directly related and indirectly related CE to completing that mandatory human trafficking prevention training, you’re now equipped to handle your renewal like a pro. Remember to keep those certificates organized, mark your renewal dates on your calendar, and don’t wait until the last minute to complete your hours. Your future self will thank you!
Ready to knock out your CE requirements with courses that are actually relevant, engaging, and convenient? Discover the benefits of Texas Medical Radiologic Technologist Continuing Education with Scrubs CE and make your next renewal the easiest one yet. We’re here to support you every step of the way, because when you succeed, healthcare in Texas gets a little bit better for everyone.
Stay Certified: Everything You Need to Know About ASRT CE
Why Understanding ASRT CE Requirements Matters for Your Career
ASRT CE requirements are the continuing education (CE) standards from the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT) and the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) that ensure R.T.s maintain their certification.
Quick Answer: Core ASRT CE Requirements
- 24 CE credits required every two years (biennium) for most R.T.s
- 50 CE credits required for Registered Radiologist Assistants (R.R.A.s)
- 16 discipline-specific credits required for Sonography credentials
- All credits must be Category A or A+ approved
- Credits must be completed within your biennium (linked to your birth month)
- Report credits during annual renewal every other year
Since 1995, mandatory CE has ensured patient safety by keeping technologists current with rapid advances in healthcare technology, techniques, and equipment.
Your biennium is a two-year period starting on the first day of your birth month. For new technologists, it begins on the first day of their birth month after passing their initial ARRT exam.
You are responsible for keeping CE records for at least five years, as the ARRT does not track them for you. You’ll need this documentation if you’re selected for a random audit. To simplify this, many technologists use ASRT’s tracking services, which can automatically transfer credits to the ARRT during online renewal.
Failing to meet CE requirements results in CE probation status. This gives you a six-month window to complete the missing credits and pay a $50 fee to avoid having your certification discontinued.
Understanding Your Core Biennial CE Requirements
Staying certified as a radiologic technologist requires a commitment to ongoing learning. ASRT CE requirements ensure you remain current with new technology, techniques, and safety protocols, which is vital for patient safety.
Central to these requirements is your biennium: a personal two-year CE cycle tied to your birth month and initial ARRT certification year. For example, a technologist born in March and certified in 2022 would have a biennium from March 1, 2022, to February 28, 2024. Knowing your biennium dates is crucial for compliance.
How Many CE Credits Do You Need?
Most R.T.s holding ARRT certification need 24 approved CE credits during each biennium. If you just earned your first certification, your biennium starts on the first day of your birth month after you passed your exam, giving you two full years to complete your credits. Some credentials have different requirements, which are covered below. For complete details, always check the official ARRT Education Requirements for Obtaining and Maintaining Certification and Registration document.
Understanding Credit Categories: A vs. A+
Not all CE credits are the same. Understanding the two main categories helps you choose the right courses.
Category A credits are used by most technologists. These are courses approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM), such as the ASRT. Look for Category A approval to ensure a course counts toward your ARRT requirements.
Category A+ credits are more specialized. These courses meet specific content criteria for Registered Radiologist Assistants and must be approved by an RCEEM+ organization. R.T.s can also take A+ courses, and they will count toward general CE requirements.
Special CE Requirements for R.R.A.s and Other Credentials
While 24 credits is the standard, some credentials have more specific requirements.
-
Registered Radiologist Assistants (R.R.A.s): Need 50 approved CE credits per biennium. At least 25 must be Category A+, and 35 must be discipline-specific. R.R.A.s can also use up to 25 Category 1 credits from organizations like AMA/ACCME, AAPA, or AAFP. See the CE Requirements for R.R.A.s for full details.
-
Sonography Credentials: Require 16 discipline-specific credits related to sonography during your biennium.
-
Mammography: Professionals must meet additional federal requirements under the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA). Review these regulations at Federal CE Regulations for Mammographers.
Always verify the specific ASRT CE requirements for your credentials to avoid compliance issues.
Finding and Earning Approved CE Credits
Earning your CE credits can be a flexible and engaging process with options for every learning style and schedule. Whether you prefer online courses or live conferences, there’s a path for you.
How to Meet Your ASRT CE Requirements with Approved Activities
The ARRT recognizes a broad range of CE activities, provided they are relevant to radiologic sciences and meet approval criteria. Popular options include:
- Category A or A+ approved courses: These are the foundation of most CE plans and include online courses, webcasts, directed readings, conferences, and workshops. They must be approved by an ARRT-recognized RCEEM like the ASRT.
- Academic courses: Relevant courses (e.g., biological, physical, health sciences) from accredited postsecondary schools count if you earn a grade of C or better.
- Advanced CPR certifications: Certifications like ACLS or PALS from recognized providers (e.g., American Heart Association) can earn you up to 6 credits once per biennium. Basic CPR does not count.
- Authoring and Presenting: Publishing articles in peer-reviewed medical journals or developing and presenting pre-approved lectures can earn credits.
- Facility applications training: Onsite training on new equipment can count for up to 8 Category A credits per biennium if approved by a RCEEM.
Use the ARRT’s biennial CE search tool to find approved activities and take the guesswork out of compliance.
How CE Credits Are Calculated for Different Activities
Understanding how activities translate into credits helps you plan effectively:
- Academic courses: One semester credit hour equals 16 Category A CE credits, and one quarter credit hour equals 12 Category A CE credits. A single three-credit semester course can fulfill your entire biennium’s requirement.
- Advanced CPR certifications: ACLS or PALS provides up to 6 CE credits, claimable once per biennium.
- Other activities: Most activities are based on contact hours. One 50-60 minute contact hour equals 1 CE credit. Shorter activities can earn partial credit (e.g., 30-49 minutes = 0.5 credits). Activities under 15 minutes do not receive credit.
Credits are awarded based on the activity’s completion date, not the submission date.
Activities That Do NOT Count Toward CE Requirements
Knowing what doesn’t count is just as important as knowing what does. The ARRT does not accept the following for CE credit:
- Basic Life Support (BLS): Considered a fundamental job responsibility, not continuing education.
- Routine department meetings: Staff meetings and administrative briefings do not qualify.
- Clinical instructorships: While valuable, serving as a clinical instructor does not earn CE credits.
- Newly-earned credentials: Passing an additional ARRT exam no longer counts for bienniums beginning on or after January 2018.
- Employer-specific training: Training on internal policies, procedures, or facility-specific software is not accepted.
- Irrelevant subject matter: Courses on topics unrelated to radiologic sciences (e.g., personal finance, fine arts) will not count.
For the most current information, always refer to the ARRT’s Education Requirements for Obtaining and Maintaining Certification and Registration document.
Navigating CQR and the Structured Self-Assessment
If you earned your ARRT credential on or after January 1, 2011, you must also complete the Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR). CQR is a process to ensure your skills and knowledge evolve with the field. It is a professional tune-up that happens roughly every 10 years for each discipline you hold.
What Are the Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR)?
The CQR process applies to all R.R.A.s and any R.T. who earned their initial ARRT credential on or after January 1, 2011. It is a structured, three-step process:
- Professional Profile: You’ll review and document your work experience and the types of procedures you perform, giving ARRT a clear picture of your current practice.
- Structured Self-Assessment (SSA): This is a self-assessment, not a pass/fail exam, designed to identify potential knowledge gaps that may have developed over time.
- Prescribed Continuing Education: If the SSA reveals areas needing a refresh, ARRT will assign specific CE activities. These prescribed credits count toward your regular biennial CE requirements, allowing you to be more strategic with your learning.
The ASRT offers guidance and tools to help technologists steer this process. Explore their resources on the Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR) Resources for ASRT Members page.
Preparing for the Structured Self-Assessment (SSA)
The SSA is the core of the CQR process. It’s a tool to help you identify areas to brush up on your knowledge. While not a high-stakes exam, preparation can build confidence. The ASRT offers several resources to help you feel ready:
- Practice tests: Available for ASRT members, these simulate the computer-based testing experience for radiography, radiation therapy, CT, and MRI.
- Study modules: These cover foundational knowledge in areas like anatomy, physics, and radiation biology, perfect for a targeted review.
- Clinical refreshers: These resources cover procedural knowledge for hundreds of medical imaging and radiation therapy procedures.
- Test-taking improvement courses: These online courses help you develop better strategies for managing time and reducing test anxiety.
Using these resources can help you identify and address knowledge gaps before your SSA, and even if you receive a CE prescription, you’ll be prepared to tackle it.
The Complete Guide to ASRT CE Requirements for Reporting and Tracking
Proper reporting and tracking are crucial for maintaining your certification. It’s not just about earning credits; it’s about ensuring they are recorded correctly and transferred to the ARRT and other agencies in a timely manner.
Your Reporting Timeline and Process
While you renew your ARRT certification annually, you only report CE compliance every other year at the end of your biennium. Your biennium begins on the first day of your birth month and ends two years later on the last day of the month before your birth month.
You must complete all CE activities within your biennium and report them by the last day of your birth month. This deadline is firm. Once your renewal is submitted, no changes can be made to the reported CE activities, so double-check everything before submitting. In rare cases, you may be able to request to change the year of your CE biennium, but this is not a standard option. Plan your CE activities throughout your biennium to avoid a last-minute scramble.
How to Track Credits and Ensure They Transfer Correctly
You can track your ASRT CE requirements yourself or use a service. If self-tracking, you must maintain proof of all CE activities for at least five years for potential ARRT audits.
Many technologists use a record keeper like the ASRT. As a member, ASRT tracks your Category A/A+ credits and can automatically transfer them to the ARRT and other agencies. For this to work, your first name, last name, date of birth, and ARRT ID must match exactly between the ASRT and ARRT systems.
ASRT also facilitates automatic credit transfers for its members to other bodies, provided your profile is updated:
- ARDMS: Credits are transferred daily if your ARDMS number is in your ASRT profile.
- NMTCB: Credits transfer after your biennium ends if your certification number and dates are in your profile.
- Florida DOH: Credits transfer monthly for members with a Florida license or address. Note: 0.25 and 0.75 credit activities are not accepted.
- MDCB: Credits transfer automatically if you’ve provided MDCB with a valid ASRT ID number.
Regularly View your current CE record online via the ASRT website, especially two months before your biennium ends, to ensure accuracy.
What to Do if Your ARRT Registration Lapses
If you fail to complete your annual renewal by the last day of your birth month, your ARRT registration is considered lapsed. If it has lapsed for more than three months, automatic credit transfers from ASRT will not have occurred, and you’ll need to report CE manually upon reinstatement.
If you were non-compliant with CE, you’d likely be placed on CE probation, giving you six months to complete missing credits and pay a $50 fee. Failure to meet probation requirements results in the discontinuation of your certification. It’s always best to contact the ARRT and ASRT early if you’re facing difficulties.
Anatomy of a Valid CE Certificate
Your CE certificate is your proof of completion. To be valid for an ARRT audit, it must include all of the following preprinted information from the sponsor:
- Sponsor’s name
- Your full name (as it appears on ARRT records)
- Your ASRT or ARRT ID number
- Title for each activity
- Credit amount for each activity
- A unique reference number for each activity
- Date the activity was completed
- Signature of an authorized representative of the sponsor
- Name of the approving organization (e.g., ASRT)
- Credit category (A or A+)
- Course expiration date
Altered certificates are never acceptable. If your certificate is missing information, contact the sponsor for a corrected version.
Frequently Asked Questions about ASRT CE Requirements
Here are straight answers to some of the most common questions about ASRT CE requirements.
What are the primary ASRT CE requirements for R.T.s?
Registered Technologists (R.T.s) must earn 24 approved Category A or A+ CE credits during their two-year biennium. Your biennium is a personal CE cycle tied to your birth month and initial certification year. You report these credits every other year during your annual renewal.
How many CE credits can I earn from a college course?
Academic courses at an accredited school count if the content is relevant to radiologic sciences (e.g., biology, math, health sciences) and you earn a grade of ‘C’ or better. One semester credit hour equals 16 Category A CE credits, and one quarter credit hour equals 12 Category A CE credits. This can be an efficient way to meet your requirements while pursuing a degree.
What happens if I am audited by the ARRT?
Don’t panic. The ARRT randomly selects technologists for CE audits as a quality assurance measure. If selected, you’ll receive a letter requesting documentation for the CE credits you reported. This is why keeping accurate records for at least five years is critical. If you use ASRT’s record-keeping service, you can submit your ASRT CE credit report. Otherwise, you’ll need to provide your individual certificates. An audit is simply a verification process; being organized makes it stress-free.
Conclusion: Simplify Your CE and Stay Compliant
Staying certified is a commitment to professional growth and patient care. While ASRT CE requirements can seem complex, they are manageable once broken down. Your CE journey is a continuous cycle of learning that keeps you sharp and ready for any challenge.
Here are the key takeaways:
- Know your biennium: Understand your personal two-year timeline, which is tied to your birth month, and plan ahead.
- Earn approved credits: For most R.T.s, this means 24 Category A or A+ credits. Verify the requirements for your specific credentials.
- Track carefully: Keep meticulous records of all CE certificates for at least five years, or use a service like ASRT’s to track and transfer them for you.
- Report on time: Submit your CE compliance by the last day of your birth month during your renewal year. Double-check everything before submitting.
If you’re subject to the Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR), use ASRT’s resources to prepare for the Structured Self-Assessment. It’s a tool to help you, and any prescribed CE counts toward your biennial requirement.
Professional growth doesn’t have to be complicated. At Scrubs CE, we make continuing education accessible, affordable, and convenient. Our ARRT-approved online courses are self-paced, allowing you to learn on your schedule. You get instant certificates upon completion, so there’s no waiting for documentation.
We designed our courses to fit into your busy life, so you can earn credits at your own pace, whenever it works for you. Take control of your CE journey and stay organized, informed, and committed to excellence in patient care.
Explore our Radiology CE courses and find the perfect courses to fulfill your ASRT CE requirements. Let’s make this biennium your easiest one yet.
DRSEM Demystified: Your Handbook to California Radiation Safety
Why California Radiation Safety Matters for Healthcare Professionals
California radiation safety is governed by a unique and stringent regulatory framework. The Division of Radiation Safety and Environmental Management (DRSEM) oversees all radiation sources through its two main branches: the Radiologic Health Branch (RHB) and the Environmental Management Branch (EMB). For any healthcare professional working with radiation in California, understanding these state-specific requirements is essential for compliance and safety.
California’s rules, found in Title 17 of the California Code of Regulations (CCR), often go beyond federal standards. Key aspects include:
- Dual Regulation: The state licenses radioactive materials as an NRC “Agreement State” and also imposes its own strict rules for all X-ray machines.
- Specific CE: Fluoroscopy users must complete 4 hours of radiation safety CE and 4 hours of digital fluoroscopy CE for permit renewal.
- Strict Dose Limits: The state enforces occupational dose limits, including lower limits for minors and declared pregnant workers, all under the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle.
This guide provides a clear path through the California radiation safety landscape. We’ll cover the regulators, the rules, program requirements, and training mandates, so you can confidently meet state expectations.
Who Regulates Radiation in California: DRSEM, RHB, and EMB
In California, radiation safety is primarily managed by the Division of Radiation Safety and Environmental Management (DRSEM), a part of the California Department of Public Health (CDPH). DRSEM’s mission is to protect Californians from radiation and environmental hazards through regulation, monitoring, and emergency response. Understanding its structure is key to navigating California radiation safety.
DRSEM operates through two main branches:
Radiologic Health Branch (RHB) responsibilities
The Radiologic Health Branch is the primary point of contact for most healthcare and industrial radiation users. RHB’s responsibilities are focused on ionizing radiation and include:
- Licensing and Registration: Issuing licenses for radioactive materials and registering all X-ray machines in the state.
- Certification and Inspection: Certifying equipment operators and conducting facility inspections to ensure compliance.
- Incident Response: Investigating radiation-related incidents and monitoring for environmental contamination.
Environmental Management Branch (EMB) responsibilities
The Environmental Management Branch handles a broader scope of environmental health issues that support the state’s safety infrastructure. Its duties include:
- Waste and Hazard Management: Regulating medical waste, managing the state’s indoor radon program, and overseeing radiological cleanup at sites like former military bases.
- Emergency Preparedness: Coordinating the state’s response plans for nuclear emergencies.
Together, RHB and EMB provide comprehensive oversight, ensuring that California radiation safety standards are met across all sectors, from medical facilities to industrial sites.
California Radiation Safety Regulations, Duties, and State–Federal Differences
Navigating California radiation safety means understanding a layered system of state and federal rules. The specifics are detailed in Title 17, Division 1, Chapter 5, Subchapters 4 and 4.5 of the California Code of Regulations (CCR), which builds upon federal standards like 10 CFR Part 20.
As an “Agreement State” with the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), California has the authority to regulate most radioactive materials. The state’s regulations must be at least as strict as the NRC’s. California incorporates federal standards like 10 CFR Part 20 (“Standards for Protection Against Radiation”) directly into its own code, creating a consistent safety baseline.
You can explore the full text of these regulations here: Browse Title 17 – California Code of Regulations
Employer and employee responsibilities under California law
Both employers and employees have clear responsibilities defined in regulations and official notices like CDPH Form RH-2364 (“Notice to Employees”).
Employer responsibilities include:
- Ensuring full compliance with all state regulations and license conditions.
- Providing access to regulations, licenses, and operating procedures.
- Posting any notices of violation and providing employees with their radiation exposure data, including annual reports upon request or if a dose exceeds 100 mrem.
- Delivering comprehensive initial and refresher radiation safety training.
Employee responsibilities include:
- Understanding and following all applicable radiation protection standards and procedures.
- Promptly reporting any unsafe conditions or potential violations.
- The right to request inspections from the CDPH without fear of retaliation.
- The right to access personal exposure records and speak privately with inspectors.
To ensure transparency, facilities must post current copies of 17 CCR, 10 CFR 20, operating procedures, Form RH-2364, and any violation notices.
California vs NRC: what agreement-state status means
While California’s rules for radioactive materials are comparable to the NRC’s, the state sets itself apart with its regulation of all X-ray producing machines. The NRC has very limited jurisdiction over X-ray equipment, but California’s CDPH-RHB enforces extensive, state-specific requirements.
These additional rules for X-ray facilities often involve detailed engineering, shielding design, safety interlocks, and facility survey mandates that go beyond federal guidelines. Incident reporting protocols are also state-specific, with reports going directly to the CDPH-RHB.
The table below highlights key differences:
| Feature | Federal Regulations (NRC) | California Regulations (CDPH-RHB) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Authority | Byproduct, source, and special nuclear materials (non-Agreement States) | Byproduct, source, and special nuclear materials (Agreement State authority), ALL X-ray machines |
| X-ray Jurisdiction | Limited to certain federal facilities (e.g., VA hospitals) | Full jurisdiction over all medical, dental, industrial, and academic X-ray installations |
| X-ray Requirements | General safety standards (e.g., 21 CFR) | Additional, state-specific engineering, design, shielding, and survey requirements (Title 17) |
| Radioactive Materials | Licensing and enforcement for materials under NRC purview | Licensing and enforcement for materials under Agreement State purview (comparable to NRC rules) |
| Posting Rules | General requirements for notices, licenses, procedures | Specific list of documents to be posted, including CDPH Form RH-2364 |
| CE Expectations | Varies by profession, generally not direct NRC mandate | Specific mandates for certain users (e.g., 4-hour fluoroscopy safety, 4-hour digital) |
| Regulatory Document | 10 CFR Parts 19, 20, 30, 35, etc. | 17 CCR Div 1, Ch 5, Subch 4 & 4.5, incorporates 10 CFR 20 by reference, Health & Safety Code |
The takeaway is clear: operating in California requires adherence to both the federal baseline and the state’s additional, often more stringent, requirements, especially for X-ray equipment.
Building a Compliant Program: ALARA, Monitoring, Records, and Emergencies
A compliant California radiation safety program is built on a culture of safety, centered on the ALARA principle: keeping radiation exposure As Low As Reasonably Achievable. This goes beyond simply staying below legal dose limits; it involves actively minimizing exposure through engineering controls, clear procedures, and diligent oversight. The CDPH provides detailed guidance for building your program.
For the full picture, take a look at the official guidance:
Radiation Safety and Protection Program Requirement Guidance (CDPH)
Key Program Components
1. ALARA Program and Governance:
Your program must have a formal ALARA policy and conduct an annual program audit to ensure its effectiveness. The Radiation Safety Officer (RSO) is central to this, holding the authority to stop unsafe work and ensure all program elements are implemented and reviewed.
2. Personnel Monitoring and Dose Limits:
Protecting people is paramount. Key dose limits are:
- Adult workers: 5 rem per year (TEDE).
- Minors (under 18): 500 millirem per year.
- Embryo/fetus of a declared pregnant worker: 0.5 rem over the entire pregnancy.
Personnel dosimeters are required for anyone likely to receive over 10% of the annual limit and must be worn correctly (e.g., at the collar, outside lead aprons).
3. Area Controls and Surveys:
Areas with radioactive materials or radiation-producing machines must be designated as controlled areas with restricted access and proper signage (“CAUTION RADIATION AREA”). Regular surveys are required to check for contamination and measure exposure rates. All survey meters must be calibrated regularly, and sealed sources must undergo periodic leak testing.
4. Records and Reporting:
Meticulous record-keeping is non-negotiable. You must maintain logs for:
- Training: Who was trained, when, and on what topics.
- Exposure: Individual dose records for all monitored personnel.
- Instrument Calibration: Proof that your safety equipment is accurate.
- Incidents: Any overexposure, spill, or loss of material must be reported immediately to the CDPH-RHB, followed by a written report. Transfers and disposals of sources must also be documented.
5. Emergency Response:
Your facility needs a clear plan for emergencies. For spills, the protocol is to vacate, contain, and notify the RSO. For injuries involving radioactive material, medical care is the priority, but the RSO must be notified immediately to manage contamination.
California-Specific Requirements
X-ray Installations:
California’s Title 17 imposes strict rules for X-ray facilities beyond federal standards. This includes mandatory specifications for shielding design, safety interlocks on doors that terminate exposure, and required facility surveys to verify safety. Bypassing these safety features is a serious violation.
TITLE 17—additional X‑ray installation requirements (Stanford EH&S)
Radioactive Waste Disposal:
Waste must be carefully segregated by radionuclide, half-life, and form. Decay-in-storage is used for short-lived isotopes, while long-lived waste requires licensed waste brokers for disposal, following all Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations.
Industrial Radiography:
This high-risk field has stringent RSO duties, including the explicit authority to stop unsafe work. Key requirements include annual refresher training, semi-annual performance observations of radiographers, and quarterly physical inventories of all sealed sources.
Training, Fluoroscopy Requirements, and Practical Resources
Effective training is the cornerstone of California radiation safety. It empowers you and your team to understand and mitigate the risks of radiation exposure, protecting yourselves and your patients.
Fluoroscopy-specific education and permits
For professionals performing fluoroscopy, California has very specific continuing education (CE) mandates. These are critical for maintaining your fluoroscopy permit.
- 4 hours of CE on fluoroscopy radiation safety: This covers radiation physics, biological effects, and dose reduction techniques like collimation and pulsed fluoroscopy.
- An additional 4 hours of CE on digital fluoroscopy: This training focuses on the unique dose management considerations of digital systems, including automatic exposure control and PACS integration.
Meeting these requirements can be challenging with a busy schedule. At ScrubsCE.com, our courses are self-paced, accessible online 24/7, and provide instant certificates. We make it easy and affordable to stay compliant.
- Learn more: Why You Should Take Your Fluoroscopy Radiation Safety CEs for California
- Save money: Satisfy California Fluoroscopy CME Requirements on a Budget
- Renew with ease: California Fluoroscopy License Renewal: How to Maintain Your Fluoroscopy Permit in the State of California
- Get started now: Fluoroscopy CE Courses
Beyond fluoroscopy, all personnel working with radiation need initial and periodic refresher training covering health risks, safety procedures, and emergency response.
Equipment, shielding, and vendor essentials
Proper training must be paired with the right equipment and facility design.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Lead aprons, thyroid shields, and leaded glasses are your first line of defense against scatter radiation.
- Survey Meters and Dosimetry: Calibrated survey meters are essential for real-time area monitoring, while dosimetry services provide badges to track personal cumulative exposure.
- Facility Shielding: Structural barriers like lead-lined walls and doors are engineered to meet California’s strict Title 17 requirements, protecting staff and the public.
- Maintenance: All radiation-producing equipment requires regular maintenance and quality assurance checks to ensure safe and accurate operation.
Frequently Asked Questions about California radiation safety
What is the scope of Title 17 for X-ray vs radioactive materials?
Title 17 incorporates federal standards (10 CFR Part 20) for radioactive materials but imposes additional, state-specific requirements for all X-ray machines. These state rules cover shielding design, safety interlocks, and facility surveys.
What are the key differences from NRC regulations?
The biggest difference is jurisdiction over X-ray machines. The NRC has very limited authority, while California regulates all X-ray installations in the state. This means compliance for X-ray use is primarily a matter of state, not federal, law.
What are the basics for reporting and posting?
Employers must post the “Notice to Employees” (CDPH Form RH-2364), relevant regulations, and operating procedures. Employees have a right to their dose reports. Incidents like overexposures or lost sources must be reported to the CDPH-RHB immediately, followed by a written report.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Navigating California radiation safety is a critical responsibility. By understanding the roles of DRSEM and its branches, adhering to Title 17, and implementing a robust ALARA-based program, you can ensure a safe and compliant environment for both staff and patients.
The compliance roadmap involves knowing the regulators, following the rules, maintaining a strong program, and ensuring comprehensive training. This framework is essential for every radiologic technologist, fluoroscopy operator, RSO, and physician in the state.
We know meeting California’s specific fluoroscopy CE requirements—the 4 hours of radiation safety plus 4 hours of digital fluoroscopy training—can be a challenge. ScrubsCE.com was created to solve this problem. Our online, self-paced courses are designed for busy professionals, offering instant certificates upon completion so you can meet your licensure requirements without stress.
Ready to complete your California radiation safety CE? Our California Combos bundle the exact courses you need at a budget-friendly price.
Radiation safety is about creating a culture of protection. With the right knowledge and training, you can confidently exceed California’s standards and contribute to a safer healthcare environment.
Your Fast Track to CT CE Credits and Career Advancement
Why Computed Tomography CE Matters for Your Career
Computed tomography ce is essential for radiologic technologists to maintain credentials, stay current with technology, and advance their careers. Whether renewing your ARRT® registration or pursuing post-primary certification, understanding your CE options can save time and money.
Quick Answer: What You Need to Know About CT CE Credits
- ARRT® requires 24 Category A or A+ CE credits every two years for CT technologists
- Structured Education credits (typically 16 credits) are needed for initial CT certification
- Courses cover CT principles, safety, image formation, specific procedures, and anatomy
- Cost ranges from $10-$150 per course, with all-access passes offering unlimited credits
- Accredited providers like ASRT-approved courses ensure ARRT® and most state acceptance
- Online courses offer instant certification and self-paced learning
Computed tomography uses a series of x-ray images to create detailed cross-sectional “slices” of the body, which can be digitally stacked into 3D views. As CT technology evolves with innovations like dual-energy scanning and AI, continuing education is vital for delivering better patient care and maximizing career potential—not just for checking licensure boxes.
For busy healthcare professionals, finding time for quality education is a challenge. Fortunately, online CE courses make it easy to earn required credits on your own schedule, with immediate certification upon completion.
Navigating ARRT® Requirements for Computed Tomography CE
If you’re working in CT, you know the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT®) sets the standards for professional credentials. They ensure that technologists maintain the knowledge and skills needed for patient safety and quality imaging.
The baseline requirement is 24 Category A or A+ continuing education credits every two years to keep your ARRT® certification current. These credits must come from ARRT®-approved providers. Courses from accredited providers like ScrubsCE automatically meet these requirements, letting you focus on learning.
If you’re pursuing initial CT certification through the post-primary pathway, you’ll need to complete 16 Structured Education credits to build your CT knowledge base. This pathway is for technologists who already hold an ARRT® credential and want to add CT to their skill set. You’ll also need to document clinical experience and pass an exam.
Be aware that state licensing agencies often have their own requirements on top of ARRT® mandates. Most states accept ARRT®-approved courses, but some, like California and Florida, have specific rules. Always check with your state board to cover all your bases. For more details, check out What You Need to Know About ARRT’s Structured Education Solutions and Requirements and How Many X-Ray CE Credits Do I Need for Radiography?.
Understanding CE Credits vs. Structured Education
It’s important to understand the difference: CE credits and Structured Education aren’t the same thing.
Your biennial CE credits (24 credits every two years) keep your existing certification active by ensuring you stay current with technology, safety protocols, and best practices.
Structured Education credits are for earning a new post-primary certification. These 16 credits are more focused, giving you foundational knowledge in a specific modality like CT. They follow a defined curriculum covering everything from basic principles to advanced procedures.
The good news is that many courses can count toward both requirements. If you’re taking courses for Structured Education, those same credits often satisfy your biennial renewal needs. This overlap means you’re not duplicating effort. You can explore courses that meet both needs on our Computed Tomography Certification page.
Don’t forget the clinical experience component. ARRT® requires documented hands-on experience with CT procedures to prove you can apply what you’ve learned.
Meeting Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR)
Once certified for a while, you’ll encounter CQR, or Continuing Qualifications Requirements. This is ARRT’s way of ensuring you keep your knowledge sharp.
The CQR process involves a professional profile, a self-assessment to find knowledge gaps, and prescribed CE to target those areas. This smart approach focuses your learning where it’s needed most.
When choosing computed tomography ce courses, look for ones with CQR distribution tables. These charts show which CQR categories each course covers, making it easy to fill your gaps efficiently. Many of our courses, like our CT/MRI CE offerings, include these tables.
Your CQR activities count toward your 24 biennial credits, so you’re not adding extra work. It’s an integrated system for focused learning.
What to Expect from CT Continuing Education Courses
Computed tomography ce courses are more than a licensure requirement; they are a comprehensive journey designed to expand your knowledge, sharpen your technical skills, and keep you current with rapid advances in CT imaging.
The curriculum spans from fundamental concepts to advanced applications, starting with core principles like physics and image formation and building toward specialized topics. Quality CT CE has a practical focus, teaching you skills you can immediately apply, from new dose reduction techniques to contrast protocols. Throughout every course, patient safety remains front and center.
As we explore in 7 Ways Radiology CE Can Benefit You as a Radiologic Technologist, continuing education can open doors to new opportunities and position you for career advancement.
What Types of Computed Tomography CE Courses Are Available?
The range of computed tomography ce courses reflects the versatility of this imaging modality.
CT Principles & Instrumentation courses cover the mechanics and physics of CT, including X-ray generation, scanner components (gantry, tube, detectors), and reconstruction techniques.
Patient Care & Safety courses address communication, positioning, and contrast media administration, including how to handle adverse reactions.
Image Formation & Evaluation courses teach you to optimize image quality by working with Hounsfield Units, windowing, resolution, and artifact identification. Understanding your PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) is also covered.
Sectional Anatomy courses are essential for accurate patient positioning and recognizing anatomical variations.
When it comes to specific procedures, the options get really interesting. Cardiac CT courses focus on imaging the heart, as detailed in our Cardiac and Vascular Computed Tomography course. CT Angiography courses explore imaging blood vessels. You’ll also find specialized courses for abdomen & pelvis, head and spine imaging, musculoskeletal applications, and chest procedures.
For a comprehensive foundation, Computed Tomography for Technologists offers an excellent overview.
Key Topics Covered: Safety and Technology
Two themes run through every quality CT CE course: safety and technology.
Radiation safety is a fundamental responsibility. The cornerstone principle is ALARA, which stands for “As Low As Reasonably Achievable.” This means minimizing radiation dose while maintaining diagnostic image quality.
You’ll learn specific dose reduction techniques like adjusting scan parameters for patient size and using iterative reconstruction algorithms. For perspective, an abdominal CT can deliver radiation equivalent to about 400 chest X-rays, highlighting the importance of dose management. Children and pregnant patients require special consideration, as noted by the FDA’s Radiation Risks from CT Scans.
Contrast media safety is another critical area. Courses teach proper administration, patient screening for contraindications (like kidney problems), and how to manage allergic reactions.
On the technology side, you’ll deepen your understanding of CT scanner components and innovations. You’ll learn about the X-ray tube, detectors, and powerful computers that reconstruct images. You’ll also explore emerging innovations like Photon-Counting Detector (PCD)-CT systems and AI applications.
Our Computed Tomography course provides a thorough exploration of these safety and technology topics.
Finding and Selecting the Right CT Courses
Finding the right computed tomography ce courses is easier than you might think, thanks to the accessibility of online learning.
The most important factor is proper accreditation. When a course is approved by an ARRT®-recognized mechanism like the ASRT (American Society of Radiologic Technologists), you can trust your credits will be accepted for certification renewal.
Online, self-paced learning fits a busy healthcare professional’s schedule. You can study whenever it’s convenient, with many courses offering instant grading and certificate downloads. This allows you to complete your requirements efficiently.
How to Choose the Right Computed Tomography CE Courses for You
Selecting the right computed tomography ce courses depends on your career goals. Here’s how to make smart choices.
Start by clarifying your needs: are you renewing your ARRT® certification, addressing CQR gaps, or working toward initial post-primary certification? Your answer determines the type and quantity of credits you need.
Next, consider relevance. If you primarily scan cardiac patients, a specialized cardiac CT course offers more value than a general overview. If you’re looking to expand into new areas, broader courses can open doors.
Cost is also a factor. Individual CT CE courses typically range from $10 to $150+. Before buying courses one-by-one, consider if a course bundle or an all-access pass offers better value, especially if you need many credits. Our Radiology CE Course Combos show bundled options that deliver better value.
Also consider the format. Some technologists prefer a comprehensive e-book, while others want a test-only option if they’re already confident in the material.
State-Specific CE Considerations
While ARRT® approval is a solid foundation, your state licensing board might have its own rules.
Most states accept ARRT®-approved courses, but some have additional requirements. California, for instance, may require specific credit types like digital radiography. Florida operates its own reporting system, where approved providers like us submit your credits directly. Texas classifies credits as “Directly Related” or “Technical.”
Always verify with your specific state licensing board to ensure a course will satisfy your state requirements. A few minutes of checking can prevent the frustration of earning credits that don’t count where you practice.
We’ve compiled state-specific guidance to help. Check out resources like How to Maintain Your X-Ray License in California or our Florida Continuing Education Survey for detailed information.
The Benefits of Advanced CT Training
Pursuing advanced computed tomography ce is an investment in yourself and your patients, adding new tools to your professional toolkit. As GE Healthcare Institute notes, an advanced CT scanner is only as good as its operator. The utility of cutting-edge technology depends on the professional’s skill. Advanced training provides this expertise, creating long-term value for you and your healthcare institution.
Technologists with specialized knowledge in areas like cardiac CT or interventional procedures stand out to employers. This expertise often leads to leadership roles, specialized units, and positions with greater responsibility and better compensation.
Beyond career and financial benefits, sharpening your skills through advanced computed tomography ce directly improves patient outcomes. A technologist who understands complex pathologies and can optimize image quality while minimizing radiation makes a tangible difference in patient care. Every scan you perform with expertise contributes to more accurate diagnoses and safer experiences.
The field of CT is diverse, and advanced training lets you specialize in areas that interest you, from cardiovascular imaging to neuroimaging. Some technologists use advanced training as a springboard to other modalities. If that sounds appealing, check out How to Use Continuing Education to Advance to a Different Modality Within Radiology for guidance.
Advanced CT training helps you become the kind of technologist who gets tapped for interesting cases and helps raise the standard of care. That’s a powerful return on investment.
Frequently Asked Questions about CT CE
Here are answers to common questions about computed tomography ce.
How quickly can I get my CT CE certificate?
With our online computed tomography ce courses, you control the timeline. After passing the open-book test, you get instant grading and your certificate is available for download immediately. This is especially helpful for tight renewal deadlines.
You then submit your certificate to the ARRT® and your state board yourself. The exception is Florida, where as an approved provider, we report your credits directly to the Florida Department of Health each month. You can explore our streamlined process at our Online Testing Center.
Are online CT CE courses accepted by the ARRT®?
Yes, as long as you choose courses from reputable, accredited providers. All of our computed tomography ce courses are approved as Category A or A+ credits by ARRT®-recognized mechanisms, such as the ASRT (American Society of Radiologic Technologists), the gold standard in our field.
We make this accreditation information clear on every course page so you can feel confident that your credits will count toward your certification renewal.
Online courses offer the same quality education as in-person seminars with far more flexibility and convenience. For more details, take a look at our comprehensive guide: Most Frequently Asked Questions About CE Credits for Radiologic Technologists.
Can I use the same credits for my ARRT® and state license renewal?
In most cases, yes. You can typically use the same computed tomography ce credits for both ARRT® certification and state license renewal. This is known as credit reciprocity.
Since most state licensing agencies accept ARRT®-approved courses, the credits you earn with us usually satisfy both requirements.
However, we always encourage you to do a quick check with your specific state licensing board. Some states have unique quirks, like requiring credits in a specific topic or having particular reporting procedures. A quick visit to your state board’s website can confirm you’re covering all your bases.
Our FAQ page is packed with helpful information that can point you in the right direction.
Conclusion
Earning your computed tomography ce certificate isn’t the end—it’s the beginning of a commitment to lifelong learning. In a field with rapid technological evolution, staying current makes you a better technologist and directly impacts patient care quality. The technologists who thrive are those who accept change and see each CE course as an opportunity to grow.
ScrubsCE.com was built for your reality. We know you’re juggling a busy life, which is why our self-paced, ARRT®-approved courses are designed to fit your schedule. You can study whenever it works for you.
We also believe in affordability. Advancing your career shouldn’t break the bank, which is why we offer real value through individual courses and our all-access pass for unlimited credits.
Your credentials and skills are too valuable to let stagnate. The best time to invest in your professional development is now. Browse our comprehensive selection of CT courses and find the ones that match your career goals. Your future self—and your patients—will thank you.
Explore Our Full Range of Computed Tomography Certification Courses
Your Guide to Becoming a Limited X-Ray Tech
What is a Limited License Radiologic Tech?
A limited license radiologic tech is a healthcare professional who operates X-ray equipment to capture diagnostic images of specific body parts under the supervision of a licensed physician or radiologic technologist. These entry-level technologists perform a focused scope of radiographic procedures, typically on extremities, the chest, spine, and skull, helping physicians diagnose injuries and medical conditions.
Quick Overview: Limited License Radiologic Technologist
- Role: Perform X-rays on specific body parts (chest, extremities, spine, skull)
- Work Settings: Urgent care centers, physician offices, orthopedic clinics, chiropractic offices
- Training Time: 6-9 weeks to 58 weeks, depending on program
- Certification: ARRT Limited Scope of Practice in Radiography Exam (required in most states)
- Supervision: Work under a licensed physician or full radiologic technologist
- Career Entry: Faster path into healthcare than full RT certification
If you’re considering a career in medical imaging but want a quicker entry point than becoming a full radiologic technologist, becoming a limited license radiologic tech might be your ideal path. This role offers a way to start working in healthcare sooner while still playing a crucial part in patient diagnosis and care.
The demand for diagnostic imaging continues to grow as the population ages and healthcare facilities expand. Limited license radiologic techs fill an important gap, especially in outpatient settings, urgent care facilities, and specialty clinics where their focused expertise is exactly what’s needed.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know about becoming a limited license radiologic tech, from understanding the role and educational requirements to certification, state licensing, and career advancement opportunities. Whether you’re just starting your healthcare journey or looking to add a credential to your existing skills, this roadmap will help you steer the process.
Understanding the Role of a Limited License Radiologic Tech
If you’re curious about what a limited license radiologic tech actually does day-to-day, you’re in the right place. This role is much more than operating an X-ray machine—it’s a blend of technical expertise, compassionate patient care, and meticulous attention to detail that helps physicians diagnose everything from broken bones to chest infections.
Think of an LLRT as a focused specialist in medical imaging. While the job is considered entry-level, it’s perfect for people who want to make a real difference in healthcare without spending years in school. Many people who become LLRTs already work in healthcare as certified clinical medical assistants or certified nursing assistants, and they’re looking to expand their skills and career options.
What is a Limited License Radiologic Technologist (LLRT)?
A limited license radiologic tech, sometimes called an X-ray technician or Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist (LMRT), is trained to perform specific diagnostic X-ray procedures on certain parts of the body. The key word here is “limited”—unlike full radiologic technologists who can operate advanced imaging equipment like CT scanners and MRI machines, LLRTs focus on a narrower scope of practice.
This focused approach is actually a benefit. It means you can complete your training much faster and start working in healthcare sooner. Your training zeroes in on the essential skills you need: positioning patients correctly, operating X-ray equipment safely, understanding radiation safety protocols, and ensuring image quality for accurate diagnosis.
As an LLRT, you work under the supervision of a licensed physician or a full radiologic technologist. This doesn’t mean someone is looking over your shoulder every second—it means you’re part of a healthcare team with proper oversight to ensure patient safety and proper imaging protocols. You’re a key player in settings where broad imaging expertise isn’t needed but quality X-rays absolutely are, like urgent care centers, orthopedic clinics, and physician offices.
Your mission is straightforward but vital: capture clear, accurate images that help physicians diagnose medical conditions quickly. Whether it’s a child’s fractured arm, a worker’s injured back, or a patient’s chest X-ray to rule out pneumonia, the images you produce directly impact treatment decisions and patient outcomes.
Primary Duties and Work Environments
The daily work of a limited license radiologic tech is hands-on and patient-centered. You spend your day interacting with people who are often anxious or in pain, which means your communication skills matter just as much as your technical abilities.
Patient positioning is one of your core responsibilities. Getting the angle just right makes the difference between a clear diagnostic image and one that needs to be retaken. This requires solid knowledge of anatomy and radiographic positioning techniques. You’ll adjust both the patient and the equipment until everything aligns perfectly for the image the physician needs.
Operating radiographic equipment safely is at the heart of what you do. You’ll set the correct exposure factors, ensure proper shielding to minimize radiation exposure, and capture images using the lowest radiation dose possible. Modern X-ray machines are sophisticated, and you’ll become expert at using them efficiently while following strict safety protocols.
Once you capture an image, processing and preparing it for physician review is your next step. In most settings today, this means working with digital imaging systems—labeling images correctly, checking quality, and making sure everything is uploaded to the patient’s medical record properly.
Patient safety and communication run through everything you do. You’ll explain procedures in simple terms to ease anxiety, answer questions, position lead shields to protect sensitive areas from radiation, and make sure patients feel cared for during what can be an uncomfortable experience. Your calm, professional demeanor helps patients trust the process.
You’ll also handle basic equipment maintenance—checking that machines are functioning correctly, reporting any issues, and ensuring your workspace meets safety standards.
Where do LLRTs work? Your focused skill set makes you valuable in outpatient and specialized settings. Urgent care centers rely on LLRTs to quickly image common injuries like sprains, fractures, and suspected broken bones. Physician’s offices, particularly in primary care and family medicine, need someone who can take basic X-rays right there in the office. Orthopedic clinics are a natural fit since you’re imaging bones and joints—exactly what an LLRT is trained to do.
Chiropractic offices use LLRTs to assess spinal alignment and skeletal issues. Ambulatory care centers and occupational medicine clinics also employ LLRTs for convenient outpatient imaging without sending patients to larger hospitals. In all these environments, you’re the person who makes diagnostic imaging accessible, efficient, and patient-friendly.
LLRT vs. Full Radiologic Technologist (RT): Key Differences
When you’re considering a career in radiologic technology, one of the first questions that usually comes up is, “Should I become a limited license radiologic tech (LLRT) or go for the full Radiologic Technologist (RT) certification?” It’s an important choice, and understanding the key differences between these two paths will help you make a decision that truly fits your career goals, timeline, and lifestyle.
Both roles are essential to diagnostic imaging, and both involve working directly with patients and X-ray equipment. However, they differ significantly in their scope of practice, the education required, where you’ll typically work, and what you can expect to earn. Let’s break down these differences so you can see which path might be the right fit for you.
Here’s a quick side-by-side comparison to give you the big picture:
| Feature | Limited License Radiologic Technologist (LLRT) | Full Radiologic Technologist (RT) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Practice | Limited to specific body parts (chest, extremities, spine, skull); basic X-ray procedures only | Broad scope including all X-ray procedures, plus advanced modalities like CT, MRI, fluoroscopy, and mammography |
| Education | Certificate programs ranging from 6-9 weeks to 58 weeks | Associate’s degree (2 years) or Bachelor’s degree (4 years) |
| Typical Workplaces | Urgent care centers, physician offices, orthopedic clinics, chiropractic offices, small outpatient facilities | Hospitals, large medical centers, specialized imaging centers, plus all LLRT settings |
| Salary Potential | Generally lower, entry-level wages | Higher earning potential with more opportunities for advancement and specialization |
Scope of Practice and Procedures
The most fundamental difference between an LLRT and a full RT is what you’re authorized to do. As a limited license radiologic tech, your scope of practice is, as the name suggests, limited. You’re trained and certified to perform X-rays on specific anatomical areas—typically bony anatomy such as extremities (arms, legs, hands, feet), the chest, spine, and skull. This focused scope is perfect for settings where these specific types of imaging are most common.
However, there are procedures you cannot perform as an LLRT. You won’t be authorized to conduct fluoroscopy (real-time moving X-ray images) or contrast studies (imaging that uses contrast dyes to visualize organs and blood vessels). These more complex procedures require the broader training of a full RT.
In contrast, a full Radiologic Technologist has a much broader scope of practice. They can perform all the basic X-ray procedures that an LLRT does, plus they’re trained in advanced modalities like CT scans (computed tomography), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), and mammography. This versatility opens doors to more diverse work environments and specialized roles within medical imaging.
Pros and Cons: LLRT vs. RT Certification
So which path should you choose? Like most career decisions, it depends on your personal circumstances, goals, and priorities. Let’s look at the advantages and limitations of each route.
For LLRTs, the biggest advantage is faster training. You can complete your education in as little as 6-9 weeks, though more comprehensive programs may take up to a year. This means you can start working and earning much sooner than if you pursued a full RT degree. Another major plus is the lower education cost—certificate programs are significantly less expensive than associate’s or bachelor’s degree programs. And finally, you get quicker entry to the workforce, which is ideal if you need to start earning income soon or want to test the waters in medical imaging before committing to a longer educational path.
On the flip side, LLRTs face some constraints. Your limited scope means you’ll only be qualified for certain positions, typically in smaller outpatient settings. The lower salary potential reflects both the shorter training period and the more limited responsibilities. And if you want to advance your career, you’ll likely need to pursue additional education to expand your credentials—there are fewer advancement options without going back to school.
For full RTs, the primary advantages include higher earning potential right from the start, more job opportunities across a wider range of healthcare settings, and specialization options that can further boost your career and salary. You’ll have the flexibility to work in hospitals, imaging centers, or specialized fields like pediatric radiology or interventional radiology.
The trade-offs for becoming a full RT are straightforward: longer education (typically two to four years) and higher cost for your degree program. You’ll also need to commit more time before you can start working in the field.
Choosing between becoming a limited license radiologic tech and a full RT comes down to your timeline, budget, and career ambitions. If you want to enter healthcare quickly and are comfortable with a focused role, the LLRT path offers a practical and rewarding entry point. If you’re willing to invest more time and money upfront for broader opportunities and higher earning potential, the full RT certification might be your better choice. And here’s the good news: many LLRTs later decide to pursue their full RT credentials through bridge programs, so your initial choice doesn’t have to be permanent.
Sonographer’s Guide to CME: Requirements, Courses, and More
Why CME Matters for Your Sonography Career
CME for sonographers is a mandatory requirement to maintain your professional credentials and keep your skills current. Here’s what you need to know:
Quick CME Requirements Overview:
- ARDMS credentials (RDMS/RDCS/RVT): 30 ARDMS-accepted CME credits every 3 years
- ARRT Sonography credential: 24 Category A CE credits every 2 years (16 must be sonography-specific)
- Specialty requirements: Additional credits may be needed for MSK (musculoskeletal) or vascular credentials
- Accepted providers: ARDMS-/ARRT-recognized organizations and other approved education providers
Most sonographers hold credentials from either the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) or the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT)—or both. Each has specific CME requirements you must meet to avoid losing your credentials.
The good news? You have many options for earning these credits. From free webinars and journal article tests to comprehensive online courses and live conferences, CME activities come in formats that fit busy schedules and tight budgets.
Your CME credits serve three key purposes: keeping your credentials active, staying current with new ultrasound technologies, and demonstrating your commitment to quality patient care. Whether you’re scanning expectant mothers, diagnosing vascular conditions, or performing musculoskeletal exams, continuing education ensures you’re providing the best possible care.
The main challenge is navigating the maze of providers, understanding which credits count for your specific credentials, and finding affordable options that improve your skills.
Understanding CME Requirements for Sonographers
Continuing Medical Education (CME) isn’t just a hoop to jump through; it’s the lifeblood of our profession. Without the latest knowledge, sonographers risk falling behind on new techniques and technologies, which could compromise patient care. CME ensures we’re constantly honing our skills and maintaining the high professional standards our patients deserve.
Maintaining your credentials, whether from the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) or the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT), is paramount. These certifications signify a commitment to excellence and a baseline of competency. Without current CME, these credentials can lapse, potentially affecting your employment and state licensure. Think of CME as your professional passport—you can’t travel far without it!
CME Requirements for Sonographers
Let’s explore the specifics of what’s typically required.
-
ARDMS Credentials: If you hold an RDMS, RDCS, and/or RVT credential, you’ll need to accumulate 30 ARDMS/APCA-accepted CME credits within a three-year period.
-
ARRT Credentials: For those holding an ARRT Sonography credential, the requirement is 24 approved CE credits every two years (a biennium). Crucially, 16 of these credits must be directly related to the sonography discipline.
It’s not always a one-size-fits-all approach, especially with specialty credentials.
-
Specialty-Specific CMEs: If you have an RMSKS credential (Registered in Musculoskeletal Sonography), you’ll need 10 ARDMS/APCA-accepted CMEs in musculoskeletal ultrasound, plus 20 in any specialty, for a total of 30. If you hold only the RMSK credential, all 30 CMEs must be in musculoskeletal ultrasound. Similarly, for the RPVI (Registered Physician in Vascular Interpretation) credential, 30 ARDMS/APCA-accepted CMEs in vascular ultrasound are required.
-
CME Waivers for New Credentials: Here’s a great perk! If you earn a new credential or pass a new specialty examination, ARDMS will waive 15 CME credits for that three-year CME period. It’s their way of acknowledging the significant learning involved. These waived credits are only valid for the period in which they’re earned.
It’s always a good idea to periodically review your registry’s current requirements, as organizations sometimes announce updates.
Decoding Credit Types: AMA PRA Category 1 vs. Others
Understanding credit types ensures your hard-earned education counts. The gold standard for many medical professionals is the AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™. This credit signifies that an activity has been approved by an organization accredited by the ACCME. Because of this rigorous process, AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™ is broadly accepted by many certification bodies, including ARDMS.
However, other credit types exist. For example, ARRT accepts “Category A or A+ activities,” which are typically approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM).
The key takeaway? Always check with your specific credentialing body (ARDMS or ARRT) to confirm which credit types they accept. ARDMS is explicit about what it doesn’t accept, including:
- Category 2 credits
- Nursing Category A credits (if not relevant to sonography)
- Category B credits
- College credits (some registries accept academic courses under specific rules)
- Basic CPR certification (advanced courses like ALS/ACLS/PALS may be accepted by some registries in limited amounts)
- Contact hours
- Unverified CME listings
While “CE” and “CME” are often used interchangeably, the specific “category” or “type” of credit matters immensely for your renewal. Always look for the stamp of approval from recognized bodies.
Finding Accepted CME for Sonographers
Let’s be honest—finding the right CME for sonographers can feel like wandering through a maze. With so many providers and courses, how do you know which ones your credentialing body will accept? You’re already juggling patient care and other responsibilities; the last thing you need is confusion about your continuing education.
Here’s the good news: plenty of reputable organizations offer CME credits specifically for sonographers, and they’re recognized by major registries. Look for courses from providers that clearly state their approvals (for example, ARDMS-accepted or ARRT Category A/A+ approved) before you invest your time and money. Quality education matters, but so does the peace of mind that your effort will count toward your renewal.
We know how important it is to find courses that are both accepted by your credentialing body and genuinely useful for your practice. That’s why we’ve built a comprehensive library of ultrasound CE courses designed specifically with sonographers in mind. Ultrasound CE Courses from Scrubs CE
Choosing the Right CME Courses for Your Specialty
Here’s where CME for sonographers gets exciting—you’re not just checking boxes, you’re shaping your career. The best continuing education doesn’t just maintain your credentials; it makes you better at what you do every day.
Think about your specialty and where you want to grow. If you’re in OB/GYN ultrasound, courses on fetal anomaly detection or advanced maternal-fetal hemodynamics will directly impact your confidence. For vascular sonographers, staying current with new diagnostic criteria for vascular diseases is crucial. Look for courses covering advanced carotid imaging or peripheral arterial and venous mapping. If you hold the RPVI credential, ARDMS requires all 30 of your CME credits to be in vascular ultrasound.
Musculoskeletal (MSK) ultrasound is one of the fastest-growing areas in our field. If this is your specialty, seek out courses on specific joint imaging, nerve entrapment syndromes, or ultrasound-guided procedures. If you hold the RMSK credential, ARDMS requires between 10 and 30 credits specifically in MSK ultrasound, depending on your other credentials.
Cardiac sonographers can sharpen their skills with education on advanced echocardiographic techniques, valvular heart disease assessment, and congenital heart defect detection. When choosing courses, favor providers that are recognized by your registry.
When choosing courses, ask yourself: Does this apply to my daily work? Does it cover new technologies or techniques? Will it help me reach my career goals? Invest in education that genuinely advances your expertise.
More info about ultrasound continuing education
Cost-Saving Strategies and Free CME Options
Let’s talk money. CME for sonographers doesn’t have to drain your bank account. One of the smartest moves is looking for course bundles or unlimited access plans. Some providers offer models where you pay one flat fee for access to their entire course library for a year. This can save you a significant amount compared to buying courses individually.
Professional organization membership often pays for itself. Many associations offer journal article tests, webinars, or member discounts on courses. Some member portals can even auto-transfer earned credits to registries, saving you time and hassle.
Don’t forget about employer reimbursement. Many hospitals and clinics budget for employee continuing education—you just have to ask your manager or HR department.
And yes, free CME options exist. Reputable professional societies sometimes offer complimentary credits through educational webinars or as a member benefit. Keep an eye out for these opportunities.
We believe high-quality education should be accessible to every sonographer. That’s why we work hard to keep our courses affordable and occasionally offer free options to help you meet your requirements without financial stress. Scrubs CE affordable and free CME options
Navigating CME Activities and Tracking Your Credits
Earning CME credits is only half the battle—knowing how to track and report them accurately is just as crucial. You’ve done the work, so let’s make sure it gets properly recorded!
Types of CME Activities Available
The beauty of modern continuing education is the variety of learning formats. Online courses and self-paced learning are a go-to choice for many busy sonographers. You can learn from your couch, during a lunch break, or while traveling, hitting pause whenever life happens. We’ve built our platform around this flexibility because we know how demanding your work is.
For more interactive experiences, live webinars offer real-time learning with experts. Missed a live session? On-demand webinars and lectures provide the same expert instruction without the scheduling constraints.
For the readers among us, journal article tests are an excellent way to earn credits while staying current with the latest research. You read a peer-reviewed article and complete a test to demonstrate your understanding.
Finally, in-person conferences and workshops, like the SDMS Annual Conference, offer valuable hands-on training and networking, though they require more planning for travel and time away.
No matter your learning style, there’s a CME format that works for you. We’ve focused on making online learning as accessible and effective as possible, so you can meet your requirements without adding stress to your life. Scrubs CE online learning options
How to Track and Report Your CME Credits
Once you’ve earned credits, proper tracking is your priority. Most credentialing organizations provide CME tracking tools to make this easier. The ARDMS CME Bank is your personal credit repository where you can upload certificates. In addition, many professional membership portals offer CME trackers that can automatically transfer earned credits to registries.
Here’s a crucial tip for automatic transfers: your personal information (name and ID number) must match exactly across all your accounts. Even small differences can prevent automatic transfers.
Now let’s talk about CME certificate requirements. Your certificates are official documentation that must meet specific standards. ARDMS requires every certificate to include your full name and ID number (can be handwritten). However, the course dates (MM/DD/YYYY), provider/sponsor names, and course title must be pre-printed. If these elements are handwritten, ARDMS will reject the credit. The number of credit hours can be handwritten.
This might seem nitpicky, but it protects the integrity of the credentialing process. Reputable providers issue certificates that automatically meet these requirements. We’ve designed our certificates to meet all these crucial standards right from the start. When you complete a course with us, you get instant access to a properly formatted certificate that ARDMS and ARRT will accept. Scrubs CE certificate and tracking support
Frequently Asked Questions about Sonographer CME
We know navigating CME for sonographers can raise a lot of questions. Let’s tackle some of the most common concerns.
What happens if I get audited by my credentialing organization?
Getting an audit notification can be stressful, but it’s a routine quality check. Each March, ARDMS randomly selects registrants who’ve completed their three-year CME period. If selected, you’ll have about one month to submit all your required CME documentation. This is why meticulous record-keeping is so important!
The four-year record keeping requirement is crucial. ARDMS requires you to maintain your CME certificates for at least four years, either in your personal files or uploaded to your ARDMS CME Bank. Don’t send documentation unless you’re specifically asked.
Missing an audit deadline is serious. Your credentials will become inactive. While you might be eligible for CME Reinstatement by meeting a later deadline, missing that second chance could lead to permanent revocation. If you get audited, respond promptly!
Can I get CME credits for passing a new specialty exam?
Yes, and it’s a great perk! ARDMS rewards your ambition with a CME waiver of 15 credits when you earn a new credential or pass a new specialty examination under an existing one. For example, if you hold an RDMS in Abdomen and then pass the OB/GYN specialty exam, ARDMS will waive 15 CME credits for that three-year period.
Just remember that these waived credits only count for the current CME period in which you earn them. They don’t roll over, so plan accordingly.
How do I become a CME provider for sonographers?
If you’re passionate about education, becoming a CME provider is a meaningful way to contribute. The process is designed to ensure all educational activities meet high professional standards. Any activity must directly relate to sonographers’ professional responsibilities, clinical practice, or patient care.
The application process involves submitting a detailed plan to an accrediting body. You’ll define the activity type, content, and educational objectives, and pay an application fee. To be widely accepted, providers must meet strict accreditation standards—such as those set by the ACCME for AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™ or by an ARRT-approved RCEEM. It’s detailed work, but it ensures that CME for sonographers maintains its value across the profession.
Conclusion: Investing in Your Sonography Career
Here’s the truth about CME for sonographers: it’s so much more than checking boxes or satisfying requirements. It’s about investing in yourself and the patients who trust you with their care.
Every course you complete, every new technique you master, every advancement you learn about—these all add up to something bigger. They transform you from someone who simply maintains credentials into a professional who actively shapes their career trajectory. And in a field as dynamic as ultrasound, where new technologies and protocols emerge constantly, that ongoing commitment to learning isn’t optional. It’s essential.
Think about how much has changed since you first started scanning. New equipment, updated protocols, emerging specialties—the sonography landscape evolves quickly. CME for sonographers ensures you’re not just keeping up; you’re staying ahead. When you understand the latest research on fetal anomaly detection or master a new vascular imaging technique, you’re not doing it for a certificate. You’re doing it because somewhere, a patient will benefit from your expanded knowledge.
The ripple effects of your continuing education extend beyond your own practice. Better-trained sonographers contribute to earlier diagnoses, more accurate assessments, and improved patient outcomes across the board. That’s something worth investing in.
We understand that balancing CME requirements with demanding work schedules, family commitments, and life itself isn’t easy. That’s exactly why we’ve built our platform around flexibility and accessibility. Our self-paced online courses work around your schedule, not the other way around. You get instant certificates, clear documentation that meets ARDMS and ARRT requirements, and the peace of mind that comes from knowing you’re fulfilling your professional obligations while genuinely improving your skills.
Whether you’re exploring a new specialty, deepening your expertise in your current field, or simply maintaining your credentials, we’re here to support your journey. High-quality education shouldn’t require sacrificing your evenings and weekends or draining your bank account. It should fit seamlessly into your professional life.
Curious about why continuing education matters beyond the requirements? Discover 5 compelling reasons to pursue ultrasound continuing education that go beyond credential maintenance.
Your career deserves attention, nurturing, and intentional growth. Every credit you earn is a step forward—not just in meeting requirements, but in becoming the sonographer you aspire to be. Ready to explore what’s possible? Browse our comprehensive ultrasound continuing education courses and find the learning that speaks to your professional goals.
The Radiographer’s Blueprint: Essential Anatomy and Physics for Sharp Images
Why Anatomical Knowledge is the Foundation of Quality Radiographic Imaging
Anatomy for radiographers is the cornerstone of producing diagnostic-quality images. Without a deep understanding of anatomical structures, their locations, and their appearance across imaging modalities, radiographers cannot consistently position patients correctly, select proper technical factors, or identify the need for repeat images.
Core essentials every radiographer must know:
- Anatomical planes and positioning – Understanding sagittal, coronal, and axial planes is critical for proper patient alignment and interpreting cross-sectional imaging.
- Tissue appearance across modalities – Knowing how bone, soft tissue, air, and fluid appear in X-ray, CT (Hounsfield Units), and MRI (T1w vs. T2w signal intensity) is key to image interpretation.
- Regional anatomy – Mastery of structures in the brain, chest, abdomen, pelvis, spine, and extremities is essential for all examinations.
- Body habitus variations – Recognizing how sthenic, asthenic, hyposthenic, and hypersthenic body types affect organ placement impacts positioning and exposure technique.
- Normal vs. abnormal – A solid grasp of normal anatomy allows you to identify potential pathologies and communicate effectively with radiologists.
Understanding how organ placement varies between body types—especially since over 85% of people are sthenic or hyposthenic—can prevent repeat exposures. As a radiographer, you apply your knowledge of 3D anatomy to create 2D or cross-sectional images that physicians use for diagnosis and treatment planning. You’re not just taking pictures; you’re creating a vital diagnostic tool.
Foundations of Radiological Imaging: Modalities and Principles
Mastering anatomy for radiographers requires understanding how each imaging modality translates the invisible into the visible. Let’s review the core technologies.
X-ray radiography is the workhorse of imaging. X-ray photons are absorbed differently by various tissues. Dense bone appears white (radiopaque), while air is black (radiolucent), and soft tissues are shades of gray. This differential absorption makes X-rays ideal for quickly identifying fractures, lung issues, and foreign bodies.
Computed Tomography (CT) uses a rotating X-ray tube to create detailed cross-sectional slices. CT quantifies tissue density with Hounsfield Units (HU), from -1000 HU (air) to +1000 HU (bone). Structures are described as hyperdense (brighter), hypodense (darker), or isodense. CT is critical for trauma, stroke assessment, cancer staging, and complex fractures.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses magnetic fields and radio waves, not radiation. It interacts with hydrogen atoms in water, providing excellent soft tissue contrast. Key sequences include: T1-weighted images, where fat is bright (hyperintense) and fluid is dark (hypointense), showing great anatomical detail. T2-weighted images, where fat and fluid are bright, are excellent for spotting pathology like inflammation. MRI is the top choice for neurological and musculoskeletal imaging.
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves for real-time imaging. A transducer’s returning echoes create a live image based on echogenicity. Dense tissue is bright (hyperechoic), muscle is darker (hypoechoic), and fluid is black (anechoic). Its real-time, radiation-free nature is perfect for obstetrics, abdominal organs, cardiac imaging, and guiding biopsies.
Nuclear medicine imaging visualizes function, not just structure. Radioactive tracers concentrate in organs based on metabolic activity, and cameras create functional maps. PET scans, for instance, highlight high metabolic activity to detect cancer. This modality is used for cancer staging, heart function assessment, and brain scans.
Here’s how these modalities stack up against each other:
| Modality | Core Principle | Type of Information Provided | Primary Clinical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray | Differential absorption of X-rays by tissues | Structural, bone density, gross pathology | Initial trauma assessment (fractures), chest infections, foreign bodies, skeletal surveys |
| CT | X-ray attenuation in cross-section, quantified by Hounsfield Units (HU) | Detailed cross-sectional anatomy, soft tissue, bone, blood vessels | Trauma, stroke, cancer staging, complex fractures, abdominal pathologies |
| MRI | Magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses interacting with hydrogen protons | Exceptional soft tissue detail, water content, functional changes | Neurological disorders (brain, spine), musculoskeletal injuries (ligaments, tendons), cancer, joint pathology |
| Ultrasound | High-frequency sound waves reflecting off tissues (echogenicity) | Real-time, dynamic imaging of soft tissues, fluid, blood flow | Obstetrics, abdominal organs (gallbladder, liver, kidneys), cardiac assessment, vascular studies, biopsy guidance |
| Nuclear Med. | Detection of radioactive tracers based on physiological function | Metabolic activity, blood flow, organ function | Cancer detection and staging, heart function, brain activity (epilepsy, dementia), bone scans, thyroid disorders |
Understanding these principles is key to producing quality images. Resources like Understanding Anatomy & Physiology 3rd Ed. can help you master how structures appear across modalities. Your job is knowing which window to use and how to interpret what you see.
Navigating the Human Body: Planes, Positions, and Body Habitus
To create a perfect diagnostic image, you must understand the body’s map: anatomical planes, positions, and body habitus. This foundation is essential for anatomy for radiographers.
Starting Point: The Anatomical Position
This is the universal reference point: standing upright, facing forward, arms at sides with palms forward, and feet together. All directional terms (e.g., anterior, lateral) refer back to this position, regardless of how the patient is actually lying.
Slicing Through the Body: Understanding Anatomical Planes
Anatomical planes are imaginary cuts crucial for understanding CT and MRI.
- The sagittal plane divides the body vertically into right and left sections. The midsagittal plane creates two equal halves.
- The coronal (or frontal) plane runs vertically, dividing the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions.
- The axial (or transverse) plane runs horizontally, dividing the body into upper and lower sections. Axial CT and MRI images are typically viewed as if looking up from the patient’s feet.
- An oblique plane is any slice not parallel to the main three planes.
Radiographic Positioning: Where Does the Beam Enter?
Positioning describes the X-ray beam’s path, known as a projection.
- In an AP (anteroposterior) projection, the beam enters the front and exits the back.
- A PA (posteroanterior) projection is the reverse, entering the back and exiting the front.
- Lateral positions involve side-to-side beam travel, 90 degrees from an AP or PA view.
- Oblique positions rotate the patient, so the beam passes through diagonally.
- Decubitus positions are used to find air-fluid levels. The patient lies down, but the X-ray beam is always horizontal (parallel to the floor).
Body Habitus: Why One Size Doesn’t Fit All
Body habitus, the general shape of a person’s body, significantly impacts organ location.
- Sthenic (50% of population): Average, athletic build. Organs are in their expected textbook locations.
- Hyposthenic (35%): Slender and taller. Organs are lower and more vertical.
- Asthenic (10%): Very slender with a long, narrow torso. Organs sit very low and vertically.
- Hypersthenic (5%): Broad, deep chest and large abdomen. Organs are high and more horizontal.
This matters because a patient’s habitus affects your centering point, exposure factors (kVp and mAs), and image receptor size. For example, the stomach can be 6-8 inches higher in a hypersthenic patient than an asthenic one. Assessing a patient’s build helps you adjust your technique proactively, reducing repeat exposures.
For a deeper dive, Fundamentals of Radiographic Positioning and Anatomy is an excellent resource. Understanding these concepts transforms you from a technician into a thinking radiographer who can adapt on the fly.
A Regional Guide to Anatomy for Radiographers
Mastering regional anatomy for radiographers means knowing not just where structures are, but how they appear on different imaging modalities. Let’s tour the body’s major regions.
Brain, Head, and Neck Anatomy
This intricate region houses the brain, sensory organs, and critical vascular structures.
On brain MRI, T1w images show fat as bright and CSF as dark, providing excellent anatomical detail. On T2w images, both fat and fluid are bright, highlighting pathology like edema or inflammation. Head CT is vital for trauma. We use bone windows to see the skull base, orbits, and paranasal sinuses for fractures, and soft tissue windows to evaluate brain parenchyma for hemorrhage or mass effect. Neck CT reveals the cervical spine, thyroid gland, and major blood vessels. The Anatomy Coloring Workbook can help reinforce these complex relationships.
Spine and Chest Anatomy
The spine is our central pillar, and the chest contains our vital heart and lungs.
The chest X-ray is a frontline tool. Many use the ABCD rule for systematic review: Airways, Breathing (lungs), Cardiac (mediastinum), and Diaphragm. Chest CT offers greater detail, showing individual bronchopulmonary segments, pulmonary vessels, and the mediastinum. The diaphragm appears as a smooth dome separating the chest and abdomen.
Spine imaging covers the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions. While X-rays show alignment and bone, CT and MRI reveal intervertebral discs, the spinal cord, and neural foramina, which is crucial for assessing conditions like sciatica. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 8th Ed. provides comprehensive coverage.
Abdomen and Pelvis Anatomy
This region is a mix of solid organs, hollow tubes, and bones. Abdominopelvic CT is a primary tool for evaluating pain, trauma, and cancer. It visualizes solid organs like the liver (with its hepatic segments), spleen, and kidneys, and hollow organs like the bowel and bladder, all framed by the pelvic bones.
Clinically, the abdomen is divided into four quadrants:
- Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ): Liver (right lobe), gallbladder, pancreas head, right kidney.
- Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ): Liver (left lobe), stomach, spleen, pancreas tail, left kidney.
- Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ): Cecum, appendix, ascending colon, right ovary/tube.
- Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ): Descending/sigmoid colon, left ovary/tube.
This system helps localize pathology, such as suspecting appendicitis with RLQ pain.
Upper and Lower Limb Anatomy
The extremities are frequently imaged for injuries. In the upper limb, shoulder MRI is invaluable for evaluating the rotator cuff muscles. Wrist MRI reveals the eight carpal bones and associated ligaments, crucial for diagnosing conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome. Plain X-rays of long bones (humerus, radius, ulna) and joints remain essential for fracture detection.
In the lower limb, knee MRI is the standard for soft tissue injuries, especially to the ACL, PCL, and menisci. For the ankle, specific X-ray views like the mortise view are used to visualize the joint space clearly. We also routinely image the long bones (femur, tibia, fibula) and joints of the lower limb for fractures and degenerative changes. Part 1: Anatomy & Physiology in Health and Illness 13th Ed. offers comprehensive coverage of these systems.
Advanced Techniques and Clinical Application
Mastering fundamental anatomy for radiographers opens the door to advanced techniques that improve diagnostic accuracy and patient care.
Enhancing Visualization: A Guide to Contrast Agents
Contrast agents are specialized substances that highlight anatomical structures that would otherwise be difficult to see.
In CT imaging, iodine-based contrast is administered intravenously (IV contrast) to make blood vessels and highly vascular tumors appear bright white. This is essential for assessing organ perfusion and vascular issues. The way tissues improve—their improvement patterns—provides diagnostic clues. For GI studies, barium-based contrast is given orally or rectally to coat and outline the digestive tract on X-rays and CT scans, revealing obstructions or masses.
MRI contrast uses gadolinium-based agents. Instead of blocking X-rays, gadolinium alters the magnetic properties of nearby water molecules, making tissues appear brighter on T1-weighted images. This is highly effective for detecting tumors, inflammation, and evaluating blood vessels, especially in the brain.
Common Pitfalls and Artifacts in Radiological Anatomy
Even with perfect technique, artifacts can appear on images. Recognizing them is a key skill.
- Motion artifact from patient movement causes blurring that can obscure details. We combat this with clear communication, immobilization, and short exposure times.
- Beam hardening is a CT artifact that occurs when X-rays pass through dense material like bone or metal. It creates dark streaks that can obscure adjacent soft tissues.
- Metal artifacts from surgical clips or joint replacements create significant distortion on both CT (streaks) and MRI (signal voids), making nearby anatomy difficult to read.
- Patient positioning errors, even slight rotation on a chest X-ray, can mimic pathology, such as making a normal heart appear enlarged. Meticulous positioning is crucial for diagnostic accuracy.
A vital skill is recognizing normal anatomical variants. Many people have accessory bones that can look like fractures or unusual organ positions that are harmless. Experience and continuous learning help distinguish these normal variations from true abnormalities.
From Anatomy to Pathology: The Radiographer’s Role in Diagnosis
While radiographers do not make diagnoses, our role is foundational to the process. We compare every image against a mental normal anatomy baseline. Our ability to spot deviations from this baseline is critical.
- Fracture detection relies on seeing subtle cortical breaks or displacements.
- Mass effect, where a tumor or fluid pushes structures from their normal position, requires knowing exactly where those structures should be.
- Fluid collections in the pleural space or joints can be subtle, but knowledge of normal anatomy makes them stand out.
As the WHO manual of diagnostic imaging emphasizes, fundamental imaging techniques are indispensable. By producing high-quality images that clearly show relevant anatomy, we act as the first line of quality control and are essential in aiding radiologists. Our anatomical expertise directly contributes to accurate diagnoses and effective patient treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Anatomy for Radiographers
Here are answers to some common questions about anatomy for radiographers.
What is the difference between density in CT and intensity in MRI?
These terms both describe image brightness but measure different physical properties.
CT density measures X-ray attenuation in Hounsfield Units (HU). It reflects how much a tissue physically blocks X-rays. Dense bone has a high HU value and appears bright white (hyperdense), while air has a low HU value (-1000) and appears black (hypodense). Water is the baseline at 0 HU (gray).
MRI intensity measures the proton signal strength from hydrogen atoms in water. It depends on tissue properties like water content and how protons react to magnetic fields and radio waves, not physical density. On T1-weighted images, fat is bright (hyperintense); on T2-weighted images, fluid is bright. Brightness is described as hyperintense or hypointense.
In short: CT density is about X-ray absorption, while MRI intensity is about magnetic signal strength.
How does a patient’s body habitus affect radiographic technique?
A patient’s body habitus changes organ location and requires adjustments to imaging technique.
For a hypersthenic patient (broad, deep torso), organs like the heart and stomach sit higher and more horizontally. You must raise your centering, increase exposure factors (kVp and mAs) to penetrate more tissue, and may need a larger image receptor.
For an asthenic patient (slender, long torso), organs are lower and more vertical. You must lower your centering and decrease exposure factors.
Most patients are sthenic or hyposthenic, for whom standard techniques are designed. Recognizing and adapting to other body types is crucial for avoiding repeat images and ensuring diagnostic quality.
Why are anatomical planes crucial for interpreting CT and MRI scans?
Anatomical planes are the coordinate system for cross-sectional imaging, allowing you to mentally reconstruct 2D slices into a 3D visualization.
The axial, sagittal, and coronal views each provide a unique perspective on the same anatomy. Understanding which plane you are viewing is essential for lesion localization. By tracking an abnormality across different planes, you can pinpoint its exact 3D location and its relationship to surrounding structures.
This precision is vital for surgical planning, as surgeons need a detailed roadmap. It also enables clear communication among the healthcare team. Anatomical planes are not just academic; they are the practical framework for navigating the human body in modern imaging.
Conclusion: Sharpen Your Skills and Advance Your Career
From understanding imaging physics to mastering anatomical planes and body types, it’s clear that anatomy for radiographers is the foundation of our profession. This knowledge transforms a technically correct image into a truly diagnostic one, directly impacting patient care.
Our field is constantly evolving, which makes lifelong learning a core competency. Staying current ensures we deliver the highest image quality and maintain patient safety. This commitment to professional development is what defines excellence in radiography.
We know finding time for continuing education is challenging. That’s why Scrubs CE offers flexible, self-paced continuing education courses designed for busy professionals. Learn on your schedule and get instant certificates to meet your licensure requirements without hassle. We’ve built our course catalog with working radiographers in mind, because we believe advancing your career shouldn’t mean putting your life on hold.
Ready to sharpen your skills? Your patients and your career will benefit.
Explore our full catalog of X-Ray CEU courses to master your craft.
Beyond the Price Tag: What Makes Expert-Led Courses Truly Shine?
Why Expert-Led Courses Matter for Your Healthcare Career
Expert led courses connect you directly with seasoned practitioners who bring real-world experience into your continuing education. When you’re evaluating these courses, here’s what truly sets the best ones apart:
Key Features of High-Quality Expert-Led Courses:
- Instructors with 10+ years of field experience who understand practical challenges
- Real-world case studies that mirror what you encounter daily
- Current, up-to-date content that reflects the latest industry standards
- Practical application beyond textbook theory
- Accredited programs that meet licensure requirements
As a busy healthcare professional, you don’t have time for courses that simply repeat what you can read in a manual. You need learning that actually improves how you work with patients and advance your career.
The difference between a basic online course and a truly expert-led one comes down to depth and relevance. For example, 91% of authors at platforms like ScrubsCE bring at least a decade of hands-on experience to their teaching. This isn’t just about credentials on paper—it’s about learning from someone who has faced the same challenges you do.
The principle of combining academic excellence with real-world cases and insights from leading industry experts applies whether you’re taking a course in MRI technology, mammography, or nuclear medicine. The instructor’s practical wisdom makes all the difference.
But experience alone isn’t enough. The best expert-led courses also structure content for working professionals. They fit into your demanding schedule, provide immediate takeaways, and help you maintain licensure while building genuine skills.
In the sections ahead, we’ll break down what to look for when choosing an expert-led course, how to evaluate instructor credentials, and which features deliver real career impact.
The Best Benefits of Learning from True Experts
As a healthcare professional, you know that quality education directly impacts patient care and career growth. While many courses just check a box for CE requirements, expert led courses offer something more.
Learning from a seasoned professional provides unparalleled credibility. At ScrubsCE, 91% of our course authors have at least 10 years of hands-on experience, sharing battle-tested knowledge you can trust. This experience translates into in-depth knowledge that goes beyond textbooks, explaining the why behind procedures and how to adapt when things don’t go as planned.
Perhaps the most valuable benefit is real-world context. Experts illustrate concepts with actual cases, making the material immediately relevant to your daily work. You learn to problem-solve like an experienced practitioner. This also provides a form of mentorship by proxy, offering insight into the thought processes and professional philosophies that drive successful careers.
These benefits are essential for anyone serious about advancing their skills. To dive deeper into why this kind of continuous learning matters so much for radiologic technologists, check out these 5 Benefits of Continuing Radiology Education.
Gaining Unparalleled Depth and Nuance
Excellent expert led courses provide depth and nuance you won’t find in generic content. Instead of surface-level information, you gain practical wisdom from instructors who have steerd rare cases and adapted to evolving technologies. They share the “tricks of the trade” that improve your work.
These instructors are often at the forefront of industry best practices, helping you stay ahead of the curve. Most importantly, they provide actionable insights, translating their experience into practical steps you can apply immediately to improve your daily practice.
For more on how continuing education can improve your capabilities as a radiologic technologist, explore 7 Ways Radiology CE Can Benefit You as a Radiologic Technologist.
Boosting Your Career with Validated Skills
Expert led courses boost your career with validated, sought-after skills. In a competitive environment, proven competencies are what move you forward.
Employer recognition increases when you can show that your skills were developed under recognized experts. This adds weight to your qualifications and improves your resume, as certificates from reputable programs demonstrate a commitment to excellence. These courses also provide skill validation through assessments and practical applications, assuring employers of your new competencies.
Finally, learning from an expert builds increased confidence. This assurance translates into better job performance, a willingness to tackle new challenges, and improved patient interactions, whether you’re aiming for a promotion or seeking greater professional satisfaction.
To find courses that can genuinely advance your professional standing, take a look at The Top X-Ray Continuing Education Courses That Pay Off in the Long Run.
How to Identify High-Quality Expert-Led Courses
Not all expert led courses are created equal. To avoid wasting time on subpar education, it’s crucial to know how to identify high-quality options. For a general overview of what this type of professional development entails, you can review the principles of continuing education.
Here’s what to look for:
- Instructor Vetting: The best platforms carefully select instructors with proven, hands-on expertise. For example, seeing that most authors have over a decade of field experience is a strong indicator of quality.
- Comprehensive Curriculum: The course material should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the latest industry practices and technologies.
- Learner Testimonials: Feedback from peers can reveal if a course delivers on its promises of relevance and engagement.
- Practical Components: Look for real-world case studies and interactive exercises. This is where theory meets practice.
- Quality Assurance: Top platforms use learner feedback to continuously improve their courses and ensure content remains current.
Curious about what makes our courses stand out? See what makes a top-rated course at ScrubsCE.
Evaluating the Instructor’s Real-World Expertise
The instructor can make or break your learning experience. When evaluating an instructor, look beyond academic credentials to their industry experience. Have they spent years doing the work and facing the same challenges you do?
Also, consider their professional achievements, such as published works or contributions to research, which signal a leader in the field. Equally important is their teaching ability. The best instructors can break down complex topics and use their own experiences to illustrate key points. Take time to read an instructor’s bio to ensure you’re learning from someone who is both a subject matter expert and an effective teacher.
Want to learn more about the experts behind our courses? Visit our About page to meet our instructors.
Analyzing the Course Structure and Content
A course’s structure and content are critical for your success. The best expert led courses are thoughtfully designed.
- Learning Objectives: Look for clear, specific, and measurable objectives that align with your professional goals.
- Real-World Case Studies: These are essential in healthcare education, allowing you to see how experts approach clinical scenarios and make decisions under pressure.
- Up-to-Date Content: In a rapidly evolving field like medical imaging, course material must be regularly refreshed to reflect current best practices and technologies.
- Engagement Elements: Quality courses include interactive components like quizzes and practical exercises to ensure learning is an active, not passive, experience.
Ready to explore what we offer? Check out our All Courses page. And if you’re looking to maximize both your learning and your budget, find Why a Combo E-Course is a Good Fit for Your Radiology CE.
A Spectrum of Learning: Matching Courses to Your Career Goals
Your career isn’t one-size-fits-all, and neither is continuing education. Expert led courses are designed to meet you where you are and help you get where you want to go, whether that’s mastering a new technology or developing leadership skills.
Think about your current career stage. Are you looking to transition to a new modality, maintain your license, or step into a leadership role? Each path requires different skills and guidance. The best courses offer genuine growth, providing insights from experts that stick with you long after the course ends.
This spectrum of learning recognizes that professionals have different needs. Some require deep technical knowledge, while others need to build the soft skills of great leaders. If you’re thinking about expanding into a new area of radiology, you might find this helpful: How to Use Continuing Education to Advance to a Different Modality Within Radiology.
Technical and Specialized Skill Development
In healthcare imaging, staying technically sharp is essential as equipment, protocols, and safety guidelines evolve. Specialized expert led courses are invaluable for this.
Our course library is built for working technologists. We offer courses covering a range of specializations:
- Radiology CE Courses cover foundational and advanced techniques.
- MRI CE Courses dive into specifics like safety, new sequences, and artifact recognition.
- Mammography CE Courses focus on the nuances of breast imaging and screening guidelines.
- Nuclear Medicine CE Courses address the unique challenges of working with radioisotopes.
The difference is the expertise. Instructors with thousands of procedures under their belt know what works in real clinical settings, not just in theory. Many of these courses also provide focused preparation for modality-specific certifications.
Advancing Your Career with Leadership and Foundational Skills
The skills that got you here may not get you to the next level. While technical excellence is crucial, leadership and foundational skills are what drive career advancement.
If you’re taking on more responsibility, you’ll need to understand management principles, effective communication, and strategic thinking. Expert instructors who have led teams can teach these skills from experience, offering practical approaches for everything from patient communication to departmental advocacy.
Beyond leadership, there are foundational principles that apply across your entire career, such as problem-solving and critical thinking. Professionals who advance often combine their technical expertise with these strong interpersonal and strategic skills. This complete package makes you invaluable to your organization.
To explore how we can help you build both your technical skills and your professional capabilities, take a look at all we offer: Explore professional education options at ScrubsCE.
Frequently Asked Questions about Expert-Led Courses
When you’re thinking about investing your time and money in continuing education, it’s completely normal to have questions. We’ve heard them all, and we’re here to give you straight answers that help you decide if expert led courses are right for your career.
How much do expert-led courses cost and are they worth it?
The cost of expert led courses varies, from subscription models to per-course pricing. However, the real question is about value. These courses can directly impact your earning potential, job security, and confidence by providing insights you can’t get from a textbook.
For healthcare professionals, meeting licensure requirements efficiently is key. Our Radiology CE Course Combos are designed to provide comprehensive coverage while maximizing your budget. The return on investment isn’t just financial; it’s also the peace of mind and professional satisfaction that come from mastering your craft. When viewed as an investment in yourself, the cost is often well worth it.
How do I know which expert-led course is right for my professional development?
Choosing the right course starts with a little reflection and research. First, assess your career goals. Are you aiming for a promotion, a new modality, or more confidence in your current role? Your goals will guide your choice. For understanding requirements, our guide on How Many X-Ray CE Credits Do I Need for Radiography? can be helpful.
Next, research the course itself:
- Instructor Bio: Look for instructors with real-world experience in the subject you want to learn.
- Course Syllabus: Ensure the topics and learning objectives align with your skill gaps and goals.
- Prerequisites: Check that you have the necessary foundational knowledge to succeed.
Finally, consider your learning style and schedule to find a course that fits your life.
How do these courses ensure the quality and relevance of the content?
It’s fair to ask how platforms ensure their content is accurate, current, and useful. Quality assurance relies on several key processes:
- Expert Vetting: Reputable platforms carefully screen instructors for deep expertise and teaching ability. At ScrubsCE, for instance, most authors have over a decade of hands-on experience.
- Peer Review: Many platforms have other experts review course materials to catch errors and ensure they meet professional standards.
- Regular Updates: In a field like healthcare, content must be kept current. Quality platforms commit to regular updates to reflect the latest research and standards.
- Learner Feedback: The best platforms use feedback from students to make continuous improvements.
These measures protect your investment and ensure your CE credits represent knowledge you can use. For more on meeting requirements, check out Satisfying Radiology Continuing Education Requirements for the Biennium.
Conclusion
The key takeaway is that expert led courses are a genuine investment in yourself, your patients, and your future. They offer the credibility of learning from seasoned professionals, the practicality of gaining real-world insights, and the opportunity for career advancement through validated skills.
When you learn from true experts, you absorb wisdom that goes beyond facts, seeing how they solve complex problems and stay current in an evolving field. Choosing wisely is key, and we’ve covered how to evaluate instructors and content to ensure you get real value.
At ScrubsCE, we understand the needs of busy healthcare professionals. Our courses are taught by experienced practitioners, designed to fit your schedule, meet CE requirements, and genuinely improve how you work. We’re here to help you become the best professional you can be.
Continuing education doesn’t have to be a chore. With expert guidance, it becomes an opportunity to excel, build confidence, and provide even better patient care.
Ready to experience the difference? Explore our expert-led X-Ray CEU courses to advance your career and find how learning from the best can help you be your best.
Renewing Your Radiologic Technologist License: Smooth Sailing Ahead
Why Rad Tech License Renewal Matters for Your Career
Rad tech license renewal is a mandatory process that keeps you legally authorized to practice. Most states require renewal every two years, which involves completing continuing education (CE) credits and maintaining your ARRT certification.
Quick Answer: Rad Tech License Renewal Requirements
- Frequency: Every 2 years (biennial cycle)
- CE Credits: Typically 24 hours of approved continuing education
- ARRT Renewal: Annual renewal required separately (by birth month)
- State License: Biennial renewal through your state health department
- Fees: Range from $55-$150 depending on your state
- Deadline: Usually 60-90 days before expiration (check your state)
Staying current is essential for patient safety and career advancement. While tracking regulations, CE credits, and deadlines can seem daunting, the process is straightforward once you understand the requirements. Knowing the difference between ARRT certification and state licensing, understanding your CE obligations, and staying ahead of deadlines will make the entire process smooth and stress-free.
Over 75% of states require licensure for radiologic technologists, each with specific rules. While most diagnostic and therapeutic radiographers need 24 CE credits every two years, some specialties have different requirements. You must also maintain your ARRT certification separately through an annual renewal process.
Understanding the Foundation: ARRT Certification vs. State Licensing
One of the most common points of confusion in rad tech license renewal is the difference between ARRT certification and a state license. They are distinct credentials, and you need both to practice legally in most states.
Think of your ARRT certification as a national credential demonstrating your professional competence and ethical standards. It’s recognized nationwide and valued by employers, but it is technically voluntary.
Your state license, however, is your legal permission to work. Over 75% of states require a license, issued by a state health department or radiation control board. Practicing without a license in these states is illegal. Many states use ARRT certification as a basis for licensure, but each state has its own application and renewal process. You must manage both credentials, which have different renewal schedules and requirements. If you’re unsure of your state’s rules, Contact a state licensing board. For state-specific details, see resources like More info about Florida radiologic technology licenses.
ARRT Annual Renewal
Your ARRT certification must be renewed annually to remain in good standing. This is separate from your biennial state license renewal. The deadline is always the last day of your birth month. To renew, you must comply with the ARRT Rules and Regulations and maintain ethical standards.
While renewal is annual, continuing education (CE) is reported on a biennial cycle. You don’t need to submit CE credits every year, but every two years. Additionally, those certified in 2011 or later must complete Continuing Qualifications Requirements every 10 years.
The annual renewal fee is currently $30 for your first discipline and $15 for additional ones. However, starting with renewals due in January 2026, ARRT is moving to a flat fee of $65 for all renewals. The easiest way to renew is online through your ARRT account. For more on educational requirements, see A guide to continuing education for X-ray technologists.
State-Specific License Renewal
While ARRT provides national recognition, your state license grants the legal authority to work. Most states use a biennial (every two years) renewal cycle. This process is managed by your state’s health department or radiation control board, such as the Radiation Control Program in Massachusetts or the Department of Public Health-Radiologic Health Branch in California.
These agencies exist to protect the public by ensuring all practicing technologists meet state-mandated standards. This means your CE requirements, fees, and application procedures are determined by state law and can differ significantly from one state to another.
For example, California requires mailed payments and has specific CE requirements for digital radiography. You can find details at More info about California X-ray licenses. Similarly, Colorado has its own unique processes, which you can learn about at More info about Colorado radiologic technology licenses. Always verify your specific state’s requirements to ensure you remain legally authorized to practice.
Your Core Renewal Checklist: CE Credits and Documentation
Continuing education (CE) credits are the heart of your rad tech license renewal. They ensure you stay current with the latest techniques and technologies in an evolving field. Both ARRT and most states operate on a CE biennium, a two-year period for completing your required hours. Keeping accurate records of your completed courses is essential, especially in case of an audit.
General Continuing Education (CE) Requirements
The standard requirement is 24 approved continuing education credits every two years. This applies to both ARRT and most state licenses. The majority of these credits should be in technical subjects directly related to your work, such as radiation safety, patient care, and imaging techniques.
Some states, like Florida, allow a small number of credits (e.g., 3 of 12) to be in personal development topics like CPR, but the rest must be technical. Florida also requires a one-hour HIV/AIDS update course. You can complete your credits at any point during the two-year cycle. For a breakdown by credential, see How many X-ray CE credits do I need?. For strategies on meeting these requirements, read Satisfying radiology continuing education requirements for the biennium.
Specialty-Specific CE Requirements
If you hold specialty certifications, your CE requirements will be more targeted. You’ll still need 24 total credits, but a portion must be in your specialty.
- Mammography: Technologists often need mammography-specific credits. California, for example, requires 10 of the 24 credits to be in mammography. Learn more in our Mammography technologist license renewal guide.
- Digital Radiography: Many states mandate CE in digital imaging. California requires at least 4 of 24 credits in this area.
- Fluoroscopy: To ensure safety with higher radiation doses, specific CE is required. California fluoroscopy permit holders need 4 of 24 credits in fluoroscopy radiation safety. See our California fluoroscopy license renewal guide for details.
Even with multiple certifications, the total requirement is typically 24 credits. A single course can often satisfy multiple specialty requirements simultaneously.
Finding Approved CE Courses and Providers
Choosing approved courses is critical for a smooth rad tech license renewal. Your safest option is to select courses from ARRT-approved providers, designated as Category A or A+. Use the ARRT’s Find approved CE activities with the ARRT search tool to locate them. While most states accept ARRT-approved courses, always double-check with your state board, as some have their own lists of approved providers.
Online CE courses offer the flexibility busy professionals need. At Scrubs CE, we provide a library of online radiology CE courses designed to meet your renewal needs, allowing you to learn at your own pace. Explore some options at The top X-ray radiology CE credits you can earn online.
Not all health-related courses are accepted. For example, California does not accept MRI, ultrasound, or CPR courses for CRT renewal. After completing a course, save the certificate of completion for at least four years in case of an audit.
Navigating the Rad Tech License Renewal Process Step-by-Step
You’ve completed your CE credits and gathered your documentation. Now comes the moment where everything comes together: actually submitting your rad tech license renewal. This part is more straightforward than you might think, but understanding the timelines, submission options, and fees will help you avoid any last-minute surprises.
Key Timelines and Deadlines
Timing is everything when it comes to rad tech license renewal. Missing a deadline doesn’t just mean a late fee—it can mean you’re technically working without a valid license, which is a serious legal issue.
Your state license typically operates on a biennial renewal cycle, meaning you’ll renew every two years. Most state health departments will send you a renewal notice 60 to 90 days before your expiration date. If you haven’t received your notice 45 days before expiration, don’t wait—reach out to your state board directly.
Your expiration date is usually tied to your birth month, similar to your ARRT renewal. While most states do offer a grace period if you miss the initial deadline, this almost always means paying a late fee. Your annual ARRT renewal has its own separate deadline. For state-specific timelines, like for More info about Idaho radiologic technologist licenses, always check your state’s official health department website for the most current information.
The Rad Tech License Renewal Process: Online vs. Paper
When it’s time to submit your renewal, you’ll typically have two options: online or paper. The method you choose can significantly impact both convenience and how quickly your renewal is processed.
Online renewal is usually the fastest and most convenient option. You can access your state’s licensing portal, complete the form, upload CE certificates, pay by card, and often receive instant confirmation or a temporary permit. For example, you can Renew your license in Florida through their online portal.
Paper applications are still an option, though slower. You’ll need to download the form, fill it out, and mail it with copies of your documents and a check or money order. Some states, like California, only accept mailed payments for renewals. Other states may encourage online submission; Texas, for instance, charges a $50 fee for paper applications when an online option is available. If your state offers online renewal, it’s usually the best choice.
Understanding Fees and Penalties for Rad Tech License Renewal
Renewal fees are part of maintaining your professional credentials, and they can vary quite a bit depending on where you practice and whether you renew on time.
- Active Renewal Fees: Paid before expiration, these typically range from $55 (Florida) to $150 (Massachusetts).
- Late Renewal Penalties: If you renew during the grace period, expect an additional fee, such as Washington’s $50 penalty.
- Expired License Reactivation Fees: These are significantly higher. In California, reactivating a license expired for up to five years costs $224 per category, compared to the standard $104. Florida charges $155 to reactivate an expired license.
If you hold multiple certifications, you may face additional fees for each. Some states also add a small convenience fee for online payments. All fees are almost always non-refundable, so double-check your application and payment details before submitting.
When Things Don’t Go to Plan: Expired Licenses and Special Cases
An expired license is more than an administrative oversight; it can have serious career consequences. However, most situations are fixable, and special provisions exist for circumstances like military service.
What Happens if Your License Expires?
Once your license expires, you are no longer legally authorized to practice. Your license status becomes “expired” or “lapsed.”
You must stop working immediately. Practicing with an expired license violates state regulations and can lead to severe penalties. To restore your license, you must go through a reinstatement or reactivation process, which is more complex and expensive than a standard renewal. Fees are significantly higher; for example, California charges up to $224 per category to reactivate a license expired for less than five years, and Florida charges $155.
You may also need to complete additional CE hours. If a license remains expired for an extended period (typically 5-10 years), it can become null and void. At that point, you would have to re-apply for initial licensure as a new graduate. For more on staying current, see our guide on radiology continuing education requirements in Pennsylvania.
Consequences of Not Renewing on Time
Failing to complete your rad tech license renewal on time can lead to a cascade of professional problems. State licensing boards can impose sanctions like fines, reprimands, or even license revocation, all of which become part of your permanent public record.
Your employer will likely suspend you or terminate your employment, as they cannot legally allow an unlicensed technologist to work. Practicing without a license can also have legal ramifications and damage your professional reputation. The ARRT Standards of Ethics also require you to maintain current credentials. The best strategy is to set multiple reminders and complete your renewal well before the deadline.
Special Considerations for Military Personnel
Many states offer accommodations for military service members and their families to help them manage professional licenses during relocations and deployments.
- Military spouses often qualify for expedited license application processing in a new state.
- Military education and experience may count toward state licensing requirements, which is valuable for those transitioning to civilian practice.
Provisions vary by state. Some offer waivers for renewal fees or extensions for CE completion for those on active duty. For example, Washington state technologists can find specific information on how military service affects their certification. Always contact your state licensing board directly to learn about the benefits available to you.
Frequently Asked Questions about Rad Tech License Renewal
Here are answers to some of the most common questions about rad tech license renewal.
How do I verify my radiologic technologist license status?
Verifying your license is simple and can be done in several ways:
- State License Lookup Portal: Most state health departments have an online verification tool on their website where you can search by name or license number.
- ARRT Directory: You can verify your national credentials through the ARRT’s online directory.
- Temporary Authorization: After renewing online, many states provide a printable temporary authorization to use while you wait for your physical license to arrive.
Your license information is generally public record, which promotes transparency and public safety.
What are the requirements for initial licensing as a radiologic technologist?
While this guide focuses on renewal, the initial licensing process sets the foundation. Key steps include:
- Graduating from an accredited educational program in radiologic technology.
- Passing a primary pathway examination administered by the ARRT.
- Submitting a state-specific application with required documentation, including transcripts and proof of ARRT certification.
- Completing a criminal background check.
- Paying an initial application fee.
Some states have alternative pathways, but ARRT certification is the most common route. For related tips, see More info about Massachusetts CE tips.
Are there any upcoming changes to renewal fees or processes?
Yes, the regulatory landscape can change. The most significant upcoming change is from the ARRT. Starting with renewals due in January 2026, the ARRT will switch to a single flat renewal fee of $65 for all annual renewals, regardless of the number of credentials you hold. This will simplify the process and may save money for those with multiple certifications.
State-level changes occur independently. The best way to stay informed is to regularly check your state’s official licensing board website and subscribe to professional newsletters from organizations like the ARRT. This ensures you are aware of any updates to fees, processes, or requirements for your rad tech license renewal.
Conclusion
By now, you should feel more confident about your rad tech license renewal. The process is manageable once you understand the key components: your ARRT certification and your state license. Both are crucial and require your attention.
The secret to a stress-free renewal is planning. Set reminders for your annual ARRT renewal and your state’s biennial deadline. Keep your CE certificates organized as you earn them so you’re prepared when it’s time to submit your application.
CE requirements are an opportunity to improve your skills and stay current with new technologies, making you a more valuable technologist. Each state has its own rules, so always verify the latest information on your official licensing board’s website.
Maintaining your license is a mark of professionalism and a commitment to providing the best patient care.
Ready to complete your CE requirements? Explore our library of ARRT-approved radiology CE courses. Our courses are convenient, affordable, and self-paced, with instant certificates to help you stay current and advance your career.
Don’t Miss a Beat: The Ultimate ARRT CE Renewal Playbook
Why Understanding Your ARRT CE Renewal Matters
ARRT CE renewal involves completing continuing education credits every two years and renewing your credentials annually to maintain your certification. Here’s a quick overview:
Quick Overview of ARRT CE Renewal Requirements:
- Complete CE Credits: Most R.T.s need 24 CE credits every two years (R.R.A.s need 50)
- Annual Renewal: Renew your credentials each year by the last day of your birth month
- Report CE: Submit your CE credits every other year during your annual renewal
- Pay Fees: Currently $30 for your first discipline, $15 for additional (changing to $65 flat fee in 2026)
- Stay Current on CQR: Complete Continuing Qualifications Requirements every 10 years (if certified after 2011)
Staying current with your ARRT certification is essential for patient care and required by employers and the ARRT. However, the renewal process, with its overlapping two-year CE bienniums and annual deadlines, can be confusing.
Once you understand how the pieces fit together, ARRT CE renewal becomes straightforward. This guide breaks down the entire process, from finding approved CE to handling compliance issues. We’ll walk you through each step so you can maintain your credentials without stress and focus on providing excellent patient care.
Understanding Your ARRT CE Requirements
To keep your ARRT certification active, you must manage two overlapping timelines: your CE biennium and your annual renewal. Understanding how they work together makes ARRT CE renewal much less mysterious. Your CE biennium is the two-year window for earning CE credits, while the annual renewal is the yearly process of paying fees and attesting compliance. Every other year, you report your completed CE credits during your annual renewal.
Here’s a quick comparison of how these two pieces fit together:
| Feature | CE Biennium | Annual Renewal |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Earn and report continuing education credits | Renew certification, pay fees, attest compliance |
| Frequency | Every two years | Every year |
| Timing | Starts on your birth month, lasts 24 months | Starts two months before your birth month, due by the last day of your birth month |
| CE Reporting | Required every other year | Attest to compliance every year, report CEs every other year |
| Fees | No direct fee for the biennium itself, but fees for CE activities | Annual renewal fee applies |
| Compliance | Complete required CE credits | Pay fees, attest to Rules & Regulations, Standards of Ethics, and CE completion |
For more detailed information about radiography requirements specifically, take a look at our guide on How Many X-Ray CE Credits Do I Need for Radiography?.
What is a CE Biennium vs. an Annual Renewal?
Let’s clarify the most confusing part of ARRT CE renewal: the CE biennium versus the annual renewal.
Your CE biennium is a 24-month period for completing CE credits, starting on the first day of your birth month. For example, a March birthday could mean a biennium from March 1, 2024, to February 28, 2026.
Your annual renewal occurs every year. The renewal window opens two months before your birth month and closes on the last day of your birth month. During this time, you pay fees and attest to following ARRT’s Rules and Regulations and Standards of Ethics.
You renew annually, but you only report your CE credits every other year at the end of your biennium. One year you simply renew and attest; the next, you renew and report your completed CE.
Understanding these separate timelines helps you avoid the panic of realizing you need credits right before your deadline. For practical tips on planning ahead, check out our article on Satisfying Radiology Continuing Education Requirements for the Biennium.
How Many CE Credits Do I Need?
The number of CE credits for your ARRT CE renewal depends on your credential. Most technologists need 24 credits every two years, but there are key variations:
- R.T. (Registered Technologist): 24 credits per biennium for most disciplines, including radiography and mammography.
- R.R.A. (Registered Radiologist Assistant): 50 credits per biennium. At least 25 must be Category A+ and 35 must be directly related to R.R.A. practice.
- Sonography Credential: 24 total credits, with 16 being discipline-specific to sonography. ARRT may expand discipline-specific requirements to other modalities in the future.
If you hold multiple certifications, you only need to meet the requirement for your highest credential. Credits can often satisfy requirements for multiple certifications simultaneously.
For the most current and detailed breakdown of requirements, Review the official ARRT Education Requirements directly from ARRT. They update this document regularly, so it’s always your best source for the latest information.
Finding and Completing Approved CE Activities
Now that you know your credit requirements, the next step is finding and completing activities that ARRT will accept for your ARRT CE renewal. Not every educational activity counts. ARRT has specific criteria, ensuring the credits you earn represent genuine professional development.
We’ve helped thousands of radiologic technologists steer this process, and we’ve gathered everything you need to know in our comprehensive guide on CE Credits for Radiology: How Can I Get Them?.
What Types of Activities Are Accepted for CE Credit?
The gold standard for ARRT CE renewal is Category A and Category A+ credits. These are activities approved by an ARRT Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM). Category A+ credits are specifically for Registered Radiologist Assistants (R.R.A.s).
Other accepted activities include:
- Academic courses: Earn 16 CE credits per semester hour or 12 per quarter hour for relevant courses at accredited institutions.
- Advanced CPR: Certifications like ACLS or PALS can provide up to six CE credits once per biennium (basic BLS does not qualify).
- Authoring an article: Publishing in an ARRT-accepted peer-reviewed journal earns CE credits.
- Facility applications training: Up to 8.0 Category A credits per biennium for training on new equipment (cannot be used for Structured Education or CQR).
- State-approved activities: Activities approved by licensing boards in Florida, Kentucky, Massachusetts, or Oregon are accepted.
Activities that do not count include clinical instructorships, basic BLS, and earning a new credential itself (though the coursework to earn it may count).
We’ve made it easy to find the right courses for your needs. Whether you’re looking for general Radiology CE Courses, specialized Mammography CEUs, or focused CT/MRI CE, we’ve got you covered with ARRT-approved options.
How Do I Find Approved CE Activities?
Finding approved activities for your ARRT CE renewal shouldn’t be difficult. The most reliable resource is ARRT’s own biennial CE search tool. This database lets you filter activities by topic, provider, and credit type, guaranteeing that your chosen course will be accepted.
When browsing courses, look for clear indicators of approval, such as “Category A” or “Category A+” and mention of an ARRT-recognized RCEEM. These markers confirm the course meets ARRT’s standards.
As an ARRT-approved provider, we simplify this process. All our courses are evaluated by an ARRT RCEEM, so you can enroll with confidence. We provide high-quality, self-paced learning that fits your schedule, with instant certificates upon completion.
Looking for the convenience of online learning? We’ve compiled our recommendations in The Top X-Ray Radiology CE Credits You Can Earn Online, featuring courses that combine flexibility with quality.
The bottom line: stick with ARRT-approved providers and use official search tools to ensure your activities will count.
The Complete Guide to the ARRT CE Renewal Process
You’ve completed your CE credits—congratulations! Now it’s time to make it official. The ARRT CE renewal process is straightforward once you understand the path. We’ll walk you through when to report, what fees to pay, and how to complete your renewal. If you’re eager to get started on your next round of credits, our guide on How to Enroll in X-Ray CE Fast can help.
When and How to Report for Your ARRT CE Renewal
You only report CE activities every other year during your annual renewal. The reporting window opens two months before your birth month and closes at 11:59 p.m. Central Time on the last day of your birth month. You have one additional month after your biennium ends to report, providing some flexibility.
Reporting is done through your ARRT online account. When the renewal period opens, log in and click “Renew.” You’ll enter details for each CE activity, such as the course title, provider, completion date, and credits.
Crucially, ARRT does not track your CE activities. You must keep all participation certificates for at least one year after reporting in case of an audit. Some CE providers may transmit credits directly to ARRT, which will appear in your account. Verify these and add any others manually. Review everything carefully before submitting, as no changes can be made afterward. For those who appreciate working smarter, bundling your CE requirements can save time. Find Why a Combo E-Course is a Good Fit for Your Radiology CE.
Navigating the Annual Renewal and Fees
You must renew your credentials every year by 11:59 p.m. Central Time on the last day of your birth month. Missing this deadline has serious consequences.
The current fee for ARRT CE renewal is $30 for your first discipline and $15 for each additional one. For postprimary credentials using NMTCB or ARDMS credentials, the fee is $45 for the first and $15 for each additional.
Important Change: Starting with renewals due in January 2026, ARRT will switch to a flat fee of $65 for all renewals, covering all your credentials. This may be a cost savings for those with multiple certifications. Knowing this change helps you budget for the future.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Your ARRT CE Renewal
Ready to complete your ARRT CE renewal? Here is a simple, step-by-step guide:
- Log into your ARRT online account. Your dashboard contains your specific deadlines and requirements.
- Click the “Renew” button. This appears on your dashboard when your renewal window opens (two months before your birth month).
- Complete the ethics attestation. You must confirm your compliance with the ARRT Standards of Ethics and Rules and Regulations.
- Report your CE activities (if it’s your reporting year). Enter the details for each completed course. Verify any credits automatically transferred and add any others.
- Pay your renewal fee. Use a credit or debit card and ensure the payment is successful before the deadline.
- Print or save your confirmation. This is your proof of renewal and includes a list of the CE you reported.
With organized documentation, the entire process can take less than 30 minutes.
Explaining CQR and Handling Compliance Issues
Life gets busy, and sometimes keeping up with your ARRT CE renewal requirements can feel overwhelming. Whether you’re navigating Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR) or wondering what happens if you miss a deadline, we’re here to help. The most important thing is to stay informed about the ARRT Rules and Regulations and the ARRT Standards of Ethics so you can stay on track.
What are the Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR)?
Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR) is ARRT’s 10-year assessment to ensure you’re keeping pace with the evolving field.
CQR applies to you if you earned your initial certification on or after January 1, 2011. You have a three-year window to complete the process once your compliance period opens.
The CQR process has three steps:
- Complete a professional profile detailing your work experience.
- Take a structured self-assessment (online or at a test center) to identify knowledge gaps.
- Complete prescribed CE activities based on your assessment results. These prescribed activities often count toward your regular biennial CE requirements.
Your ARRT dashboard helps you track your CQR progress. It’s best to start early in your three-year window to avoid stress. For a deeper dive into structured education, see our article on What You Need to Know About ARRT’s Structured Education Solutions and Requirements.
What Happens If I Miss a Deadline?
If you fall behind on your ARRT CE renewal requirements, it’s important to act quickly.
- Missing CE Credits: If you don’t complete your CE by the end of your biennium, you can still complete your annual renewal. ARRT will place you on CE probation, giving you a six-month extension (with a fee) to earn and report the missing credits. Failure to do so will result in your certification being discontinued.
- Missing the Annual Renewal Deadline: This is more serious. If you miss the deadline (the last day of your birth month), your credentials are immediately discontinued. You will need to apply for reinstatement and pay a fee.
To avoid these issues, mark your deadlines carefully. Staying ahead of requirements saves you money, hassle, and stress.
Frequently Asked Questions about ARRT Renewal
Let’s tackle some of the most common questions that come up when you’re navigating your ARRT CE renewal.
Can I change my CE biennium dates?
Your CE biennium dates are set upon initial certification and are tied to your birth month. They remain the same even if you add new credentials. However, if your biennium timing creates persistent scheduling conflicts, ARRT allows you to Request to change the year of your CE biennium. You can only change the year, not the month, as it will always align with your birth month.
Do credits from earning a new certification count towards CE?
Earning a new ARRT certification itself does not fulfill your CE requirements. However, the structured education activities you completed to earn that credential can count toward your biennial CE. The activities must be Category A or A+ and completed during your current biennium. This is a great way to strategically use your professional development to meet multiple goals. If you’re thinking about expanding into a different modality, check out our guide on How to Use Continuing Education to Advance to a Different Modality Within Radiology for more insights.
Where can I find more help with my renewal?
Your ARRT online account is the best place for personalized information about your ARRT CE renewal, including your specific deadlines and CQR status. The ARRT website also has a comprehensive renewal resources section. For specific questions, you can call ARRT directly at 651.687.0048 and select the option for renewal, reinstatement, or continuing education.
We’ve also put together a comprehensive resource that covers many common questions. Check out our Most Frequently Asked Questions About CE Credits for Radiologic Technologists for practical answers.
Conclusion
You now have the information needed to manage your ARRT CE renewal without stress. By understanding your biennium, tracking deadlines, and finding approved courses, you can easily stay compliant.
The key to a smooth renewal is to stay organized, know your credit requirements, choose approved courses, and maintain compliance with ARRT’s ethical and regulatory standards. This turns renewal into a simple routine.
Continuing education is more than a requirement; it’s an opportunity to improve your skills, improve patient care, and keep your credentials valid.
At Scrubs CE, we make this process easier. We offer high-quality, self-paced courses designed to fit your busy schedule, meeting ARRT’s standards and providing instant certificates upon completion.
Ready to knock out your CE requirements? Explore our full catalog of ARRT-accepted Radiology CE Courses today and take the first step toward stress-free renewal.
California CE Requirements: Everything You Need to Stay Licensed
Why California CE Requirements Matter for Your License
California CE requirements vary by profession, but nearly all licensed healthcare providers must complete continuing education every two years to maintain an active license. Understanding your specific obligations is essential to avoid license suspension or renewal delays.
Quick Overview by Profession:
| Profession | CE Hours Required | Renewal Period | Key Mandatory Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| RN, APRN, LVN, PT | 30 contact hours | Every 2 years | Implicit bias (1 hr, one-time) |
| Pharmacist | 30 hours | Every 2 years | Law & Ethics webinars, Cultural competency |
| Dentist | 50 units | Every 2 years | Infection Control, Dental Practice Act, Opioid Prescribing, BLS |
| MD | 50 hours (AMA PRA Category 1) | Every 2 years | Pain management, DEA SUD training (8 hrs, one-time) |
| DO | 50 hours (20 AOA Category 1A/1B) | Every 2 years | Pain management, DEA SUD training (8 hrs, one-time) |
| Respiratory Care Practitioner | 30 hours | Every 2 years | Clinical Practice (15 hrs), RCP Leadership (10 hrs) |
| Optometrist (TPA-Certified) | 50 hours | Every 2 years | Ocular disease (35 hrs) |
| Veterinarian | 36 units | Every 2 years | Self-study limit: 6 units |
California’s CE landscape is complex, as each licensing board sets its own rules for required hours, mandatory topics, and approved providers. For example, nurses have a one-time implicit bias training requirement, while dentists must take specific courses on infection control and the Dental Practice Act. This guide breaks down the CE requirements for California’s major healthcare professions, helping you understand exactly what you need to do to stay licensed.
General CE Compliance: What Every California Healthcare Professional Should Know
While California CE requirements seem overwhelming, most follow a similar framework. Understanding these general rules will help you stay compliant, regardless of your license.
Most California healthcare licenses use a two-year renewal cycle, giving you 24 months to complete your required CE. The key is organization: track your courses, verify providers are approved by your board, and keep detailed records in case of an audit.
Record-keeping is critical. Save every certificate of completion. Most boards require you to retain this documentation for several years (e.g., four years for nurses and pharmacists, three renewal periods for dentists). Store them in a safe physical or digital folder. You don’t want to be scrambling for old emails during an audit.
California licensing boards conduct random compliance audits to verify CE completion. If selected, you’ll receive a notice to submit copies of your certificates. For nurses, Title 16, California Code of Regulations, Sections 1451(c) and (d) makes it clear all RNs are subject to audits. Failure to comply can result in fines or disciplinary action.
First-time renewals often come with exemptions. Many boards, including those for RNs and pharmacists, exempt newly licensed professionals from CE during their first renewal. Respiratory Care Practitioners have reduced requirements (15 hours instead of 30). However, these exemptions are not universal, so always verify with your specific board.
Exemptions or extensions may be available for circumstances like physical disability, prolonged illness, or caring for a disabled family member. Active-duty military personnel practicing outside California may also qualify for exemptions or military fee waivers.
Key Steps for Meeting California CE Requirements
- Verify Provider Approval: Before enrolling, confirm the provider is approved by your specific California licensing board. Many boards recognize national accreditors like ACCME, ACPE, or ANCC. Use the DCA License Search tool to check a provider’s status.
- Understand Course Formats: Boards have different rules for in-person, live online, and self-study courses. Live courses involve real-time instructor interaction (in-person or webinar), while self-study courses are pre-recorded or text-based.
- Check Self-Study Limits: Many professions limit the number of CE hours you can earn through self-study. For example, dentists cannot exceed 50% of their required units from non-live courses, and veterinarians are limited to six units.
- Certify, Don’t Submit: You typically don’t submit certificates with your renewal. Instead, you certify under penalty of perjury that you’ve completed the hours. This is why record-keeping is vital—you must be able to prove it if audited.
Specialized and Mandatory Training Topics
California requires training on several critical public health topics, often across multiple professions.
- Implicit Bias: A one-hour, one-time training is required for many healthcare professionals, per AB 1407. For RNs, this is required during the first renewal, even if otherwise exempt from CE.
- Ethics: Pharmacists must complete two hours of mandatory law and ethics webinars issued directly by the Board of Pharmacy.
- Pain Management: Physicians (MDs and DOs) have a one-time requirement covering pain management, end-of-life care, and the addiction risks of Schedule II controlled substances.
- Cultural Competency: Pharmacists and pharmacy technicians must complete one hour of CE on cultural competency, addressing health disparities and care for diverse populations.
- Opioid Prescribing: Dentists must complete a two-unit course on prescribing Schedule II opioids to address the opioid crisis.
California CE Requirements for Medical and Healthcare Professionals
Now that we’ve covered the general rules, let’s get specific. California CE requirements vary significantly by license type.
Nursing (RN, APRN, LVN, PT)
Nurses (RN, APRN, LVN, PT) must complete 30 contact hours every two years. Keep your CE certificates for four years for potential audits.
- First Renewal: You are exempt from the 30-hour requirement if it’s your first renewal within two years of passing your licensing exam.
- Implicit Bias: A one-time, one-hour implicit bias training is mandatory for all, even first-time renewers, per
[AB 1407](https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billNavClient.xhtml?bill_id=202120220AB1407). - NPs and Gerontology: Starting Jan 1, 2025, NPs whose patient base is at least 25% seniors (65+) must ensure 20% of their CE (6 hours) is in gerontology or dementia care.
- Prescriptive Authority: NPs need 3 hours on Schedule II controlled substances. Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs) need 2 hours covering neonatal abstinence syndrome.
- DEA Requirement: All DEA-registered practitioners must complete a one-time 8-hour course on substance use disorders (SUDs).
- Licensed Midwives (LMs): Require 36 contact hours every two years.
For the latest, visit the [Continuing Education for License Renewal](https://www.rn.ca.gov/licensees/ce-renewal.shtml) page from the [California Board of Registered Nursing](https://www.rn.ca.gov).
Physicians (MD & DO)
Physicians must complete 50 hours of CE every two years.
- MDs: Require 50 hours of AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™ from ACCME-accredited providers.
- DOs: Require 50 hours, with at least 20 hours of AOA Category 1A or 1B credit.
- Pain Management: A one-time 12-hour training in pain management and end-of-life care is required within four years of licensure or by the second renewal.
- Geriatric Care: General internists and family physicians with a patient base of 25% or more seniors (65+) must complete 20% of their CME (10 hours) in geriatric medicine or dementia care.
- DEA Requirement: A one-time 8-hour training on SUDs is required for all DEA-registered practitioners.
- Radiology/Fluoroscopy Permits: Holders of these permits have additional, specific CE requirements.
Check the [MD License Renewal Instructions](https://www.mbc.ca.gov/Licensees/License_Renewal/Physicians_and_Surgeons.aspx) for current information.
Dentists and Dental Auxiliaries (RDA, RDH)
CE requirements are for a two-year renewal period. Keep records for three renewal periods.
- Dentists: 50 CE units.
- RDA, RDH, and other auxiliaries: 25 CE units.
Mandatory Courses for All:
- Infection Control: 2 units, board-approved.
- Dental Practice Act: 2 units, board-approved (includes ethics).
- Basic Life Support (BLS): Must include a live, in-person skills session. Max 4 units.
- Opioid Prescribing (Dentists only): 2 units on prescribing Schedule II opioids.
Limitations:
- No more than 50% of total CE can be from non-live courses (correspondence/self-study).
- No more than 20% of total CE can be for practice management or business-related topics.
Visit the [Dental Board of California CE Info](https://dbc.ca.gov/licensees/continuing_education.shtml) for details.
Pharmacists and Pharmacy Technicians
Pharmacists and technicians must complete CE every two years and retain certificates for four years.
- Pharmacists: 30 hours.
- Advanced Practice Pharmacists (APh): 40 hours (10 must be relevant to clinical practice).
- First Renewal: Exempt from CE requirements.
Mandatory Topics:
- Law & Ethics: Two hours must come from mandatory Board-issued webinars.
- Cultural Competency: One hour is required for all renewals after Jan 1, 2024.
CE must be from providers recognized by ACPE or CPhA. For full details, see the [Continuing Education Information - CA State Board of Pharmacy](https://pharmacy.ca.gov/licensees/personal/ce.shtml).
Respiratory Care Practitioners (RCPs)
As of January 1, 2024, RCPs need 30 hours of CE for renewal.
- Breakdown: 15 hours in clinical practice, 10 hours in RCP leadership, and 5 flexible hours.
- Live Requirement: At least 15 of the 30 hours must be from live courses (in-person or interactive online).
- First Renewal: Only 15 hours are required.
Find specifics on the [RCP Continuing Education](https://rcb.ca.gov/licensees/ce.shtml) page.
Radiologic and Imaging Professionals
California CE requirements for radiologic technology vary significantly based on the specific licenses and permits you hold. Your CE must be approved by the CDPH Radiologic Health Branch (RHB).
- X-Ray Technologists: See our guide on
[How to Maintain Your X-Ray License in California](https://scrubsce.com/how-to-maintain-your-x-ray-license-in-california/). - Fluoroscopy Permit Holders: Learn more in our article on
[California Fluoroscopy License Renewal](https://scrubsce.com/california-fluoroscopy-license-renewal-how-to-maintain-your-fluoroscopy-permit-in-the-state-of-california/). - Nuclear Medicine Technologists: We answer your questions here:
[What are Continuing Education Requirements for Certified Nuclear Medicine Technologists in the State of California?](https://scrubsce.com/what-are-continuing-education-requirements-for-certified-nuclear-medicine-technologists-in-the-state-of-california/). - Multiple Permits: Our
[California Combos](https://scrubsce.com/california-combos/)page helps clarify overlapping requirements.
CE Requirements for Other Healthcare-Related Professions
California’s CE rules extend to a diverse range of professions, including those who care for animals and help people see clearly.
Veterinarians and RVTs
Veterinarians and Registered Veterinary Technicians (RVTs) must complete CE for each renewal cycle.
- Veterinarians: 36 units required.
- RVTs: 20 units required.
There are limits on self-study (any learning without a live instructor): six units for veterinarians and four units for RVTs. A unique option allows veterinarians to earn CE credit for providing [pro bono spay/neuter services](http://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/codes_displaySection.xhtml?sectionNum=4846.5.&lawCode=BPC) at qualified shelters, a great way to fulfill requirements while supporting animal welfare.
Optometrists
For optometrists, California CE requirements depend on your certification level.
- TPA-Certified: 50 hours every two years, with 35 hours focused on ocular disease.
- Non-TPA Licensed: 40 hours every two years.
- Glaucoma Certification: Requires 10 hours of glaucoma-specific CE, which counts toward the 35-hour ocular disease requirement.
Up to 25 hours can be completed through self-study or correspondence courses. New licensees may be exempt for their first renewal if licensed within one year of graduation. For a complete breakdown, consult the [Optometrist CE Fact Sheet](https://www.optometry.ca.gov/formspubs/ce-fact-sheet.pdf).
Frequently Asked Questions about California CE
Navigating California CE requirements can be tricky. Here are answers to some common questions.
What happens if I am audited for CE compliance?
First, don’t panic. An audit is a routine spot-check, not a punishment. Your licensing board will send a notification by mail with instructions and a deadline. You will be asked to submit copies of your CE certificates proving you completed the required hours.
This is why record retention is crucial. You must be able to produce documentation for the required period (e.g., four years for nurses per [Title 16, California Code of Regulations, Sections 1451(c) and (d)](https://govt.westlaw.com/calregs/Document/IF63826D34C8111EC89E5000D3A7C4BC3?viewType=FullText&originationContext=documenttoc&transitionType=CategoryPageItem&contextData=(sc.Default)), and three renewal periods for dental professionals). Failure to provide proof can lead to fines, probation, or license suspension. If you’ve kept organized records, an audit is a simple process.
Are there exemptions for first-time license renewals?
Yes, but it varies significantly by profession. You cannot assume you are exempt.
- Registered Nurses are generally exempt from the 30-hour requirement for their first renewal but must still complete the one-hour implicit bias training.
- Pharmacists are fully exempt from CE during their first renewal period.
- Respiratory Care Practitioners have a reduced requirement of 15 hours instead of 30.
- Optometrists licensed within one year of graduation are exempt for their first renewal.
The golden rule: Always check directly with your specific licensing board to confirm your eligibility for any exemption.
Can I use courses from other states for my California CE requirements?
Often, yes. Many California boards accept courses from nationally recognized accrediting bodies, making it easier for those licensed in multiple states. For example:
- Physicians: The Medical Board accepts courses awarding AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™.
- Nurses: Courses approved by the ANCC are generally accepted.
- Pharmacists: Courses from ACPE-accredited providers are accepted.
However, be aware of California-specific requirements. For instance, the California Board of Pharmacy requires pharmacists to complete Board-issued law and ethics webinars that cannot be substituted. Some boards, like the Dental Board, may allow you to petition for credit for an unapproved course by submitting detailed documentation.
The best approach is to verify before you enroll. Check your board’s website or contact them directly to ensure a course and provider are accepted for your California license renewal.
Conclusion: Simplify Your California CE Compliance
Keeping up with California CE requirements is complex, with varying hours, mandatory topics, and board-specific rules. Compliance is your responsibility.
Proactive planning is the key to avoiding stress. Know your renewal date, identify your specific requirements, and choose courses from board-approved providers. Most importantly, keep every certificate in a safe, organized place. Future-you will be grateful if an audit notice arrives.
We created Scrubs CE to simplify this process. Our online continuing education courses are convenient, affordable, and designed to meet the specific requirements of California licensing boards. With a self-paced format and instant certificates, you can learn on your schedule and get the proof of completion you need without delay.
Your commitment to ongoing learning is an investment in your career and in better patient care. By staying informed and planning ahead, you can meet your obligations with confidence.
Ready to tackle your CE requirements? [Explore our X-Ray CEU courses to meet your California requirements](https://scrubsce.com/category/x-ray-ceu/) and see how straightforward continuing education can be.
See Clearly: A Comprehensive Look at Modern Breast Imaging Techniques
Why Advanced Breast Imaging Matters More Than Ever
Advanced breast imaging refers to diagnostic techniques that go beyond standard 2D mammography to improve breast cancer detection, particularly for women with dense breast tissue or high cancer risk. These methods include 3D mammography (tomosynthesis), breast MRI, molecular breast imaging (MBI), and emerging technologies like contrast-improved mammography.
Key Advanced Breast Imaging Techniques:
- Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (3D Mammography): Creates layered images to reduce tissue overlap, improving cancer detection and reducing false-positive callbacks by 15-40%.
- Breast MRI: Uses magnetic fields and contrast agents for 90-100% sensitivity, especially valuable for high-risk women.
- Molecular Breast Imaging (MBI): Detects cancer cell activity using radioactive tracers, finding 3x more cancers when combined with mammography in women with dense breasts.
- Contrast-Improved Mammography (CEM): Highlights abnormal blood flow patterns using iodine contrast, offering a faster, less expensive alternative to MRI.
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer among women, with over 287,000 new cases expected annually in the U.S. While traditional 2D mammography has been the standard since the 1970s, its sensitivity drops from 87% in fatty breasts to just 63% in dense breasts—a condition affecting about 50% of women.
This detection gap spurred the development of advanced imaging. These newer methods find more cancers earlier, reduce unnecessary biopsies, and guide more precise treatment. For healthcare professionals, understanding these techniques is essential for providing optimal care and staying current with evolving standards. The shift toward personalized, risk-based screening means that one-size-fits-all mammography is becoming a thing of the past, requiring knowledge of multiple modalities.
Beyond the Standard View: Why Traditional Mammography Isn’t Always Enough
While traditional 2D mammography has saved countless lives, its limitations drive the need for advanced breast imaging.
The biggest challenge is dense breast tissue, which affects about half of all women. On a mammogram, both dense tissue and cancer appear white, making it difficult for radiologists to distinguish between them. This is like trying to spot a white golf ball in snow. As a result, mammography’s cancer detection rate drops from 87% in fatty breasts to as low as 50-63% in very dense breasts. You can learn more about how dense breast tissue affects mammography results and its screening implications.
Another issue is tissue overlap. A standard 2D mammogram is a single, flat image where normal breast structures can stack up, creating confusing shadows or hiding cancers. This leads to two frustrating outcomes:
- False-positives: When a mammogram looks suspicious but is ultimately normal. Between 5% and 15% of screened women are called back for more tests, causing anxiety and contributing to the roughly $4 billion spent annually on false-positive follow-ups.
- False-negatives: The more worrisome outcome, where cancer is present but the mammogram appears normal. This is more common in women with dense breasts, allowing a tumor to grow undetected.
These limitations underscore why continuing education is critical. Healthcare professionals must stay current with mammography CE courses to understand when to use advanced techniques. Fortunately, new tools are available to address these challenges.
A Clearer Picture: Key Advanced Breast Imaging Modalities
When traditional mammography is inconclusive, advanced breast imaging provides a clearer picture. These sophisticated techniques improve cancer detection rates, especially in dense breast tissue, and reduce false positives. They enable a move away from a one-size-fits-all approach toward supplemental screening custom to each patient’s risk profile.
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (3D Mammography): The New Standard in Advanced Breast Imaging
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), or 3D mammography, overcomes the primary limitation of 2D mammography: tissue overlap.
How it works: The X-ray tube moves in an arc over the breast, capturing multiple low-dose images from different angles. A computer reconstructs these into a series of thin image “slices,” each about 1mm thick. Radiologists can scroll through these layers, effectively “seeing through” the breast tissue to spot abnormalities that might otherwise be hidden.
Benefits: DBT improves cancer detection for women of all breast densities and is particularly effective for finding invasive cancers in dense breasts. It also reduces callbacks by 15-40% compared to 2D mammography, meaning less anxiety and fewer unnecessary follow-up appointments for patients.
Radiation dose: The radiation from DBT is slightly higher than a 2D mammogram but remains well within FDA safety limits. The significant improvement in detection is widely considered a favorable trade-off. As DBT becomes more common, healthcare professionals can deepen their expertise through comprehensive Mammography CE Courses.
Breast MRI: High-Sensitivity Detection for Specific Patient Groups
Instead of X-rays, Breast MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images.
How it works: A contrast agent (gadolinium) is injected into a vein. Cancerous areas, which have increased blood flow, absorb the agent and “light up” on the images. This gives MRI an impressive sensitivity rate of 90-100%, regardless of breast density.
Best uses: This high sensitivity makes MRI the gold standard for screening high-risk women, such as those with a lifetime risk over 20% or BRCA gene mutations. It is also invaluable for:
- Staging known cancer: Determining tumor size and detecting additional cancer sites in the same or opposite breast.
- Guiding treatment: MRI findings influence treatment plans for about 25% of patients, helping to refine surgical approaches or identify candidates for pre-surgical chemotherapy.
Limitations: Breast MRI is expensive, less accessible than mammography, and can have higher false-positive rates that lead to more biopsies. The procedure also requires patients to lie still in a narrow tube for 30-45 minutes. Patients can find more info on breast MRI to understand what to expect.
Molecular Breast Imaging (MBI): A Functional Approach to Detection
MBI focuses on cell function rather than anatomy.
How it works: A small amount of a radioactive tracer is injected, which is absorbed more by active cancer cells. A special gamma camera detects the tracer, creating images that highlight areas of high metabolic activity. Because it focuses on cell activity, breast density does not interfere with its effectiveness.
Benefits: For women with dense breasts, adding MBI to mammography finds three times more cancers than mammography alone. It also has a lower false-positive rate than mammography, reducing unnecessary callbacks and biopsies.
Role: MBI is used as a supplementary test alongside mammography for women with dense breasts. Its radiation dose is comparable to a mammogram and is FDA-approved. As its use grows, it offers a powerful tool for a historically underserved patient group. For more details, see a closer look at molecular breast imaging.
The Future is Now: Emerging and Experimental Techniques
The field of advanced breast imaging is constantly evolving, with researchers exploring new ways to detect cancer earlier and more accurately. These emerging technologies promise to overcome current limitations and improve patient comfort.
Promising Technologies on the Horizon
Several innovative technologies are showing promise in clinical research:
- Contrast-Improved Mammography (CEM): Uses an iodine-based contrast dye to highlight areas of increased blood flow, a common sign of cancer. CEM offers MRI-like information at a lower cost and in less time, making it a promising alternative for diagnostic workups and screening women with dense breasts.
- Ultrasound Elastography: Measures tissue stiffness, as cancerous tumors are typically firmer than benign tissue. This technique can help distinguish between concerning and harmless lesions, potentially reducing unnecessary biopsies.
- Optical Imaging: Uses light instead of radiation to detect abnormalities. By measuring how different tissues absorb and reflect light, this experimental method offers a radiation-free and compression-free approach.
- Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT): Measures differences in how cancer cells and normal cells conduct electricity. Using small electrical currents, EIT creates a map of conductivity without radiation or compression.
These cutting-edge tools are not yet routine but are moving closer to clinical practice. You can learn more about them from the American Cancer Society’s overview of Newer and Experimental Breast Imaging Tests.
The Role of AI in Advanced Breast Imaging
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming an invaluable partner for radiologists. AI algorithms, trained on millions of images, excel at AI-assisted analysis by flagging suspicious areas that the human eye might miss.
Key applications include:
- Automated tumor segmentation: AI can instantly and precisely outline a tumor’s borders on 3D images like MRI, which is crucial for accurate measurement and monitoring treatment response.
- Improved diagnostic accuracy: By providing a “second opinion,” AI can help reduce false positives and catch subtle cancers, improving overall accuracy without replacing the radiologist’s judgment.
- Reduced workload: AI can triage cases and handle routine analysis, freeing radiologists to focus on complex cases. This is especially helpful in facilities facing staff shortages.
As AI tools evolve, staying current is essential. For those looking to sharpen their interpretation skills, our Breast Imaging Case Review Series offers practical learning from real clinical scenarios. The future lies in combining these innovations for a more comprehensive, patient-centered approach to breast cancer detection.
Clinical Application: Integrating Advanced Imaging into Practice
Knowing about advanced breast imaging technologies is one thing; applying them strategically is another. The goal is to create a personalized screening and treatment roadmap for each patient based on their unique risk factors, breast density, and clinical situation. This approach improves early detection, guides surgical decisions, and helps monitor treatment efficacy.
| Factor | Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) | Breast MRI | Molecular Breast Imaging (MBI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best Use Case | General screening, especially with dense breasts; Diagnostic follow-up | High-risk screening; Staging known cancer; Evaluating treatment response | Supplemental screening for dense breasts (adjunct to mammography) |
| Dense Breast Efficacy | Significantly improved detection, reduced callbacks | Very high sensitivity (90-100%) | Very high sensitivity, density has minimal effect, finds 3x more cancers with mammography |
| Radiation | Slightly higher than 2D mammography, but within safe limits | None (uses magnetic fields and radio waves) | Low-dose radioactive tracer, comparable to mammogram |
| Cost/Access | Becoming more widely available, often covered by insurance | Higher cost, less accessible, can be resource-intensive | Moderate cost, growing availability, often supplementary |
Choosing the Right Test: Factors and Recommendations
Selecting the appropriate imaging test requires considering several factors:
- Patient risk factors: A woman with a lifetime breast cancer risk over 20% (e.g., due to BRCA mutations or strong family history) requires a different strategy than an average-risk woman. For high-risk patients, breast MRI is an essential screening tool.
- Breast density: With breast density notification laws, more patients are aware of their tissue type. For those with dense breasts, supplemental screening with DBT or MBI is crucial for seeing through tissue that can hide cancers.
- Cost and accessibility: Practical realities like insurance coverage and technology availability influence decisions. MRI is expensive and less accessible, while DBT is becoming more common. These factors must be steerd with the patient.
- Radiation exposure: Though doses from DBT and MBI are low and within FDA safety limits, cumulative exposure is a consideration. Clinicians use tools like the ACR Appropriateness Criteria® to make evidence-based choices for specific scenarios, such as ACR Appropriateness Criteria® for DCIS.
Guiding Treatment and Improving Outcomes
After a cancer diagnosis, advanced breast imaging becomes even more critical for planning and monitoring treatment.
- Pre-operative staging: Breast MRI is the go-to tool for understanding the true extent of the disease. It accurately measures tumor size, detects multiple tumors, and checks the opposite breast, which is essential for planning the right surgery.
- Supporting breast conservation: For patients opting for a lumpectomy, MRI’s detailed mapping helps surgeons remove all cancerous tissue while preserving healthy breast. MRI findings alter surgical plans for about 25% of patients, ensuring a more custom approach.
- Assessing treatment response: When chemotherapy is given before surgery (neoadjuvant therapy), breast MRI is the most accurate method for monitoring if the tumor is shrinking. This allows for treatment adjustments and informs the surgical plan.
- Post-treatment surveillance: Advanced imaging remains important for follow-up, especially for patients with dense breasts or complex surgical changes.
By personalizing care, advanced imaging leads to better outcomes. Staying current with these practices is essential, and continuing education covers key topics to keep you at the forefront. You can explore 7 Topics You Will Cover in Mammography Continuing Education.
Conclusion
We’ve come a long way together on this journey through breast cancer detection. What started as a single X-ray view has blossomed into a sophisticated array of tools that help us see what we couldn’t see before. This shift toward advanced breast imaging isn’t just about better technology—it’s about better care for every patient who walks through your imaging suite door.
Think about where we started: traditional 2D mammography, a workhorse that has served us well but struggles with dense breast tissue. Then we explored Digital Breast Tomosynthesis, which slices through tissue overlap like flipping through the pages of a book. We finded how Breast MRI brings best sensitivity for our high-risk patients, catching cancers that might slip past other methods. Molecular Breast Imaging showed us how looking at cell activity rather than just structure can reveal hidden cancers in dense breasts. And we glimpsed tomorrow’s possibilities—Contrast-Improved Mammography, Ultrasound Elastography, and AI-assisted analysis—all working to make detection earlier, more accurate, and more comfortable for patients.
Here’s what matters most: early and accurate detection saves lives. These advanced techniques aren’t just impressive technology. They help you find cancers sooner, spare patients from unnecessary callbacks and biopsies, and guide surgeons toward more precise treatment plans. Every improvement in detection means someone’s mother, sister, or friend gets a better chance at beating this disease.
But here’s the thing—technology only works when the people using it understand it deeply. The field changes fast. What was cutting-edge five years ago is now standard practice. What’s experimental today might be routine tomorrow. That’s why your commitment to learning isn’t just about checking boxes for licensure. It’s about being the kind of professional who can confidently guide patients through their options and use these powerful tools to their fullest potential.
At Scrubs CE, we get it. You’re busy. You need education that fits your schedule and actually teaches you what you need to know. That’s why we’ve built courses that are self-paced, practical, and focused on real-world application. We want you to finish a course and think, “I can use this tomorrow.”
Ready to deepen your expertise in this dynamic field? Explore our comprehensive Mammography CEUs and find courses designed specifically for professionals who care about staying current. Your dedication to learning directly translates to better outcomes for your patients—and that’s what this is all about. Let’s keep learning together, because every image you interpret could be the one that changes someone’s life.
Is a Florida Radiologic Technologist License Required? All You Need to Know
Why Florida Radiologic Technologist License Matters for Your Career
Radiologic technologist license florida is a mandatory requirement to legally practice in the state. If you want to work with ionizing radiation on patients in Florida, you must hold an active certificate issued by the Florida Department of Health—regardless of whether you have ARRT or NMTCB credentials.
Quick Answer: Do You Need a Florida License?
Yes. Florida law requires all radiologic technologists to obtain state certification before administering ionizing radiation to humans. Here’s what you need to know:
- Mandatory Certification: Florida Statute 468.302(1) requires certification unless you qualify for specific exemptions
- Six Certification Types Available: From Basic X-Ray Machine Operator to Radiologist Assistant
- Two Pathways to License: By examination (new applicants) or endorsement (out-of-state practitioners)
- General Requirements: Be 18+, have good moral character, hold a high school diploma/GED, and pass a background check
- Renewal Requirements: 12 CE hours every 2 years plus a one-hour HIV/AIDS course
- Strong Job Market: Nearly 27,000 certified imaging professionals work in Florida with average salaries around $71,000
Florida has one of the largest populations of certified radiologic technologists in the United States. With projected 4% job growth through 2032 and approximately 7,342 total openings expected throughout the decade, the career outlook remains strong.
The state’s licensing process is overseen by the Florida Department of Health’s Medical Quality Assurance Services, which works to ensure all practitioners meet minimum requirements for safe practice with radiation-emitting equipment.
Whether you’re a recent graduate looking to start your career or an experienced technologist relocating to Florida, understanding the state’s specific certification requirements is your first step toward a rewarding healthcare career.
Florida Radiologic Technology Certifications and Requirements
Understanding your certification options is the first step toward working as a radiologic technologist in Florida’s thriving healthcare landscape. The state offers multiple pathways depending on your career goals, from basic x-ray operation to advanced specialties like nuclear medicine and radiation therapy.
Whether you’re just starting your healthcare journey or looking to expand your scope of practice, knowing which radiologic technologist license florida certification fits your goals will help you chart the right educational path. Let’s explore what Florida requires and which certification type might be right for you.
Types of Radiologic Technology Certifications
Florida recognizes six distinct radiologic technology certifications, each designed for different roles and responsibilities in medical imaging. Your choice will determine your scope of practice, work environment, and educational requirements.
The Basic X-Ray Machine Operator certification is the most accessible entry point. If you’re working in a physician’s office, podiatrist’s office, or urgent care center performing routine skeletal x-rays, this limited certification might be all you need. It requires less extensive training than other certifications but also restricts where and what you can image.
General Radiographer certification is the most common and versatile option. This is your go-to if you want to work in hospitals, imaging centers, or outpatient facilities performing a wide range of diagnostic x-ray procedures. General radiographers have the broadest scope of practice and the most career flexibility.
For specialized fields, Florida offers three advanced certifications. Nuclear Medicine Technologists work with radioactive materials to create diagnostic images and deliver targeted treatments. Radiation Therapy Technologists operate linear accelerators and other equipment to deliver precise radiation treatments to cancer patients. Both specialties require additional education beyond general radiography and offer higher earning potential.
The Radiologist Assistant certification represents the highest level of practice. These professionals work directly with radiologists, performing advanced procedures like fluoroscopy and assisting with interventional radiology. This certification requires significant additional education and clinical experience.
Finally, Florida also recognizes specialty certifications in areas like computed tomography (CT), mammography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and cardiovascular-interventional technology. These typically require you to first hold general radiography certification, then complete additional specialized training.
You can find more info about certification options on the Scrubs CE website, including detailed comparisons of each pathway.
General Requirements for a Radiologic Technologist License in Florida
Before you can apply for any radiologic technologist license florida, you’ll need to meet several foundational requirements that apply across all certification types. These ensure you have the basic qualifications and background to work safely with ionizing radiation.
First, you must be at least 18 years old. Florida takes this seriously because radiologic technology involves significant responsibility for patient safety and radiation protection.
You’ll need to demonstrate good moral character, which Florida evaluates through a comprehensive background screening process. This includes fingerprinting and a criminal background check as outlined in Florida Statute 435. Certain criminal convictions may disqualify you from licensure, though the Department of Health reviews each case individually.
A high school diploma or GED equivalent is mandatory for all certification types. You’ll need to provide official documentation of your education when you submit your application to the Florida Department of Health.
Beyond these universal requirements, you’ll need to complete the specific educational and examination requirements for your chosen certification type. The application process itself involves submitting detailed documentation, paying the required fees, and waiting for the Department of Health to review and approve your credentials.
The state takes these requirements seriously because radiologic technologists work with potentially harmful ionizing radiation. Every requirement exists to protect both you and your future patients.
Educational and Training Program Requirements
Your educational pathway depends entirely on which certification you’re pursuing. Florida doesn’t take a one-size-fits-all approach—different roles require different levels of preparation.
For General Radiographer certification, you’ll need to complete a formal educational program accredited by the Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology (JRCERT). These programs typically result in an Associate of Applied Science (AAS) degree and take about two years to complete. They combine classroom instruction in anatomy, radiation physics, patient positioning, and radiation safety with extensive hands-on clinical experience in real healthcare settings.
The clinical component is crucial. You’ll spend hundreds of hours working under supervision in hospitals and imaging centers, learning to position patients correctly, operate complex equipment safely, and produce diagnostic-quality images. This practical experience ensures you’re job-ready when you graduate and prepared for the national certification exam.
Basic X-Ray Machine Operator certification follows a different path. This more limited certification requires completion of a Florida Department of Health-approved training program specific to basic x-ray operation. These programs are shorter than full radiography programs but still cover essential topics like radiation safety, basic positioning, and equipment operation within the limited scope of practice.
For advanced specialties like Nuclear Medicine and Radiation Therapy, you’ll typically need a bachelor’s degree from a program accredited by the appropriate national accrediting body. These programs build on foundational radiologic sciences with specialized coursework in radiopharmaceuticals, treatment planning, or advanced imaging modalities.
Radiologist Assistant programs require the most extensive education—usually a bachelor’s or master’s degree with advanced clinical training. You’ll need to already be a certified radiographer before entering these programs.
All programs include rigorous clinical training requirements to ensure you develop both technical competence and professional patient care skills. You can find accredited programs in Florida through the Florida Department of Health’s resource page.
Choosing the right educational program is one of the most important decisions you’ll make. Look for programs with strong clinical partnerships, experienced faculty, and high exam pass rates. Your education sets the foundation for your entire career in radiologic technology.
Florida Radiologic Technology Certifications and Requirements
Understanding your path to a radiologic technologist license florida requires familiarity with the certification landscape in the Sunshine State. Florida offers multiple certification options, each designed for specific career paths and responsibilities within medical imaging. The Florida Department of Health oversees these certifications to protect patients and maintain professional standards across the field.
Before you begin your application, you’ll want to know exactly which certification matches your career goals. Whether you’re planning to work in a busy hospital emergency department, a specialized cancer treatment center, or a small outpatient clinic, there’s a specific certification that fits your aspirations.
Types of Radiologic Technology Certifications
Florida recognizes six distinct types of radiologic technology certifications, each with its own scope of practice and educational pathway. Choosing the right one now can save you time and help you build the career you actually want. If you’re still exploring your options, we have more info about certification options to help you decide.
The Basic X-Ray Machine Operator certification is the entry point for many technologists. This certification allows you to perform basic radiographic procedures in physician offices, chiropractic clinics, or podiatry practices. You’ll complete a shorter training program—typically 80-120 hours—and your scope of practice focuses on extremity imaging and chest x-rays. It’s a great starting point if you want to enter the field quickly.
The General Radiographer certification is what most people think of when they picture a radiologic technologist. This is the comprehensive credential that opens doors to hospital positions, imaging centers, and a wide range of healthcare settings. You’ll need to complete an accredited Associate of Applied Science (AAS) degree program, which typically takes two years and includes extensive clinical rotations. With this certification, you can perform the full spectrum of diagnostic x-ray procedures on all body parts.
Nuclear Medicine Technologists work with radioactive materials to create images that show how organs and tissues are functioning, not just what they look like. This specialty requires completion of a nuclear medicine technology program and prepares you for work in hospitals, cancer treatment centers, and specialized imaging facilities. You’ll administer radiopharmaceuticals and operate sophisticated gamma cameras.
Radiation Therapy Technologists are the professionals who deliver targeted radiation treatments to cancer patients. This certification requires specialized education in radiation therapy techniques, patient positioning, and treatment planning. It’s a deeply rewarding specialty where you’ll build ongoing relationships with patients throughout their treatment journey.
The Radiologist Assistant certification represents the advanced practice level in radiologic technology. These professionals work directly with radiologists to perform advanced imaging procedures, evaluate image quality, and in some cases, provide preliminary image interpretations. This certification requires additional education beyond the general radiographer level and typically involves a bachelor’s degree or higher.
Finally, specialty certifications in areas like Computed Tomography (CT) and Mammography allow you to expand your skills and marketability. These post-primary certifications build on your general radiographer license and typically require additional clinical experience and specialized training. CT technologists operate advanced cross-sectional imaging equipment, while mammography technologists specialize in breast imaging for cancer screening and diagnosis.
General Requirements for a Radiologic Technologist License in Florida
No matter which certification path you choose, Florida has baseline requirements that apply to all applicants. You must be at least 18 years old when you apply—this is non-negotiable and straightforward.
Good moral character is another universal requirement. Florida takes this seriously, and it’s evaluated primarily through your criminal background check. The state follows Florida Statute 435, which lists disqualifying offenses. Certain convictions can prevent you from obtaining licensure, though the Department of Health does consider factors like how long ago the offense occurred and evidence of rehabilitation.
You’ll need a high school diploma or GED equivalent. This is your foundation, and you’ll need to provide official documentation during your application. If you completed high school outside the United States, you may need to have your credentials evaluated by an approved agency.
The criminal background check is mandatory for all applicants. You’ll submit fingerprints through an approved vendor, and the Florida Department of Law Enforcement and FBI will review your history. This process typically takes 2-4 weeks, so plan accordingly when timing your application.
Educational and Training Program Requirements
Your educational pathway depends entirely on which certification you’re pursuing. For General Radiographer certification, you’ll need to complete a program accredited by the Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology (JRCERT). These programs are typically offered at community colleges and result in an Associate of Applied Science (AAS) degree.
JRCERT accreditation matters—it’s not just a formality. Accredited programs meet national standards for curriculum, clinical education, and student outcomes. Florida won’t accept your application if you graduated from a non-accredited program, so verify your program’s accreditation status before enrolling.
Your education will blend classroom learning with hands-on clinical experience. Expect to study anatomy, physiology, radiation physics, patient positioning, and radiation protection. The clinical component is where you’ll apply this knowledge in real healthcare settings, working with actual patients under supervision.
Basic X-Ray Machine Operator programs have less intensive requirements. These shorter training programs focus on fundamental radiographic techniques for limited anatomical areas. You won’t earn a degree, but you’ll complete the specific training hours required by Florida law.
For specialized certifications like Nuclear Medicine or Radiation Therapy, you’ll need to complete specialized educational programs specific to those disciplines. These programs often require a full bachelor’s degree and include both didactic coursework and extensive clinical training in your specialty area.
Clinical experience isn’t just a box to check—it’s where you’ll develop the practical skills and professional judgment that make you valuable to employers. Most programs require hundreds of clinical hours, and you’ll perform procedures on real patients while being evaluated by clinical instructors.
Ready to start your journey? You can find accredited programs in Florida through the Florida Department of Health’s resource page. Take time to research programs, visit campuses, and talk to current students before making your decision. Your education is an investment in your future, and choosing the right program makes all the difference.
Your Online Path to Mammography CE Credits
Why Mammography Technologists Need Continuing Education Credits
Mammography continuing education credits online are required for radiologic technologists to maintain their certification and licensure. The FDA’s Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) mandates 15 mammography-specific CE credits every 36 months, while the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT®) requires 24 total credits biennially.
Where to Find Online Mammography CE Credits:
- ASRT®-Approved Providers – Look for courses approved by the American Society of Radiologic Technologists
- AHRA®-Approved Providers – The American Healthcare Radiology Administrators also designates approved courses
- RCEEM Recognition – Ensure providers are recognized by an ARRT® Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism
- State-Specific Approval – Verify acceptance by your state licensing board (California, Texas, Florida have specific requirements)
- MQSA Compliance – Confirm courses count toward your 15 mammography-specific credits
As one technologist with 27 years of experience shared, “I learned about new modalities” that weren’t available when they first started. This reflects a common challenge: the field evolves rapidly with technologies like digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), making regular education essential.
The good news is that online courses offer a practical solution with immediate certificate generation, self-paced learning, and the ability to study from anywhere without travel or time off work. Most include downloadable materials, online testing, and instant access to completion certificates.
Whether you’re fulfilling MQSA requirements, preparing for ARRT® renewal, or meeting state mandates, mammography continuing education credits online provide a practical solution for busy healthcare professionals.
Understanding Mammography CE Requirements
Keeping track of continuing education requirements is a critical part of being a mammography technologist. These credits are not just red tape; they ensure you are sharp, current, and providing the best possible care. Staying up-to-date on the latest techniques gives you confidence that matters to anxious patients.
The Importance of Continuing Education
Breast imaging has changed dramatically, with digital mammography, 3D tomosynthesis, and artificial intelligence becoming standard. Failing to keep up means missing critical knowledge that directly impacts patient outcomes.
Staying current with advanced modalities means you can recognize subtle differences in image quality and understand the nuances of newer equipment. This is the difference between catching something early and missing it.
Improved patient outcomes happen when we combine technical skills with current knowledge. Better positioning techniques reduce callbacks, and understanding pathology helps us communicate more effectively with radiologists. Quality control knowledge ensures every image meets the highest standards.
Finally, maintaining credentials is non-negotiable. As we covered in our guide to Mammography Technologist License Renewal: What You Need to Know, letting your credits lapse can put your career on hold.
Decoding MQSA and ARRT® Mandates
You must track two main sets of requirements with different timelines, which can be confusing.
The Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) is the federal law governing mammography facilities. It requires you to complete 15 continuing education units specific to mammography every 36 months. A key detail is that you need at least 6 CEUs related to each modality you use, such as standard digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis.
The ARRT® biennial renewal works on a two-year timeline. For this, you need 24 total credits. These must be Category A or Category A+ credits, approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM) like the ASRT® or AHRA®.
The good news is your mammography-specific credits can usually count toward both requirements. If you earn 15 MQSA-compliant credits in a two-year period, those can also count toward your 24 ARRT® credits. You’d just need 9 more credits in any radiologic technology topic to complete your ARRT® requirement.
Every state has its own rules too, which is why we created our comprehensive guide on Mammography Continuing Education Requirements. California and Florida, for example, have additional state-specific mandates. The key is finding courses that clearly state their approvals for MQSA, ARRT® Category A, and specific state boards.
Finding Reputable Mammography Continuing Education Credits Online
When searching for mammography continuing education credits online, you’re investing in your career and patient well-being. It’s crucial to separate reliable providers from those that might cause issues at renewal time. Choosing a CE provider is like choosing a dependable colleague: you need someone qualified and trustworthy.
What to Look for in a High-Quality Online CE Provider
Approval by recognized accrediting bodies like the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT®) and the American Healthcare Radiology Administrators (AHRA®) is foundational. These ARRT®-designated organizations evaluate courses, and without their approval, your credits may not be accepted.
Equally important is ARRT® RCEEM recognition. The provider itself must be recognized by an ARRT® Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism, ensuring your courses will be accepted for ARRT® renewal. At ScrubsCE, all our courses are approved by an ARRT® RCEEM.
Practicality also matters. Look for clear pricing with flexible options like individual courses, package deals, or test-only options. Instant certificate generation is a game-changer; you should be able to download your certificate immediately after passing a post-test.
Responsive customer support is essential for any questions or technical issues. At ScrubsCE, we pride ourselves on being accessible. Also, look for positive reviews and testimonials from fellow technologists for valuable insights into course quality and platform ease-of-use.
A quality provider offers course variety covering digital mammography, DBT, quality control, and patient care. Finally, look for explicit guarantees of acceptance by state licensing boards, the ARRT®, and for MQSA compliance. At ScrubsCE, we guarantee that all our mammography continuing education credits online will be accepted by these bodies.
Verifying Course Acceptance
After finding a provider, you must verify that their courses will be accepted by your state board, the ARRT®, and for MQSA compliance.
State licensing boards are the first checkpoint. Some states, like Florida, require providers to be specifically approved and to report CE activities directly to the state. At ScrubsCE, we are a Florida-approved provider and handle this reporting for you. California requires that CE courses address the application of X-rays to the human body and be approved by an ARRT® credentialing body. All ScrubsCE courses meet these criteria.
For ARRT® acceptance, ensure the provider offers Category A or A+ credits through RCEEM recognition. This designation confirms the content meets ARRT® quality standards. We guarantee all CEUs you earn at ScrubsCE are approved by an ARRT® RCEEM.
MQSA compliance is non-negotiable. Your courses must meet the 15 mammography-specific CEU requirement every 36 months, with at least 6 CEUs for each modality you use. Many of our courses at ScrubsCE are designed to fulfill these critical requirements. A reputable provider makes all this information easy to find on their website.
Navigating Your Online CE Course Experience
Once you find a reputable provider, the online course experience is designed to be streamlined and user-friendly. Modern e-learning platforms eliminate barriers like rigid schedules and travel expenses, offering an experience that fits into your life.
Common Course Topics and Formats for Mammography Continuing Education Credits Online
Available courses reflect the real-world complexity and evolution of breast imaging. You’ll find courses covering digital mammography, from image acquisition to evaluation. Essential courses on digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) explain the theory, benefits, and challenges of this 3D imaging approach.
Understanding breast anatomy remains foundational, with courses diving deep into development, pathology, and hormonal influences. Quality control courses cover MQSA requirements, QC procedures, and initiatives like EQUIP. You’ll also find courses on breast biopsy targeting techniques and the importance of patient care and communication.
Beyond these, courses address emerging techniques like elastography and contrast-improved mammography. For more details, see our article on 7 Topics You Will Cover in Mammography Continuing Education.
Formats are designed to match your learning style, including e-books and downloadable transcripts, video lectures, and interactive modules with quizzes and exercises.
How Online Mammography CE Courses Typically Work
The process to earn your mammography continuing education credits online is wonderfully straightforward.
First, you’ll purchase your course, choosing from options like test-only or complete packages. You get immediate access to all materials through an online portal.
Next is self-paced learning. Study whenever and wherever works for you, on any device. Our courses remain available for 365 days from purchase, so there’s no pressure. Many courses, like Mammographic Imaging: A Practical Guide, allow you to download transcripts for offline work.
When you feel confident, you’ll take a multiple-choice post-test in the online testing center. A passing score (usually 80%) is required, but multiple attempts are typically allowed.
Upon passing, you get an immediate certificate download. No waiting for mail—just download, print, or save your certificate right away. This instant access is a lifesaver when approaching a deadline.
Maximizing the Benefits of Online Learning
Earning mammography continuing education credits online is a game-changer for professional development. It offers a smart, sustainable way to continue learning that fits your schedule and budget, going beyond simply meeting requirements.
Cost, Convenience, and Career Growth
Compared to traditional in-person seminars, online learning has striking benefits. It eliminates costs for travel, hotels, and meals, as well as the need to use vacation days or lose income from taking time off work. The money saved can be substantial.
Even more valuable is your time. Online courses offer the flexibility to learn around demanding schedules, shift work, and family commitments. You can log in whenever you want, pause as needed, and pick up where you left off.
To maximize savings, look for package deals. Our Mammography Package, for example, includes 26 credits across 8 courses at a significant discount. Some packages include comprehensive series like our Breast Imaging Case Review Series. If you already have study materials, a “test-only” option can save even more money.
The career benefits are real, too. Consistently updating your knowledge makes you more valuable to your employer and better positioned for advancement.
Meeting Specialized Requirements with Mammography Continuing Education Credits Online
Online courses are particularly effective for meeting specific, targeted requirements like Structured Education and the ARRT®’s Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR).
For initial mammography certification, the ARRT® requires 16 credits of Structured Education. Comprehensive online series are designed to fulfill this requirement by covering the prescribed curriculum in an organized way. Our Breast Imaging Essentials: The Series is built for this purpose.
For the CQR prescription, you receive a personalized list of topics needing additional education based on your assessment results. Online learning allows you to find courses that precisely match your prescribed content areas, rather than sitting through a broad conference. Many platforms offer tools to help you match courses to your CQR prescription, making the process efficient and stress-free.
By strategically choosing your mammography continuing education credits online, you’re not just maintaining credentials—you’re actively shaping your expertise in a way that respects your time and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions about Online Mammography CE
Here are answers to some of the most common questions about earning mammography continuing education credits online.
How many CE credits do I need for mammography?
You need to meet requirements from multiple bodies. The MQSA requires 15 mammography-specific CEUs every 36 months, with at least 6 CEUs related to each modality you use (e.g., digital mammography, DBT). For your ARRT® biennial renewal, you need 24 total CE credits. Your MQSA credits can count toward this total if they are Category A or A+. Always check your state licensing board for additional requirements, as states like Florida and California have specific rules. Our guide on Mammography Continuing Education Requirements covers these details.
Are online mammography CE credits accepted by the ARRT® and for MQSA?
Yes, absolutely, as long as the courses are approved by an ARRT® Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM). Organizations like the ASRT® and AHRA® serve as RCEEMs, evaluating courses to ensure they meet quality standards. At ScrubsCE, all our courses are approved by an ARRT® RCEEM, meaning they meet both ARRT® and MQSA standards. We also guarantee acceptance by state registries. Reputable providers will always clearly state their approvals.
How quickly can I get my certificate of completion?
With mammography continuing education credits online, the process is immediate. Once you complete the course materials and pass the post-test (usually with an 80% score), your certificate of completion is generated instantly. You can download, print, or save it right away. This instant access is a major benefit, especially when you’re approaching a renewal deadline and need proof of completion quickly. No more waiting for a certificate to arrive in the mail.
Your Next Step in Professional Development
Now it’s time to take action. Staying compliant with MQSA and ARRT® mandates is about committing to excellence in patient care. Earning your mammography continuing education credits online is the smartest, most efficient way to honor that commitment while respecting your schedule and budget.
Choosing an accredited provider like ScrubsCE gives you immediate access to a comprehensive library of courses designed for your real-world needs, whether you’re fulfilling MQSA, ARRT®, or specialized CQR requirements. The flexibility of online learning adapts to your life. Study when you can, take the test when you’re ready, and instantly download your certificate.
Every course you complete improves your skills, improves patient outcomes, and builds your confidence. Your professional development can be an empowering journey. Take control today and find how straightforward earning your mammography continuing education credits online can be.
Ready to take the next step in your career? Explore our full catalog of Mammography CE Courses and find the perfect fit for your continuing education needs.
The Nuclear Perfusion Scan: What It Is and Why It Matters
Why Understanding Nuclear Medicine Myocardial Perfusion Matters for Your Practice
Nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) is a key diagnostic tool that visualizes blood flow to the heart muscle using radioactive tracers. As one of the most common non-invasive techniques for managing coronary artery disease (CAD), understanding MPI is crucial for any healthcare professional.
Quick Answer: What is Nuclear Medicine Myocardial Perfusion?
- Function: Shows blood flow to the heart at rest and during stress.
- Method: Uses a small dose of a radioactive tracer absorbed by healthy heart tissue.
- Types: SPECT (Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography) and PET (Positron Emission Tomography).
- Uses: Diagnosing CAD, assessing heart attack damage, and guiding treatment.
- Accuracy: High sensitivity for detecting blockages (PET 92.6%; SPECT 88.3%).
- Safety: Low radiation exposure, with tracers cleared from the body in 1-2 days.
MPI plays a decisive role in diagnosis and risk stratification for CAD, the leading cause of death in the United States. The technique works by identifying “cold spots” on the scan, which are areas of reduced blood flow or damage. This allows physicians to distinguish reversible ischemia (a temporary blood flow shortage) from permanent damage (infarction).
What makes MPI particularly valuable is its prognostic power. Studies show that a normal scan is associated with an excellent prognosis—only a 0.6% annual risk of major adverse cardiovascular events. Conversely, abnormal scans predict a significant increase in risk, highlighting the test’s importance in guiding patient care, from medical therapy to revascularization procedures.
Understanding Myocardial Perfusion Imaging (MPI)
Myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI), often called a nuclear stress test, creates a detailed map of the heart’s blood flow. Its primary purpose is to identify areas of the heart muscle not receiving adequate blood supply, which is crucial for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD). The test distinguishes between myocardial ischemia (a temporary, reversible reduction in blood flow during stress) and myocardial infarction (permanent damage from a heart attack, seen as a defect at both rest and stress). MPI also helps assess myocardial viability, determining if weakened heart muscle is still alive and can recover with treatment, which guides decisions about interventions like bypass surgery or angioplasty.
The Main Types of MPI: SPECT vs. PET
Nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion imaging primarily uses two technologies: SPECT and PET.
SPECT (Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography) is the most widely available and cost-effective option. It uses a gamma camera to detect tracers like Technetium-99m (Tc-99m) or Thallium-201 to create a 3D picture of blood flow. Studies show SPECT has 88.3% sensitivity for detecting significant coronary artery blockages with 74% specificity, making it a reliable workhorse for cardiac imaging.
PET (Positron Emission Tomography) is a more advanced option with superior accuracy. It uses tracers like Rubidium-82 (Rb-82) or N-13 ammonia and offers several advantages. PET provides clearer images, especially in obese patients, and delivers a lower radiation dose. Its key benefit is the ability to provide quantitative measurements of myocardial blood flow (MBF) and coronary flow reserve (CFR). This data offers deeper insight into coronary function, as a low CFR is strongly linked to an increased risk of cardiac death. Meta-analyses confirm PET’s higher accuracy, with 92.6% sensitivity for detecting significant blockages. While more expensive and less available, PET is the superior technology for quantitative analysis and complex cases.
Why Your Doctor Might Order a Myocardial Perfusion Scan
Your provider might recommend a nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion scan for several key reasons:
- To investigate symptoms like unexplained chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or unusual fatigue that could indicate a heart problem.
- To follow up on abnormal EKG results, as an MPI can reveal if electrical issues are caused by poor blood flow.
- To diagnose coronary artery disease (CAD) by identifying narrowed or blocked arteries. You can explore scientific research on atherosclerosis to learn more about the underlying disease.
- To assess damage after a heart attack, determining the extent of scar tissue and identifying areas at risk.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of treatments like angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery.
- For pre-operative risk assessment before major non-cardiac surgery.
- To monitor known CAD, tracking disease progression to adjust treatment plans.
The Myocardial Perfusion Scan Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
A nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion scan is typically a two-part test comparing blood flow to your heart at rest and during stress. A small amount of a radioactive tracer is injected via an IV, and a special camera (SPECT or PET) tracks where the blood flows. Healthy areas light up, while areas with poor flow appear dim. The entire process takes a few hours but provides a comprehensive picture of your heart’s health.
How to Prepare for Your Scan
Proper preparation is vital for accurate results. Your healthcare team will provide specific instructions, which generally include:
- No caffeine for 24 hours before the scan. This includes coffee, tea, soda, and chocolate, as caffeine can interfere with stress medications.
- Fasting for 4-6 hours before your appointment (water is usually permitted).
- Medication adjustments. You may be asked to temporarily stop certain heart medications, like beta-blockers. Never stop medications without your doctor’s explicit instructions.
- Wear comfortable clothing and athletic shoes for the exercise portion of the test.
During the Scan: Rest vs. Stress
The procedure involves these main steps:
- IV Placement and Rest Scan: An IV line is placed in your arm. The first dose of tracer is injected, and after a waiting period (15-45 minutes), you’ll lie still while a camera takes the resting images.
- Stress Test: Next, your heart is stressed, either through exercise on a treadmill or with a pharmacological stress agent like Lexiscan (regadenoson) that mimics exercise. Your EKG and vital signs are monitored throughout.
- Stress Scan: At peak stress, a second dose of tracer is injected. You will then return to the camera for the second set of images. Comparing the rest and stress images allows doctors to identify areas of ischemia.
For professionals seeking to learn more, more info about Nuclear Medicine CE Courses can provide deeper insights into these protocols.
Potential Risks and Post-Scan Recovery
Nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion scans are very safe. The tracer itself rarely causes side effects. If a stress medication is used, you might feel temporary flushing or a mild headache, but these effects fade quickly.
The radiation exposure is low, comparable to a CT scan. The diagnostic benefit of identifying potentially life-threatening heart disease almost always outweighs this minimal risk.
Recovery is simple. You can resume normal activities immediately. Drinking plenty of fluids will help flush the tracer from your body over the next 24-48 hours. The test has an excellent safety profile, with millions performed worldwide each year.
Interpreting Scan Results and The Role of Nuclear Medicine Myocardial Perfusion
After the scan, a physician analyzes the images by comparing blood flow patterns at rest and during stress. The radioactive tracer highlights areas with good blood flow (“hot spots”), while areas with poor flow appear as “cold spots” or defects.
The key is the comparison between rest and stress images:
- Reversible defects indicate ischemia. A “cold spot” that appears during stress but looks normal at rest signifies a temporary blood flow shortage, typically due to a coronary artery blockage. This condition is often treatable.
- Fixed defects suggest infarction (scar tissue). A “cold spot” that is present on both rest and stress images indicates permanent heart muscle damage from a prior heart attack.
Cardiologists often use a Summed Stress Score (SSS) to quantify the extent and severity of perfusion defects. A higher SSS score correlates with a worse prognosis, making nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion a powerful tool for risk stratification.
What Abnormal Results Mean and Next Steps
An abnormal scan indicates that parts of your heart are not receiving enough blood, which is associated with a significantly higher risk of death or heart attack (11.8% vs. 3.3% for normal scans). However, these results provide a clear roadmap for treatment.
Based on the severity of the findings, next steps may include:
- Medical Therapy: For mild ischemia, lifestyle changes and medications are often the first line of treatment.
- Revascularization: For more significant ischemia, procedures may be recommended to restore blood flow. These include angioplasty and stenting to open narrowed arteries or coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) for more widespread disease.
Your doctor may also order a coronary angiogram for a more detailed look at the arteries. For more information on imaging standards, professionals can consult Guidance on SPECT Myocardial Perfusion Imaging from the IAEA.
Using MPI to Assess Treatment and Predict Outcomes
The value of nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion extends beyond initial diagnosis. It is used to evaluate the success of interventions like bypass surgery or stenting by confirming that blood flow has been restored. For patients with known CAD, periodic scans can monitor disease progression.
Most importantly, MPI has powerful prognostic value. A normal MPI scan is associated with an excellent prognosis, with a major adverse cardiovascular event rate of just 0.6% per year. This ability to predict outcomes allows clinicians to personalize care, applying aggressive treatment to high-risk patients while providing reassurance to those at low risk.
MPI vs. Other Cardiac Imaging Modalities
While nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion imaging is a cornerstone of cardiac diagnosis, it is part of a larger toolkit. Choosing the right test, or using a multimodality approach, depends on the specific clinical question.
Here’s a comparison of the major cardiac imaging modalities:
- SPECT/PET MPI: Excellent for assessing ischemia and viability. SPECT is widely available, while PET offers higher accuracy (92.6% sensitivity), quantitative blood flow data, and lower radiation. Their main role is functional assessment of blood flow.
- Cardiac MRI (CMR): Offers high accuracy (88% sensitivity, 90% specificity for perfusion) with the major advantage of zero radiation exposure. It provides comprehensive information on heart structure, function, and tissue characterization (e.g., scarring) in a single exam. It is an excellent choice for younger patients or when detailed anatomical and functional data is needed.
- CT Perfusion (CTP): When combined with coronary CT angiography (CCTA), this technique provides both anatomical detail of the arteries and functional perfusion data in one session (86% sensitivity, 92% specificity). This integrated approach is valuable for assessing the significance of a visible blockage, but it involves a moderate to high radiation dose and iodinated contrast.
- Myocardial Contrast Echocardiography (MCE): This ultrasound-based technique is portable, radiation-free, and cost-effective. It offers real-time imaging of perfusion and wall motion at the bedside, with good accuracy (83% sensitivity) and strong agreement with MPI (kappa 0.81). Its quality can be limited by patient body type and operator skill.
Limitations of Nuclear Medicine Myocardial Perfusion
Despite its strengths, MPI is not always the best choice. Key limitations and contraindications include:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Nuclear imaging is generally avoided. Stress echo or CMR are safer alternatives.
- Severe Respiratory Disease: Patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma or COPD may not be candidates for certain pharmacological stress agents.
- Acute Cardiac Emergencies: Stress testing is unsafe for patients with an ongoing heart attack or unstable angina.
- Obesity: Severe obesity can cause artifacts (especially with SPECT), potentially leading to false-positive results. PET or CMR may be preferred.
- Inadequate Stress: An inadequate exercise test may fail to reveal ischemia, potentially leading to a false-negative result.
- Balanced Ischemia: In rare cases of severe, multi-vessel disease, blood flow may be uniformly reduced, causing the scan to appear deceptively normal.
- Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB): This conduction abnormality can cause false-positive defects on exercise stress tests. Pharmacological stress is preferred.
Conclusion
Nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion imaging is a powerful diagnostic tool that provides clear, actionable answers about heart health. By visualizing blood flow at rest and under stress, MPI allows clinicians to diagnose coronary artery disease, distinguish treatable ischemia from permanent scar tissue, and assess a patient’s risk for future cardiac events. A normal scan offers powerful reassurance (a 0.6% annual event rate), while an abnormal scan provides a roadmap for life-saving interventions.
For healthcare professionals, mastering these imaging techniques is essential for providing the best patient care. As the field evolves with new tracers and improved cameras, staying current directly translates to better patient outcomes. Understanding the relative strengths of MPI, cardiac MRI, and CT perfusion enables more informed diagnostic strategies.
At ScrubsCE.com, we understand your commitment to excellence. Our convenient, self-paced online courses are designed to fit your busy schedule while delivering the in-depth knowledge you need. Dive deep into complex topics like nuclear medicine myocardial perfusion and earn your continuing education credits on your own time.
Ready to improve your expertise? Explore our comprehensive Nuclear Medicine CE courses and see how staying current can transform your practice.
Beyond the X-Ray: Navigating Radiology CE Courses for Career Advancement
Why Radiology Continuing Education Matters for Your Career
Radiology ce courses are accredited programs that help imaging professionals maintain ARRT® certification, meet state licensure requirements, and advance their careers. These courses cover specialized topics across modalities like X-ray, CT, MRI, and mammography.
Quick Guide to Radiology CE Courses:
- Purpose: Maintain ARRT® certification and state licensure while expanding clinical knowledge
- Requirements: Most technologists need 24 Category A credits per biennium (2-year period)
- Course Types: Modality-specific training (CT, MRI, Mammography), Structured Education (SE), Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR)
- Formats: Online courses, e-books, webinars, self-paced home study
- Accreditation: Look for ASRT-approved courses accepted by ARRT®, NMTCB, and ARDMS
- Cost: Options range from individual courses ($9.99+) to unlimited annual access plans ($49.99-$54.95)
- State-Specific: Some states like California, Florida, and Texas have additional requirements
The radiology field moves fast with new technologies, evolving protocols, and changing safety standards. Continuing education is more than a checkbox for licensure renewal—it’s your pathway to staying current, expanding your skills, and opening doors to specialized roles.
As one radiologic technologist shared: “I find that this is one of the best resources for obtaining CEU’s. I wish I would have found this site sooner.”
Whether fulfilling basic ARRT® requirements, transitioning to a new modality, or preparing for advanced certification, understanding your CE options helps you make strategic choices for both compliance and career growth.
Why Radiology CE is Essential for Your Career
While continuing education might seem like just another requirement, radiology ce courses are your ticket to staying relevant, growing your career, and delivering the best possible patient care. The radiology field doesn’t stand still; new protocols, equipment, and safety standards emerge constantly. Keeping pace is essential.
Compliance is straightforward: You need CE credits to maintain your ARRT® certification and state license. Most technologists need 24 credits per biennium (a two-year cycle), plus any state-specific requirements. It’s non-negotiable, but it doesn’t have to be a burden. Our article on The Importance of Continuing Education (CE) for X-Ray Technologists details how to stay compliant.
The real value of CE goes beyond credentials. Taking courses that interest you sharpens skills for your daily work, from new techniques and equipment knowledge to updated radiation safety protocols. This directly translates into better patient care: more accurate positioning, clearer images, and safer procedures.
Career advancement is another major benefit. The radiology field offers incredible opportunities to specialize. Strategic CE choices can help you transition into new modalities like MRI or CT, opening doors to different roles, increasing your earning potential, and making you more valuable to employers. If you’re exploring new specialties, check out How to Use Continuing Education to Advance to a Different Modality within Radiology.
Every course is an investment in yourself—you’re building expertise and staying current with technology. For a comprehensive look at the benefits, our guide 7 Ways Radiology CE Can Benefit You as a Radiologic Technologist covers everything from confidence building to networking.
Radiology ce courses are about staying sharp, advancing your career, and providing care that makes a difference. Approached with this mindset, CE becomes an opportunity, not an obligation.
Decoding ARRT ae and State-Specific CE Requirements
Navigating ARRT ae mandates and state rules for continuing education can feel overwhelming, but understanding the basics makes it manageable. The foundation of your CE journey is the ARRT ae biennium, a two-year reporting period during which most certified technologists must complete 24 CE credits. These must be Category A credits, approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM) like the ASRT (American Society of Radiologic Technologists).
For official guidance, visit the ARRT and ASRT websites.
All of our radiology ce courses are ASRT-approved for Category A credit, so you can be confident they count toward your ARRT ae certification. For a detailed breakdown, see our guide on Satisfying Radiology Continuing Education Requirements for the Biennium.
Structured Education (SE) vs. Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR)
Beyond the standard 24 credits, you may encounter two other categories: Structured Education (SE) and Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR). They serve very different purposes.
Structured Education (SE) is for technologists pursuing post-primary certification in a new specialty, like moving from radiography to CT or MRI. SE courses provide the required academic foundation (e.g., 16 hours for ARRT ae) before you begin clinical experience.
Continuing Qualifications Requirements (CQR) are about maintaining long-term competency. Every ten years, ARRT ae requires a CQR process, which involves a prescribed self-assessment to identify knowledge gaps. You then complete targeted CE to address those specific areas, ensuring your skills stay sharp.
For a comprehensive explanation, read What You Need to Know About ARRT’s Structured Education Solutions and Requirements. You can also find detailed information in the ARRT ae handbook on their official website.
Navigating State-by-State Mandates
While ARRT ae sets the national standard, each state can establish its own state-specific requirements for licensure renewal. It’s essential to stay informed about your state’s rules.
- California, for instance, has specific mandates for fluoroscopy certification. Our radiography courses satisfy California’s requirements; simply use the ASRT number from your completion certificate for state board submission. Learn more in our guide on How to Maintain Your X-Ray License in California.
- Florida often requires courses to be approved by the Florida Department of Health, Bureau of Radiation Control (DOH-BRC). Our courses of 1 credit or more are approved in Florida. Our guide on Florida Radiologic Technology License options offers more insight.
- Texas emphasizes that CE courses must be “directly related” to your scope of practice, highlighting the need for relevant, accredited courses.
Always consult your state’s licensing board for their specific requirements. Our State Agencies page is a helpful starting point for finding this information.
A Guide to the Different Types of Radiology CE Courses
The world of continuing education in radiology is diverse, with courses for every specialty and learning style. Understanding what’s available helps you make smart choices that align with your career goals. If you’re just starting, our guide Radiology and X-Ray Continuing Education Courses: Getting Started can help.
Modality-Specific Radiology CE Courses
Most radiology ce courses focus on specific imaging modalities, allowing you to build expertise or branch into a new area.
- X-Ray (Radiography): Courses cover positioning, physics, and advanced digital techniques. We offer 21 X-Ray courses for $39.99. Explore our Continuing Education Courses for X-Ray Technologists.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Dive into advanced protocols, 3D reconstruction, and image interpretation. We provide 15 CT courses for $35.00.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Tackle MRI physics, advanced sequences, and specialized applications. Access 22 MRI courses for $39.99. For a full selection, visit CT/MRI CE.
- Mammography: Focus on screening techniques, breast pathology, and quality control. We offer 9 mammography courses for $29.99. See our Mammography CE Courses.
- Nuclear Medicine: Explore radiopharmaceuticals and SPECT/CT and PET/CT imaging. Find courses at Nuclear Medicine CE.
- Ultrasound: Cover diverse applications from abdominal to musculoskeletal imaging. Visit our Ultrasound CE Courses.
- Fluoroscopy: Focus on radiation safety and interventional procedures. See our Fluoroscopy CE Courses.
Beyond modalities, you’ll find courses on broader topics like cross-sectional anatomy, radiation safety, and patient communication. Practical, case-based courses like “A Bone to Pick” (1 CE credit) or “Spinal Imaging Surprises” (2 CE credits) reflect real-world clinical challenges.
Course Formats for Every Learning Style
Radiology ce courses come in various formats to fit your schedule and preferences.
- Online Home Study: The most popular option, offering the flexibility to learn at your own pace, from anywhere.
- E-books and PDFs: Many courses offer downloadable content for offline study. You can read on a tablet or print materials, then take the test online.
- Webinars: These offer an interactive experience with expert presenters and Q&A sessions. They can be live or recorded for convenience.
Most online courses are self-paced, allowing you to start and stop as needed, which is invaluable for balancing work and life. After completing a course, you’ll take a post-test at an Online Testing Center. Once you pass, you receive an instant certificate. Our process makes it easy to Enroll in X-Ray CE Fast and get your documentation without delay.
How to Choose the Right Radiology CE Provider
Finding the right provider for your radiology ce courses is about choosing a reliable, transparent partner for your professional journey. Focusing on a few key areas will help you make a confident choice. For quick questions, our FAQ page can help.
Understanding Accreditations and Approvals
Not all CE credits are equal. Accreditation is what makes your radiology ce courses count, so before investing time and money, ensure credits will be accepted by your certifying body and state licensing board.
The gold standard is ASRT Category A credit, which meets the stringent standards of the ARRT®. Reputable providers will clearly display their ASRT approval. Depending on your specialty, also verify acceptance by other organizations:
- Nuclear Medicine: Nuclear Medicine Technology Certification Board (NMTCB)
- Ultrasound: American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS®) and Alliance for Physician Certification and Advancement (APCA®)
- MRI: American Registry of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologists (ARMRIT®)
We are proud that all our courses are accepted by ARDMS and NMTCB, and our MRI courses are accepted by ARMRIT®. Always verify that a provider’s courses are approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM) to ensure your credits are valid.
Evaluating Cost vs. Value in Radiology CE Courses
Continuing education is an investment, and you deserve real value. Radiology ce courses are available at prices to fit any budget without sacrificing quality.
While some providers charge on a per-credit basis, costs can add up. A more cost-effective option is an unlimited access plan. For a single annual fee (often around $49.99), you can get access to an entire library of courses. This offers tremendous value for fulfilling biennium requirements or for continuous learning.
Package deals and combo courses are another smart option, bundling related courses at a discount. They are perfect for meeting Structured Education requirements or diving deep into a modality. Explore our Radiology CE Combos and read about Why a Combo E-Course is a Good Fit for Your Radiology CE. We also offer group rates for teams of 5 or more.
Most importantly, look for transparency. A good provider is upfront about pricing, with no hidden test fees or certificate charges. You should pay once and be done. Our modality packages, like 21 X-Ray Courses for $39.99 or 15 CT Courses for $35.00, offer clear, straightforward pricing. A provider that combines accredited content with honest, budget-friendly pricing is a partner who respects your professional needs and your wallet.
Frequently Asked Questions about Radiology CE
Navigating radiology ce courses can raise questions. Here are answers to some of the most common ones we hear from imaging professionals.
How many CE credits do I need for ARRT® renewal?
Most radiologic technologists need 24 Category A CE credits during each two-year biennium for ARRT® renewal. Your biennium is a personal two-year window with specific start and end dates, so be sure to track your timeline. While ARRT® sets this baseline, your state might have additional requirements, such as extra credits or specific topics. Always check both your ARRT® and state-specific mandates. Our guide, How Many X-Ray CE Credits Do I Need for Radiography?, breaks this down for you.
Can I complete all my radiology CE courses online?
Yes, you can complete all your CE credits online. It’s the most popular and flexible method. Online radiology ce courses are designed to fit your schedule, allowing you to study anytime, anywhere. You have control over your learning pace and can access downloadable content, take online tests, and receive instant digital certificates. This home study convenience makes continuing education accessible to everyone. Our article on The Top X-Ray Radiology CE Credits You Can Earn Online highlights some excellent options.
What’s the difference between Category A and A+ credits?
Both credit types are approved by an RCEEM like the ASRT®, but they serve different professional levels.
Category A credits are the standard for most radiologic technologists. They cover essential topics like radiation safety, patient positioning, and modality-specific skills. If you hold a primary ARRT® certification, Category A credits are what you need to stay current. All Scrubs CE courses are ASRT-approved for Category A credit.
Category A+ credits are for Registered Radiologist Assistants (R.R.A.s) and other advanced-level professionals. These credits come from higher-level educational activities that cover more complex clinical topics. If you are an R.R.A., you will likely need a certain number of A+ credits to maintain your specialized certification. For most technologists, Category A credits will fulfill all requirements.
Conclusion
We hope you see that radiology ce courses are more than a requirement—they are powerful tools to keep you sharp, compliant, and ready for the evolving field of medical imaging. By choosing the right courses, you are investing in yourself, expanding your clinical knowledge, and positioning yourself for new opportunities like mastering a new modality or earning an advanced certification.
The key is to make strategic choices. Look for providers offering accredited, high-quality content (like ASRT-approved Category A courses) in flexible formats that fit your schedule. Evaluate cost versus value, where unlimited access plans or combo packages can offer significant savings.
At Scrubs CE, we understand the challenges you face. We’ve built our library of radiology ce courses to be convenient, affordable, and high-quality. Our ASRT-approved courses fit into your life with self-paced learning, instant certificates, and no hidden fees. Whether you need a few credits or want to dive into a new specialty, we have you covered.
Ready to advance your career? Explore our comprehensive library of Radiology CE Courses today and take the next step in your professional development.
The Importance of Continuing Education (CE) for X-Ray Technologists
Did you know that the national job
outlook for X-ray technologists will be very good for the next decade? Many senior citizens now need X-rays and diagnostic procedures to asses their health conditions. So, you can expect to find many employers who appreciate your radiology skills.
You already went through a certificate or degree program Tto become an X-ray technologist, but your education doesn’t end there. Continuing education is a requirement to stay in a radiology career.
So, why is continuing education important? You probably think of it as a means to maintain your licensure or learn something new. But its benefits go beyond these key purposes.
Read on to learn all about the importance of continuing education for X-ray technologists.
1. You’ll Need Continuing Education to Renew Your License or Certification
To keep your license or certification, you must complete radiology continuing education courses. You’ll also need to pursue continuing education to prepare for periodic evaluations.
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists® (ARRT®) has rules for keeping your certification. You’ll need to complete at least 24 continuing education credits every two years also known as a biennium.
If you don’t meet this requirement, you’ll find yourself on probation. You can even lose your license to practice as an X-ray technologist.
The ARRT® accepts a variety of continuing education options to meet this requirement. For example, you can take regular classes, attend approved professional seminars, attend lectures, or learn through self-study courses.
The ARRT® also has continuing qualifications requirements. If you can’t meet them, you risk losing certification. This process includes an assessment that happens every 10 years. The continuing qualifications process involves testing your current skills to find any gaps you may have. The assessment is not graded, but if your X-ray technology skills don’t meet the requirements, the ARRT® will require some specifically geared continuing education courses.
If you don’t take the assessment test, you will have to take 36 CE hours, selected by ARRT® in specific skills within your modality.
2. Continuing Education Can Help You Further Your Medical Career
The importance of CE for healthcare professionals goes beyond your current job. It can also prepare you for new career paths in medicine or allow for specialization within a medical imaging department.
After working a while as an X-ray
technologist, you might consider a leadership role such as a lead X-ray technologist or radiology manager. These are common career paths.
Continuing education also provides a path to expand your radiology skill set to another modality within the medical imaging department and more certifications from the ARRT® .
For example, you could take some continuing education courses to prepare for MRI technologist certification or mammography.
Having multiple specialties can help in the job market making it easier to find a new position. You’ll want to check on your state licensure and the ARRT® requirements to make sure your continuing education aligns with your future goals.
3. Continuing Education Helps You Keep Up With New Developments in Radiology
Your initial radiology education prepared you for the job at that time. But it didn’t teach you developments that would come after graduation.
New digital X-ray technologies have emerged. They reduce radiation which helps protect patients. Imaging tools can now provide an alternative to surgery in some cases. There are even systems that allow medical professionals to evaluate patients’ X-rays remotely.
By pursuing healthcare continuing education, you stay informed and up-to-date with new developments.
4. Continuing Education Helps You Do Better Work
The importance of continuing education can help you do a better job. This leads to better patient care and higher patient satisfaction.
You might have forgetten some of the stuff you learned while studying to become a radiologic technologist, but continuing education can refresh your memory and keep you current with advanced technologies.
Continuing education can also teach you the best practices in X-ray technology and patient care. For example, case studies of previously performed procedures can give you valuable insight and some new techniques to try.
Your employer will also take notice when they do your performance evaluations. Your dedication and improved skills can lead to pay increases, awards, or even a promotion.
5. Continuing Education Can Improve Your Image
Healthcare continuing education can also improve your reputation as an x-ray technologist.
You’ll find more confidence in working with patients and other medical professionals. You might even lead the way in newer and better techniques. Others will see you as more professional and trust in your work.
When you express professional confidence in your work, patients will feel more comfortable during procedures.
Meeting continuing education requirements can also help you join professional organizations in radiology. Joining these organizations can help further boost your image as a professional in X-ray technology.
Now You Understand the Importance of Continuing Education
As you’ve learned, the importance of continuing education goes beyond allowing you to keep your credentials.
It helps you care better for your patients and improve your professional skills. It also gives you better career prospects and keeps you informed of the latest X-ray technology trends.
So, get started looking for continuing education options. You might start by signing up for online radiology courses.
Feel free to reach out to us to learn more about our continuing education courses.
What You Need to Know About X-Ray Continuing Education Requirements
Have you considered switching career paths to become an x-ray technologist? It would be a great choice. The median pay for radiologic technologists in the United States is approximately $61,240 per year. Techs in specialties such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) make on the average $71,670.
The job outlook for radiologic technologists is good with a projected growth of approximately nine percent through 2028. These numbers anticipate increased medical care needs as the large Baby Boomer population continues to age.
Becoming a radiologic technologist and maintaining your certifications requires an investment in education. This includes x-ray continuing education (CE) after you get certified.
The radiology continuing educationn requirements can feel overwhelming, especially when you work full-time and have a family. Fortunately, you have plenty of options when it comes to affordable and achievable online courses.
Read on to learn more about continuing education in radiology and how to find the right program for you.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Radiologic technologists perform diagnostic imaging procedures on patients. These can include services such as x-ray examinations, computer tomography (CT) scans, and MRIs.
Because of the nature of their work, radiologic technologists must have formal training in:
- Patient care and safety
- Examination techniques
- Patient positioning
- Anatomy
- Radiation safety
- Equipment protocols
Some radiologic technologists also choose to specialize in sonography, mammography, cardiovascular, or interventional radiography.
Technologists work closely with physicians who interpret the radiologic images captured by technologists. These interpretations, in turn, are used to diagnose or rule out injury or disease. The working relationship between an x-ray technologist and physician is very important.
To maintain their certifications, radiologic technologists need to keep their credentials up-to-date. Continuing education courses allow them to do this no matter what their specialty is.
Learn More About X-Ray Continuing Education
What are x-ray continuing education requirements? And how do they work?
Every two years, radiologic technologists must earn 24 credits of continuing education.
When does the two-year period begin? Known as the biennium, it starts on the first day of your birth month. All CE credits for the biennium must be achieved the month prior to your birth month.
Approved continuing education (CE) credit should add up to 24 credit hours. It should focus on the application of x-ray technology to the human body.
What to Know Before Choosing X-Ray Continuing Education Courses
Credits and approvals for x-ray CE courses are provided by organizations (RCEEMs) such as The Association for Medical Imaging Management® (AHRA®)
There is a wide range of CE courses to choose from, but make sure they’re either Category A or Category A+. These categories denote courses approved and accredited by an RCEEM for ARRT®.
Besides ensuring the x-ray CE courses you take are fully accredited, double-check that the study area is acceptable. Before registering for courses, verify that any course you’re considering meets all of your CE requirements. Fortunately, you don’t have to go it alone.
We’re here to help. Contact us today to discuss the best courses for your current needs.
X-Ray CE Courses and Combos
How many credits of continuing education do you need? And how does CE work?
You’ll receive a renewal notice from ARRT®. You can document your CEs online at ARRT’s® website.
You also need to maintain evidence of continuing education course completion for four years after the date you earned the credits.
Now that you have a better understanding of how radiologic continuing education works let’s explore the options available to you for completing these requirements.
By far, the easiest way to stay up on all of your continuing education requirements is through online education via e-courses. Not only e-courses prove to be both affordable and flexible, but you can do the learning around your daily schedule. Courses can be completed from the comfort of your own home. That includes taking your x-ray continuing education post-tests online.
When you work with the right continuing education company, online testing is provided at no extra charge.
You can also get courses bundled into combos. This allows you to fulfill specific requirements for states like California, that require continuing education in radiation protection or fluoroscopy safety. Doctors may also be required to take afFluoroscopy radiation safety course also.
Find out more about online CE course bundles including California combo CE courses that are ASRT® or AHRA® approved.
Benefits Associated with X-Ray Continuing Education
Besides keeping your certifications and credentials current, x-ray continuing education comes with many benefits.
In our fast-paced world, technology is advancing at a rapid pace. X-ray continuing education helps you learn about new technologies and trends in the industry.
It also keeps your job skills sharp and makes you more marketable when you’re looking for a new position. X-ray continuing education courses also increase the chances for a promotion or raise.
But more importantly, these courses are designed to help you improve patient interaction and care and reduce your risks of making mistakes. It’s a win-win for you, your patients, and the facility where you work.
Take Your Skills to the Next Level
Whether you’re at the beginning of a new biennium or coming to the close of one, don’t procrastinate when it comes to x-ray continuing education. It’s never too soon to raise the bar at work and improve your patients’ experience.
What’s more, classes are easily completed at home, and you can fit them into your schedule. So, what are you waiting for? Check out our comprehensive list of ARRT® Category A x-ray CE courses today, and then get ready to learn.
Most Frequently Asked Questions About CE Credits for Radiologic Technologists
Radiologic technologists and other medical imaging allies must complete continuing Education for continued ARRT® certification.
Why? Because medical radiology is always changing and improving. Computers, techniques, even AI contribute to the constantly updating challenge the radiologic imaging professionals face to better serve the patient. Radiology continuing education helps you keep pace with the latest science and provide you with an opportunity to broaden your horizons and become a well-rounded medical professional.
The process for acquiring CE credits for radiologic technologists can be a bit confusing, especially during your first two years. So, we gathered up the most frequently asked questions about CE credits and answered them below.
After completion of your educational journey toward a radiologic technologist certification or degree, you must earn your 24 CE credit hour requirement for the two year period, also known as the biennium. When choosing a continuing education course, be sure that it is approved by a qualified RCEEM such as the Association for Medical Imaging Management® (AHRA®) for acceptance by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists® (ARRT®).
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists® (ARRT®) is the credentialing organization. ARRT® designs and administers certification testing and sets the ethics and continuing education requirements needed to maintain your license.
How Many CE Credits Do You Need Per Biennium?
To keep your radiologic technologist certification with the ARRT® active, you need to complete 24 CE credits every biennium, which is every two years.
Per ARRT®: The CE Requirements are linked to a two-year period (biennium) that is defined in relation to the R.T.’s birth month. The biennium begins on the first day of the R.T.’s birth month. The biennium extends for two years to the end of the month prior to the birth month. For example: An R.T. who has a March birth month must complete their continuing education credits by the end of February. Their assigned biennium is from March 1 through February 28 (or 29th). It’s very important to complete your Radiology CE requirements by the end of the month prior to your birth month.
How Does One Earn Credits?
You can earn credits in a variety of ways, including classes, conferences, and other educational activities. Some of the opportunities include:
- Seminars
- Directed readings
- In-service
- Home Study Courses
- Online programs
- Lectures
However, those credits need to meet the criteria published by the ARRT®. For example, the ARRT® doesn’t accept credits that are part of your job requirements. Attending meetings, poster sessions, or holding an elected office doesn’t count. Neither do activities that aren’t related to radiologic technology or healthcare.
Additionally, all 24 credits need to be an A or A+ credit. We cover those in the next section.
What is a Category A or A+ Credit?
Radiology Assistants must take A+ continuing education credits according to ARRT® . If you are a radiologic technologist, mammographer, etc., you can take A or A+ credit courses as noted in ARRT’s continuing education document.
How Are Credits Submitted?
When you succssfully complete your continuind education course, achieving 75% or better, you’ll receive a certificate of completion from the sponsor. That certificate validates your credit. It’s important to hold on to this certificate because you must submit information from it to the ARRT® for renewal of your license. If you are randomly audited, you will have to provide a copy of the certificate to ARRT® and/or your state.
Are You Up-to-Date With Your CE credits for Radiologic Technology?
Two years go by fast. Set up reminders for yourself. Get your 24 hours of X-ray CE courses done by the end of the month before your birth month.
Are you looking for ways to get your credits and save money? Get in touch to learn how we help radiologic technologists across the U.S. complete their continuing education credits on time and on budget.
5 Trends Transforming Radiology Continuing Education You Need to Know
There are more than 250,000 radiologic and MRI
technologists in the U.S. If you are one of them, you must complete Radiology Continuing Education (CE) to renew your license. Don’t put this off due to busy work and home life schedules.
Establishing a commitment to complete CE on a regular schedule is challenging. We all know that it’s best to spread out ongoing education so you receive continuous updates. Several trends have evolved to help make this process easier.
Continue reading to learn about 5 ways radiology continuing educations is transforming.
What Is the CE Requirement for Radiologic Technologists?
All radiologic technologists must document 24 hours of CE every two years. This is a requirement for ARRT® renewal for radiologic technologists.
Be aware of your specific state requirements related to qualified CE. It’s your professional responsibility to meet all special directives. If you are unsure, contact your state board of radiology.
Current Trends in Radiology Continuing Education
Internet technology is advancing, offering new and different ways to earn CEs. This helps the ease of meeting your licensing requirements.
1. Who Can Award Radiology CE Credits?
A CE provider’s courses must be accepted by The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists® (ARRT®) in order to provide CEs. The ARRT® has partners that are deemed recognized continuing education evaluation mechanisms (RCEEMs). RCEEMs have approval to:
- Evaluate program content®
- Evaluate program quality
- Determine the integrity of the proposed CE activity
- Evaluate the CEs objectives
- Examine the course content for relevancy and accuracy
- Vet the faculty qualifications
- Evaluate the planned education methods
- Evaluate the materials developed for use in the CE activity
- Award the program or course the number of Radiology Continuing Education CE credits
RCEEMs have the authority to grant Category A designation to qualifying CE activities. This is based on the determination that the CE meets the ARRT®s requirements. An RCEEM+ may approve A+ category activities.
It’s important to know your state CE requirements. Radiologic Technologists and other imaging professionals like CT, MRI, Nuclear Medicine, Radiation Therapy and Ultrasound Technologists must ensure that the CE meets their state requirements.
2. Radiology CEUs Online
You have the option of taking CE courses in-person or using written material. Many people, though, are moving to online, webinar, or simulcast courses. The courses offer a wide variety of topics.
Do you understand the licensing CE requirements for your state? For example, radiologic technologists in Texas must include certain courses as part of their 24 CEs. They must have 12 credits focusing on “ionizing radiation”. Three of the 24 CEs must be through live instruction.
California mandates that radiologic technicians take 24 CEs related to the application of “X-ray and the human body”. They accept courses that include:
- X-ray administration
- X-ray management
- Pathology
- Diagnosis
- Quality control and safety
- Anatomy
In general, it’s usually best to make sure you have 24 hours of CE that correspond to your specialty. After that, you may take more courses that interest you. Many courses target anyone working in the field of radiology.
3. CEs Available 24 Hours a Day
Online CE courses a great option. Many radiology technologists and technicians work varied shifts and weekends. It’s often difficult to get time off work to attend a CE program.
You can choose when and where to complete your CE training. You may even be able to do it in sections if you have an interrupted schedule. This has had a positive impact on making it easier to meet licensing requirements.
4. You Can Complete CEs from Any Location
CE seminars at specific locations can provebe expensive and time-consuming. With individualized CE opportunities, you can choose where you wish to complete the training. Some employers allow radiology technicians to work on CE during downtime at work.
You can complete programs at home or even a local library or coffee shop. Many professionals enjoy having increased flexibility to choose when and where to work. Having CE courses that fit in with this new way of doing business enhances learning and adherence to policies.
5. Varied Formats for Courses
The ARRT® regulations say that you can’t get credit for repeating a self-learning CE in the same biennium. You can repeat a course in a new biennium. Even though a course is provided in a different format, if it’s the same course, you cannot repeat it. Thus, it’s important to keep a rigorous record of your activities. ensure that you are meeting your state requirements and not repeating an activity in the same biennium.
Are You Keeping Up with Your CEs?
Have you established a routine for meeting your biennial CE requirements? Scrubs Continuing Education offers ASRT® and AHRA® approved Radiology Continuing Education courses.
All our CE programs are RCEEM approved for ARRT® Category A CE credits for radiologic technologists and other imaging professionals.
Selected courses are accepted by ARDMS®, NMTCB®, ARMRIT®, and CCI® (Cardiovascular Credentialing International®).
ARRT® Category A CE credits are accepted in all states. We offer state-specific requirements as well. For example, we offer fluoroscopy radiation safety, digital radiography, and nuclear medicine CE credits for California.
Scrubs CE is a DOH-BRC X-Ray CE provider for the Florida Department of Health Bureau of Radiation Control. We also offer programs to meet Texas’ requirements for X-Ray CE courses.
Buy a course today and get free online testing with an instant CE certificate.
The Top X-Ray Radiology CE Credits You Can Earn Online
In recent years, the field of radiology has exploded with more radiologic technologists signing up for the complex and technical work the field offers. Radiographic imaging is an employment opportunity for anyone interested in services and technology. If you like helping people who are dealing with a variety of medical issues this is a good fit.
It’s important to know that it’s important for every certified radiologist to earn radiology CE credits. If you’re looking to earn your credits around your own schedule with online courses, here’s what you need to know.
Which Careers Require Continuing Education?
There are a wide variety of professions that offer certifications. In the radiology field, you need to maintain your licensure through radiology continuing education, especially if you’re looking to stand out in the professional community and find a job. The right licensure and certifications give you the competitive edge for employment.
A lot of licenses require continuing education because technology, standards, and requirements change constantly. While it’s expected that you’d do some research on your own, keeping requirements ensures there’s a minimum standard for all radiologists.
Some states have special certification requirements, so it’s vital for radiologic technologists to stay informed about the changes made in their state.
Radiologic technologists, radiation therapists, and radiologists all require continuing education of some kind. Radiographers and radiologic technologists need to stay up to date on improved equipment and new x-ray technology techniques. Radiation therapists and radiologists will need to learn about new pharmaceuticals and how to integrate them using radiation as part of their medical tool kit, often to treat cancer patients.
Who Else Needs Continuing Education?
Radiologic technologists do general x-rays, but can advance to other positions in CT, Interventional Radiology and MRI for example.
Additionally, sonographers and nuclear medicine technologists also need CE credits.
Sonographers bounce high-frequency soundwaves off of tissues inside of the human body. They read echoes that get translated into an image.
Nuclear medicine involves using trace amounts of injected radiopharmaceuticals to get data from inside the body. Bones, organs, and tissues can be imaged with radiopharmaceuticals. Cameras get an image of the gamma-ray emissions that help doctors to find issues inside of a body.
Getting to Know the Requirements
Radiologic technologists and radiation therapists have to get certified through a group called the ARRT®. The American Registry of Radiological Technologists® requires that applicants first graduate from a program that they approve of. Then, they require that the graduate meets ethical standards before they’re allowed to take a certification exam, also known as the boards.
Every two years, ARRT® certified technologists need to complete 24 credits in continuing education. If they don’t, they might risk losing their certification.
Radiologists go through a different process. They’re certified by the American Board of Radiology®. Those certifications are renewed over the course of ten years, or as designated by their state, during which time a radiologists need to take CMEs.
They also need to perform a self-assessment depending on their specialty.
Choosing the Right Program
The right program for every radiologist and radiologic technologist will depend on what’s available and what state you’re in. The rules can be complicated and are often subject to change.
Sonographers and nuclear medicine technologists need to look carefully at what’s offered. They need to be recognized by certification granting organizations. This will depend from one jurisdiction to another.
CE Provider submissions are scrutinized by professional organizations. A course is determined adequate or not by peer-reviewed guidelines. Approved continuing education is available through these providers.
Even manufacturers of medical equipment can offer courses. If you’re going to be working with one specific tool, sometimes, the people who make that tool can do the best job in letting you know how to get the most out of it.
People who are merely interested in learning about radiology should not pursue continuing education credits. CE credits are for already registered technologists or radiologists.
Types of Courses
There are a number of different types of courses focused on the type of radiology specialty.
As outlined above, radiologists and radiologic technologists might need to take a course that’s based on a particular technology that they use. They might also need to learn about changes to X-ray standards if the state law has changed. Radiation therapists and radiologists will learn about how treatments can be carefully used to target different types of illnesses based on new research.
Nuclear medicine is another type of specialty that changes constantly. As more radiopharmaceuticals are developed and used constantly, healthcare providers and radiologists need to be on top of this. They also need to ensure that they’re sticking to high safety standards.
Mammography specialists will need to stay up to date as their field also changes.
Fluoroscopy is a dynamic imaging specialty where techniques are changing constantly along with equipment and new technology.
Ultrasound technologists or sonographers have seen their field change and grow over time. Continuing education focuses on new equipment and techniques, so that every sonographer can offer more effective imaging.
Radiology CE Credits Can Be Earned At Home
Thanks to the number of online courses available, it’s never been easier to stay on top of your radiology CE credits. Knowing which courses are best and which are available is also easy thanks to the availability of options.
If you’re interested in medical imaging continuing education, check out our guide to learn more.
A Guide to Continuing Education for X-Ray Technologists
You passed the boards and are now a certified X-Ray Technologist!
You have stepped into a rewarding job with an abundance of opportunities and get ready to keep learning for the rest of your career.
While you won’t be bored or out of a job as a rad tech, you will have to stay on top of some continuing education requirements to maintain your certification. You’ll be rewarded with learning about new technologies and techniques that will help you and your patients.
Keep reading for our ultimate guide to continuing education for X-Ray technologists.
Breaking Down Continuing Education Requirements for X-Ray Technologists
As a rad tech, you’ll have to complete a minimum number of continuing education courses to keep your certification current.
This is because the field of radiology is constantly growing and evolving. Keeping up with the latest science and trends is imperative to performing your job and keeping patients safe.
Having a career in the medical field generally requires a commitment to lifelong learning. If you’re willing to put in the effort, you’ll be rewarded with opportunity and a better salary.
So what exactly are the basic continuing education requirements to maintain your certification as an X-Ray technologist?
Basic CE Requirements
Rad techs who are certified by the American Registry of Radiological Technologists® (ARRT®) must complete 24 credits of continuing education every two years in order to keep their license in “active” status.
The two year period, or “biennium” is determined by your birth month. You’ll also want to keep current on your education so that you’re prepared for periodic assessments that all rad techs have to take.
If you fail to meet your continuing education (CE) requirements, you’ll end up on probation and could be subject to losing your certification.
You can earn CE credits through a number of different channels. For many X-Ray techs, taking online courses is their preferred method of continuing their education because of the level of convenience. You can also do self-study or attend lectures and seminars.
You may also be subject to additional and/or specific continuing education requirements according to your state licensure program.
CQR Requirements
X-Ray technologists must also complete a CQR Structured Self Assessment (CQR) every 10 years.
This requirement is designed to account for developments in health care technology and to ensure rad techs don’t fall behind on what are now entry levels qualifications for those newly entering the field. If you do fall behind, the ARRT® will prescribe specific continuing education courses to bring you up to speed. The good thing is that you’ll be able to use the prescribed courses to satisfy all or some of your biennium credits.
Earning Credentials
If you are certified and registered with ARRT®, you can pursue additional credentials to further your career. You may be required to complete specific courses relating to your desired career path.
How Continuing Education Can Benefit You
Completing continuing education requirements can seem inconvenient, especially when you’re busy with work and life in general. However, like most things in life, the more effort you put in, the more you will get out of the experience.
Continuing education goes beyond the minimum requirements to keep your license. Changing your mindset about continuing education can lead to a more lucrative and fulfilling career in radiology. This is because continuing education doesn’t have to be seen as a requirement, but as a tool to advance your career. Look at it as a tool to help you help your patients.
Let’s take a look at some of the ways continuing education can truly benefit you.
Improving Your Performance
When you learn more about the best ways to do your job, you’re more likely to feel confident about what you’re doing. Patients as well as supervisors are more likely to notice your increased confidence. This is especially relevant when you’re working directly with patients and others in the medical profession.
Taking CE seriously and utilizing the knowledge you gain while on the job can lead to recognition in the form of performance reviews, bonuses, raises, awards, and even promotions.
Improving Your Image
Completing your continuing education requirements and taking them seriously won’t go unnoticed by management. Employees who are eager to learn and invest in themselves within the workforce are the best candidates for new opportunities.
Continuing education can make you stand out amongst your peers.
In addition to belong to credentialing organizations you can join a professional membership society.
Taking Your Career to the Next Level
For many in the field, becoming an X-Ray technologist is just the first step in their career.
The medical field, and the field of radiology specifically, is unique in that it offers near-endless advancement opportunities for those willing to put in the work. While unexpected job loss is a reality for millions of Americans, there is no shortage of opportunities in this field.
By taking advantage of the continuing education requirements to maintain your rad tech certification and registration, you can challenge yourself to learn beyond what you already know. Continuing education is an excellent way to work towards a promotion.
Many rad techs use continuing education to earn credentials that allow them to specialize. For example, you might take CE classes that focus on an area you want to add to your skill set such as mammography or MRI technology.
Meeting Your Continuing Education Needs on Your Schedule
Continuing education for X-Ray technologists is an excellent way to stay current in the field while working your way upward. Those who are currently in the workforce can benefit from completing their CE requirements online and in the comfort of their own homes.
You don’t have to miss work to complete your continuing education requirements. Take a home study course.
Click here for a list of courses we offer and start taking your future into your own hands today.
11 Reasons to Become an MRI Technologist
At least two million workers will be needed in the healthcare industry over the next several years to meet rising demand. MRI technologists are part of that demand.
While many opportunities exist for healthcare specialists, MRI technologist is one of the best options available. MRI tech training allows good flexibility in a growing industry and earn competitive wages.
What is an MRI Technologist?
An MRI tech is a specialist within the radiology diagnostic team. An MRI tech deals with magnetic resonance imaging scans. Magnets are used to align a patient’s atoms, radio waves are bounced off the patient and send a signal to a computer that interprets the image of the patient’s internal anatomical parts.
The MRI technologist places patients into the MRI unit and scans the parts of the body that need a diagnosis. Patient care is important. Keep the patients comfortable and answer their questions about the scan.
These scans are used by physicians to help diagnose diseases or injuries, or how a patient responds to treatment.
As an MRI tech, you are responsible for ensuring that these MRI scans are high-quality. You run the scan based on the instructions from a physician so they can get accurate information about the patient’s needs. This job requires specialized training but offers many benefits to trained techs.
1. Get Started in Your Career Quickly
You need an Associate’s degree and certification to become an MRI technologist. You complete the degree program within one to two years, then you can get started on certification. This means you can get started on your MRI career within two-years.
2. Training Costs Less than Other Careers
You can complete your Associate’s degree at a community college. This costs less than a university degree.
Once you complete these educational requirements, you just have the cost of the certification program. The certification exam costs less than $200 for course materials and the exam fee. The cost is reduced if you don’t have to purchase books to study.
3. Better Shift Management
You can expect more regular working schedules. MRI scans usually get scheduled during regular business hours, however there are exceptions.
This means you don’t have to worry about late-night shifts and can make better plans for personal time. Since scans are scheduled ahead of time, you don’t have to worry about constant schedule changes, either.
4. Choice of Work Environment
As an MRI tech, you can choose your work environment. Technicians are needed in all medical settings.
This means you can choose whether you want to work in a physician’s office, a hospital or outpatient center, a lab, or a government agency. This choice will depend on how much work you want and in what setting makes you feel most comfortable.
5. Good Job Security
MRI techs have one of the fastest job growth rates of any healthcare occupation. Through 2026 MRI tech jobs are expected to grow 13%. This growth rate is higher than average for all tracked occupations, not just healthcare.
6. High Wages for MRI Technologists
MRI techs can expect more than job security. You can also expect higher wages than many in the allied health industry.
The average wage for an MRI tech can be as high as $71,670 per year. This is $12,150 more than general radiologic technologists.
7. Play a Vital Role
We all know job satisfaction is about more than the pay. We also want to feel like we add value with the work we do. As an MRI tech, you can know you play a vital role in the healthcare industry.
The images you take are an important aspect of diagnosing patients. What you do as an MRI tech helps physicians take better care of their patients.
8. A Chance to Play with New Technologies
New advances happen regularly in imaging technology. This means you get the chance to experience new and exciting technological advances in the healthcare industry.
You’ll get the chance to try out new technologies in computers and imaging systems. It’s your job to keep the systems running, so you get hands-on time with these new technologies.
9. Work Anywhere in the United States
Courses for an MRI technologist are certified by an RCEEM or RCEEM+ for The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists® (ARRT®).
Your training prepares you to work anywhere in the United States. If you need to move to another state, your certification goes with you.
10. Less Hectic Work Environment
Since you specialize, you’ll work within specific parameters. This means you always know what to expect from your job.
You’re not responsible for every patient, just the ones scheduled for scans. This makes the job of an MRI tech less physically and emotionally demanding than other healthcare professions.
11. You Get to Work with Patients
Some healthcare professions keep you behind the scenes. This is not the case for an MRI tech. You get to work one-on-one with patients as you complete scans.
Part of your job is comforting patients who are dealing with health problems. You also help answer questions about the procedures. This allows you to take a more active and satisfying role without the demands of some of the other hands-on careers.
So What Happens When You’re Done?
MRI Continuing education can help the MRI technologist keep up-to-date with new technology, feel comfortable in their ever evolving MRI profession and bring that confidence to the patient during their time of need. New technology in medical imaging brings to the imaging arena new tools for healthcare professionals to expand their abilities during procedures. Patients can be examined faster improving image collection and quality while increasing patient comfort. Healthcare decisions can be made faster supportin expedited patient care. Design advances provide incremental and occasionally major breakthroughs which can revolutionize imaging and quality.
Do you want to learn more about the options available for MRI continuing education? Check out the courses available for MRI techs and other diagnostic professionals.
Radiologic Technologists Jobs & The Importance of Continuing Education
Radiologic technologists’ are expected to grow 9% between now and 2028, adding 23,000 jobs. That means that radiologic technologist job growth rate is much faster than the average job growth rate for all occupations.
An associate degree is needed to get started as a radiologic technologist . A career in radiologic technology can offer you flexibility and a well-paying job .
Once you are certified as radiologic technologist, radiology continuing education is a necessary part of maintaining your license.
Keep reading to learn more about radiology continuing education, also known as radiology ce and x-ray ce.
What is Continuing Education for Radiologic Technologists?
To maintain your American Registry of Radiologic Technologists® (ARRT®) credentials, you must comply with a series of ongoing requirements and take part in continuing education.
Here are the requirements according to their website:
- Complete an annual renewal process
- Complete and report continuing education every 2 years
- Complete Continuing Qualification Requirements every 10 years (this only applies to Registered Radiology Assistants and Radiologic Technologists who earned their credentials on or after January 1, 2011)
Regarding specific continuing education requirements, the ARRT® states:
“As an R.T.®, you must complete and report 24 credits of approved continuing education activities every two years (or 50 credits if you’re an R.R.A.®). If you’re an R.T.® in Sonography, 16 of the 24 credits must be directly related to your discipline. You’ll have specific deadlines for completing and reporting your CE activities.“
The Importance of Continuing Education
Continuing education can benefit you in several ways if you make the most of it. Keep reading for some ways continuing education can benefit you.
Keeping Up With Technology and advances in radiographic procedures
Continuing education is mandatory for those employed in technical fields for a good reason—constantly changing technology. And with changing technology comes advances in procedures.
The medical field strives for constant improvement for the sake of patient safety and outcomes. When you decide to become a radiologic technologist, you make a commitment to lifelong learning through radiography ce.
Constant changes in technology, patient care, hospital policy, and new procedures will keep you challenged. Technologic advancements are constantly making it easier to take better images. Therefore, radiology continuing education is mandatory.
Career Advancement
The radiologic technologist field rewards those who want to put in extra effort. If you’re a radiologic technologist interested in learning about new modalities, there is a world of opportunity with continuing education.
There are many modalities beyond working as an x-ray technologist, but getting into these modalities requires a commitment to continuing education beyond the basic requirements.
These are just a few of the modalities you can get into:
- MRI
- CT
- Radiation therapy
- Special procedures
- Nuclear medicine
- Mammography
- Sonography
- Cardiac Cath
Opportunities abound, if you want to advance your career. if you are deciding on a different modality in radiology, choose a radiology continuing education course that has the 16 hour structured educational requirement to apply for the post primary exam.
Tired of being in the trenches day in and day out? Looking for something different within the field. You can earn an advanced degree and move into areas like management, sales, administration, and even education if you earn a bachelor’s, master’s, or doctoral degree.
The field of radiology is constantly growing and new positions are being created. These include the Radiologist Assistant (similar to a physician assistant, but with extra training in radiology) and the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) administrator which is a unique position including elements of radiology and IT.
Better Marketability
By keeping up with developments in the field through continuing education you’ll open up more opportunities for yourself. Radiologic Technologists with additional skills and up-to-date training earned through x-ray continuing education are more marketable to employers.
Employees that aren’t compliant with required x-ray continuing education might be in danger of losing their licensure and their job. Completing your continuing education requirements will show employers you are ready to work for them. If you transfer to another job, It will be easier for you to transition to another employer when you’re up to date.
Be sure to add your continuing education credits and accomplishments to your resume. If you go above and beyond the baseline radiology ce requirements, you might have an edge over your competition. This may mean promotion, raises, and better job opportunities.
Personal Development
If you think you’re satisfied with your current position, x-ray ce’s are needed to keep in good standing and can still benefit you.
Learning should be a lifelong process and committing to learning more through continuing education can help you develop personally as well as professionally. Chances are you find the field of radiology interesting. Completing radiology continuing education can be fun and you’ll feel more confident in yourself after learning more about your field, new technolgooy and adding skills to your resume.
If you’re only completing radiography continuing education because you have to, take a moment to consider how you can make the most of it.
Make the Most of Your Continuing Education
Continuing education for radiologic technologists is important for the health and safety of your patients. However, continuing education doesn’t have to be something you dread and try to avoid.
We offer high quality, convenient and affordable continuing education courses that you can do online, or as a homestudy course with book in hand in the comfort of your own home. You don’t have to worry about attending classes taking you away from your work or family.
We understand you are a busy professional and we strive to make achieving your continuing education requirements easy and rewarding.
Click here to view our available continuing education courses and get started.
Satisfy California Fluoroscopy CME Requirements on a Budget
Earn Radiation and Fluoroscopy CME Credits
Dynamic or real-time examination of bone, tissue and other body structures is accomplished through the use of fluoroscopy. There is the potential of health risks because of increased radiation exposure, therefore fluoroscopic procedures are highly regulated to ensure the safety of patients and staff. The state of California requires healthcare providers who operate or supervise fluoroscopy radiation to earn CME (Continuing Medical Education) credits in order to renew and maintain medical licenses, permits, and certifications. Sometimes finding CME credits in fluoroscopy can be a challenge. Scrubs Continuing Education offers inexpensive fluoroscopy CME credits.
About CME Requirements
CME (Continuing Medical Education) refers to activities or courses that help the healthcare professional maintain, develop, or increase the knowledge, skills, and professional performance and relationships of healthcare providers across many disciplines. Anyone who provides or supervises healthcare and medical services must meet the CME requirements, including physicians, surgeons, podiatrists, physician assistants, and nurses. California fluoroscopy license requirements also apply to supervisors of diagnostic/medical centers, and the radiologic technologists who operate the equipment and diagnostic machines, to earn CME credits.
Who Must Earn Fluoroscopy CME Credits?
According to the California Department of Health, CME credits are required to renew medical licenses, certifications, and permits in radiologic technology and fluoroscopy (Title 17, California Code of Regulations, section 30403). The regulations apply to any healthcare or medical professional who provides, supervises, operates or recommends fluoroscopic testing.
Fluoroscopy and radiation CME courses are required for…
- Certified radiologic technologists (CRT)
- Radiology supervisors and operators
- Fluoroscopy permit holders
- Physician Assistants & Supervisors/Operators (physicians, podiatrists, chiropractors) with fluoroscopy permits
How Many Hours Do You Need?
Everyone in the state in California who operates or provides fluoroscopic examinations must take a set amount of hours (credits) in order to maintain permits, licenses, and certifications.
Radiography – 24 CE credits in two year period, 4 of which shall be in digital radiography and 4 in fluoroscopy radiation safety
- Radiology Supervisors/Operators – 10 approved CE (Continuing Education) credits
- Fluoroscopy permit holders – 4 approved CE credits in fluoroscopy radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy in subjects related to the application of X-rays
- Fluoroscopy Certified Supervisors and Operators – 10 CE credits in a two year period, 4 of which shall be in fluoroscopy radiation safety
- Physician Assistants & Supervisor/Operators with fluoroscopy permits – 4 of 10 credits in radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy (includes California licensed Physicians, Surgeons, Podiatrists, and Chiropractors)
To see the complete requirements, visit the California Department of Health web page at: (Downloads to a pdf) Renewal Requirements
California Department of Health
Department of Health Services
Radiological Health Branch, MS 7610
(916) 327-5106
In general, the requirements must be met within two (2) years after the expiration date of a fluoroscopy permit or medical license.
How Can You Earn CME Credits?
One CE credit equals one CME credit as defined by the Medical Board of California. In order to qualify as a CE credit, the educational material must include some portion of instruction or philosophy that relates to X-ray and/or fluoroscopy examination, such as correct application, uses, the latest technology, patient safety, best practices, and the effects of radiation on the human body.
CME credits can qualify as CE credits on “hour-by-hour basis” as long as there is instruction related to X-ray applications.
There are a number of different ways to obtain CME credits:
- In-person lectures
- Conferences
- Online classes/conferences
- Books & peer-reviewed articles (case studies, research, new technology, etc.)
- Video & audio recordings
Each state has its own requirements in regards to CME credits. Most states accept what ARRT® accepts. The State of California Department of Public Health sets CE requirements for fluoroscopic radiologists and other healthcare providers who are involved in this type of diagnostic testing.
Cost of CME Courses in Radiology, Fluoroscopy, and X-rays
There are a surprising amount of ways to meet CE requirements that won’t wreak havoc on your budget. You may find some free CME courses offered by hospitals throughout California and around the country. There are online courses that can be taken from anywhere.
Earn CME Radiation Credits from ScrubsCE
Another inexpensive way to earn credits and satisfy California CME requirements is to take ScrubsCE Courses. We offer high-quality, low-cost, e-courses, which are ASRT®/AHRA®-approved for ARRT® Category A Credit Hours.
X-Ray Continuing Education Courses (radiologic technologists & imaging professionals)
California Combo Fluoroscopy Safety Combos (digital radiography & fluoroscopy radiation protection)
Fluoroscopy Radiation Safety (for fluoroscopy permit holders)
You can satisfy California radiology license requirements without busting your budget by taking advantage of inexpensive and occasionally free fluoroscopy CME courses. Get started with ScrubsCE to find cost-effective online courses.
Patient Safety in Fluoroscopy Procedures: Guidelines for the Radiologic Imaging Team
As a member of the imaging team, you have to do your best to keep patients safe during fluoroscopy procedures .
Fluoroscopy-related skin injuries have been on the rise since 1992. They are painful and can be devastating for patients.
Want to assure your patient’s highlest level of safety before, during, and after their procedures? Then keep reading to help you get started.
Common Reasons for Preventable Injury Due to Fluoroscopy
Patients are unique in their response to radiation. The majority of skin injuries from fluoroscopy procedures are preventable. There are commonalities that cause preventable skin injuries:
- Misinformed patients
- Incorrect dose management
- Lack of awareness of total dose
- Imaging team’s lack of knowledge about the risks of prolonged fluoroscopy procedures
- Failure to identify skin injuries
An important and often overlooked cause of radiation induced injury is lack of knowledge about the cumulative dose after multiple procedures. The dose delivered during each procedure may not have been enough to cause harm alone. but the cumulative effect leads to damage or injury.
Now that we have learned the most common reasons for fluoroscopy procedure radiation-induced skin injury. Now, let’s explore exactly how the radiologic imaging team can prevent them.
How to Make Sure Your Patients are Safe During Fluoroscopy Procedures
Create a plan. This plan would ideally include measures for before, during, and after the procedure. To assure patient safety during fluoroscopy, radiologists and their radiologic interventional technologists need to have a plan.
Fluoroscopy Safety Measures Before the Procedure
Training is perhaps the most obvious– yet most vital– pre-procedure safety measure. The radiologists should fulfill academic and residential training. The interventional radiologic technologists should be trained and in some cases certified as interventional technologists. Nurses should also have training. Training doesn’t stop with the information you learn in the beginning of your career in fluoroscopy. It includes any mandated continuing education requirements.
A Radiologist should inform the patient about the risks of any procedure beforehand. It may also be helpful to outline the safety measures the interventional radiology team intend to use.
Patients at higher risk include diabetics and obese individuals. Also, patients who have undergone previous radiation at the same skin location are at increased risk for injury. They should be pre-screened.
Pre-screening should also include patients who take medications that increase photosensitivity. For example, but not limited to:
- Some antibiotics
- NSAIDs
- Diuretics
- Retinoids
The radiologist and the interventional radiology technologists must take special care with pediatric and pregnant patients.
Practice informed consent with pregnant patients. Let them know about the risk of birth defects and even miscarriage. Keep in mind that pediatric patients are more radiosensitive than adults (i.e., the cancer risk per unit dose of ionizing radiation is higher). Pediatric patients have a long life ahead of them and more time for cancers to form. They are not small adults. They are children. Image Gently®.
Safety Measures During the Procedure
Notification levels of threshold radiation used should be set by the interventional radiologic imaging team. That’s a way to ensure minimum doses are used throughout the procedure.
This is especially important for patients who were pre-screened for risk of skin injury, pregnancy, and age. For pregnant women or pediatric patients, the radiologist should make tools available like shields and imaging protocols to help him or her select the right dose.
Regular inspections must be performed to ensure procedure notifications are working, . The dose-measuring program should be re-calibrated when necessary and calibration factors should be considered in notification levels during the procedure.
Lastly, the radiologist should practice a high level of awareness about dosing. At all times, he should know the current dose rate. He should also know the total dose utilized so far.
Want more information about managing radiation dose during fluoroscopy procedures? Check out the 10 steps to manage radiation dosing.
Safety Measures After the Procedure
The radiologist should first record and review dose data after each fluoroscopy procedure. This may include:
- Fluoroscopy time
- Kerma area product
- Reference air kerma
This information should be reviewed regularly. This is especially important before their next fluoroscopy procedure.
Patient data should then be transformed into an FDS. The radiologist should compare the FDS to advisory data sets. For example, the RAD-IR study of total dose and skin dose.
The facility should also have a reference for SRDL (ideally 5Gy). If notification levels surpassed the threshold reference air kerma during a procedure? The radiologist must follow-up with that patient. The patient should also scheduled for a follow-up within 4 weeks.
The peak skin dose for the procedure in which they surpassed SRDL should be recorded. Include patient table height in this estimation as well as gantry angles for all images taken.
Once above measures are completed, the radiologist might refer the patient to an oncologist. The radiogenic oncologist will address possible skin injuries due to the procedure.
Continuing Education for Radiologists and Interventional Technologists
Radiologists, radiological technologists, interventional technologists and nurses have to complete continuing education courses. It’s important, especially if you take part in fluoroscopy procedures.
That’s where Scrubs Continuing Education comes in. Browse our radiology CE courses today and discover the ARRT® Category A course that’s right for you.
8 Ways X Ray Continuing Education Can Help You with X Ray Tech Jobs
There’s been a major increase in job availability for folks who work in the medical field, including a significant increase for x-ray technologists — the field is expected to grow by 13 percent by the year 2026.
Depending on where you live and/or your modality, you may find that the competition is out there for the better jobs.
This is where continuing education can come in handy.
Read on to learn more about the benefits of continuing education and how it can help you increase your chances of getting hired for x-ray tech jobs.
Continuing Education Requirements for X-ray techs
Once you’ve passed your licensing boards and become an x-ray technologist, you’ll need to do continuing education courses on a regular basis. As an x-ray technologist, you’ll need 24 continuing education credits or CEs every two years.
The courses need to have been approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (also known as an RCEEM) for ARRT®.
Benefits of Continuing Education for X-Ray Techs
There are lots of benefits that come with taking continuing education courses while you’re in the process of searching for x-ray tech jobs. The following are some of the greatest benefits you might not have realized:
1. Your License is Active
You need continuing education credits to keep your license current. A lot of people whose jobs require continuing education credits have a tendency to wait until the last minute to complete them.
Finish your CEs sooner than later. By pursuing your continuing education credits now, you’ll be ahead of the game. As a result, you will be able to rest easy knowing that, when the time comes to renew your license, you’ll have already done the hardest part.
2. Increase Chances of Getting Hired
By working on your continuing education courses, you may be more valuable to folks who are looking to hire technologists for their practices.
This shows a dedication to the field. It also shows that you prioritize knowledge and proactivity.
3. Learn About New Technologies
The medical field is always evolving. By making continuing education a priority, you’ll be able to stay on top of these new developments.
This will help you ensure you’re doing things in the most efficient way possible. It’ll also help you to improve your skills as an x-ray tech.
4. Specialize in a Specific Area
There is a lot of flexibility when it comes to deciding which courses you want to take. You may be considering taking the boards for a different modality. You can satisfy your biennium and have the specific credits you need to sit for the boards.
This gives you the opportunity to specialize in a specific area. This, in turn, can make you more marketable and increase your chances of getting hired in the future.
5. Provide Better Patient Care
The more knowledge you have at your fingertips, the better able you’ll be to serve your patients.
As an x-ray tech, you’ll often be working with people who are nervous, in pain, or feeling ill. Don’t you want them to feel as comfortable as possible?
Continuing education courses can teach you new techniques that will allow you to do just this.
6. Increase Your Confidence
You may have passed your course and your licensing exam, but you also know that you are up-to-date with technology and techniques.
Continuing education can help you hone your skills and increase your confidence.
After passing these additional courses, you’ll feel more prepared to take on whatever comes your way on the job.
7. Hit the Ground Running
After participating in continuing education, you may require less on-the-job training.
You’ll have additional skills and will be able to dive in and start working with patients sooner.
Continuing education might also help to minimize the adjustment period you have to go through once you start working in a new practice.
8. Increase Promotion Eligibility
Finally, continuing education courses can help to increase your eligibility for promotions once you do get hired.
You’ll have more knowledge and qualifications on your side, and that’s something that will be appreciated.
If you want to be able to rise through the ranks faster after you start working as an x-ray tech, continuing education can help.
Bonus Tips for Landing X-Ray Tech Jobs
There is definitely a need for continuing education in the healthcare industry, especially for x-ray technologists. Participating in continuing education courses isn’t the only step you can take to increase your chances of getting hired, though.
Some other steps to increase the likelihood that you’ll get hired include:
- Start networking with people in the field early (preferably before you’ve finished your training)
- List references who can vouch for your dependability and credibility
- Present yourself in a professional way (dress, speech, hairstyle, etc.)
- Practice answers to common job interview questions
- Start with part-time work to get your foot in the door
Remember to be persistent in your search, too. It may take time, but if you’re persistent and continue to make an effort to put your best foot forward, you’ll eventually find the right job.
Sign Up for Continuing Education Courses Today
There are plenty of benefits that come with taking continuing education courses.
You’ll have a much easier time getting hired for x-ray tech jobs if you invest in continuing education, and you’ll get the added benefit of extra training and new opportunities to sharpen your skills.
Are you ready to get signed up for continuing education?
If so, check out the courses available on our site today. All of them are either Category A or Category A+ courses, and they’re available at great prices.
If you want to save even more money, be sure to check out our combo specials!
7 Ways Radiology CE Can Benefit You as a Radiologic Technologist
This field of radiologic technology is growing at a rapid rate, too. It’s expected to expand by 13 percent by the year 2026. There are currently more than 200,000 radiologic technologists currently working in the United States.
It’s important that you stay informed about the latest developments in your field, if you’re already working as a radiologic technologist, or if you just completed your certification and are looking for a job, Remain competitive in your field. More people are looking to become radiologic technologists every day.
X-ray CE courses need to be a top priority, especially if you’re still looking for a job. Continue reading to learn more about them and how they’ll benefit you in your search to become a radiologic technologist.
Benefits of Radiology CE Courses
You need CE courses to keep your license current. Participating in CE courses is an essential part of your job as a radiologic technologist.
When you participate in regular CE courses even before you’ve been hired as a radiologic technologist, you can reap a lot of great benefits, including the following:
1. Learn About New Technology and Techniques
Radiology CE courses give you the opportunity to learn about innovations in radiologic technology. You stay informed about the latest machines, trends and older techniques that still work in combination with the new.
Knowledge is power, and the more you know about the field of radiology and the different tools people are using in their practices, the better off you and your patients will be.
2. Maintain Good Professional Standing
Participating in continuing education courses is essential if you want to keep your license current.
In order to maintain good professional standing and make sure you’re in compliance with the law, you need to take these courses seriously.
3. Keep Your Skills Sharp and Upgraded
Continuing education also helps you to maintain and improve your skills as a radiologic technologist.
If you’ve passed your test and earned your certification, you might be convinced that you’ve perfected your technique and have learned all there is to know.
That’s definitely not the case with quickly evolving radiologic technology and techniques. The more you learn, the better you’ll be able to perform your job (once you’re hired) on a daily basis.
4. Become More Marketable
One of the best ways to make yourself more marketable and increase your chances of getting hired is to make sure you’re participating in continuing education courses.
By maintaining your x-ray license certification you show that you’re dedicated to improving your skills and being the best radiologic technologist you can be.
5. Increase Your Chances of Promotions and Raises
Once you get hired as a radiologic technologist, continuing education becomes even more important.
When you participate in these courses, you show your boss that you’re a dedicated employee. This, in turn, can help you to increase your chances of getting raises and promotions.
6. Improve Patient Experience and Outcomes
Continuing education doesn’t just teach you about new technology and techniques. It also teaches you about what you can do to help the patients you see feel more comfortable.
It’s not uncommon for folks to feel anxious or tense when they go in for an x-ray or procedure. By learning new ways to put them at ease, you can improve the patient experience.
Continuing education also helps give you the skills you need toget high-quality images, not having to retake and re-expose the patient to more radiation and making it easier for physicians to correctly diagnose their patients.
7. Reduce Risk and Radiation Exposure
Finally, continuing education also helps you to reduce mistakes and patient radiation exposure.
When you’re working in the medical field, you need to be as close to perfect as possible. As a newly certified radiologic technologist, it’s going to take a lot of extra work for you to get closer to perfection.
Continuing education will help you get there and avoid mistakes that could put your patients at your risk. If you start participating in continuing education now, you’ll have a much easier time performing your job once you do get hired.
FAQs About CE for a Radiologic Technologist
Okay, you can see that it’s important for you to make continuing education a priority if you want to continue to be an effective radiologic technologist.
You probably have some questions about what’s expected of you when it comes to continuing education, though.
Listed below are the answers to some frequently asked questions about CE for radiologic technologists:
How Many Credits Do I Need?
Radiologic technologists need to earn 24 continuing education credits every two years.
The two-year period (known as a biennium) is determined based on your birth month and the year during which you first took your examination to become a radiologic technologist.
It begins on the first day of your birth month and ends on the last day of the month prior to your birth month two years after.
Which Courses Should I Take?
There is a lot of flexibility when it comes to deciding which continuing education courses you are going to take.
However, all courses must have been awarded either Category A or Category A+ approval. This means they’ve been approved and evaluated by the AHRA® or another Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism. Courses must be accepted by ARRT®.
How Much Do Courses Cost?
The price of courses varies quite a bit, too. Most of them cost between $100 and $200, though. If you want to save money on continuing education courses, look for combo options that allow you to purchase multiple courses at once.
Start Your CE Courses Today
Now that you know more about the benefits of taking CE courses and which courses are best for a radiologic technologist, it’s time to go ahead and get signed up.
We have more than one hundred different radiology CE courses available on our site right now.
All of our courses are ASRT®/AHRA® approved for ARRT® for either Category A or Category A+ credits. They’re available at low costs, too and all of them even come with free online testing.
It’s never been easier or more affordable for you to continue your education and work toward becoming the best radiologic technologist possible.
Sign up for a course today!
Why a Combo E-Course Is a Good Fit for Your Radiology CE
If you need radiology CE credits, and if you are looking to satisfy specific requirements for your certification, you might consider a combo e-course.
Sometimes states mandate a few credit hours targeting specific topics within radiology. Maybe 1 book doesn’t cover those specific hours. A Combo could help.
All radiologic technologists must complete their continuing education to stay compliant with regulations set by The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists® (ARRT®) certification program and/or to stay compliant with state requirements.
Why a Combo eCourse Is a good Option for Radiographers
A combo eCourse is a good option for radiographers because the courses meet the required CE credit hours needed for your biennium period. There’s no heavy book to lug around. You can do everything on your computer.
The information is presented electronically which might be a more rewarding experience for the user.
When you order an e-course, you can take your test online, fax in your answer sheet, scan and email your answer sheet, or snail mail your answer sheet.
What Are the Radiology CE Requirements?
It’s mandatory that all radiologic technologists (R.T.®s) complete 24 category A or A+ credits as part of their radiology CE requirements for the biennium.
Are you asking yourself, “What’s a biennium?” Keep reading and you’ll find out.
As mentioned above, it’s a two-year educational period set in place by the ARRT®. Every radiographer is given an ARRT® ID number that’s joined with their birth month, as well as the year he or she passed their licensing exam.
The biennium begins on the first day of your birth month and ends two years later on the last day of the month before your birth month. For example, if you were born in May, you would have to have your credits completed by the end of April.
The good news is that you only need to do this for your entire career, so take advantage of the things you will learn.
How Do I Earn Credits?
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists® has a preset credit amount for you to complete and pass.
You can continue your education through eCourses for hard copy book & test courses. We have all types of online courses and tests, including but not limited to computed tomography, IR and radiology CE courses and credits.
The continuing education courses we provide are reviewed and approved by RCEEMs for ARRT® A or A+ CE credit. If your state has specific requirements regarding your credits, please reach out to your state-governing radiology licensing agency for CEU credit details.
Category A CE Credit Courses:
- Must be approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM)
- A recognized continuing education evaluation mechanism (RCEEM) is an organization that ARRT® has approved to evaluate the content, quality, and integrity of proposed continuing education (CE) activities. Specifically, RCEEMs evaluate an activity’s educational objectives, content relevancy and accuracy, faculty qualifications, and education methods and materials that will be used by radiologic technologists.
Whatever you decide, just know we have the courses you’re seeking!
Radiologic technologists, on the other hand, can study courses in both A and A+ CE categories.
In order for your CE credits to count, you must have completed and passed the 24 hour credit continuing education requirement with a passing grade is a 75 percent or above.
You’ll have three attempts to pass the test. Once you’ve accomplished that, you’ll have completed the course and a “certificate of completion” will be awarded.
When the certificate is emailed or faxed to you, be sure to update ARRT® with your earned credits. Please note: credits can’t roll over to the next biennium term and you cannot take the same course within the same biennium.
To “Ace” the Test…
We get it, looking for course work and study materials to complete your American Registry of Radiologic Technologist® biennium requirement is a lot. Fortunately, we have the radiology and X-ray continuing education credits you need to be compliant.
An eCourse in your field of work, or a package deal with our eCourse combo sets, will help you earn those 24 CE credits fast!
We have the manuals and study materials you need to stay compliant. Your radiology career requires it.
Start knocking out credit requirements today. Place your order for eCourses or regular courses today!
ARRT® Radiology Continuing Education Requirements for the Biennium
ARRT® requires 24 continuing education credits within two years, a period known as a biennium.
Your biennium begins the first day of your birth month and ends on the last day of the month BEFORE your birth month two years later. So, if your birth month is June, you would have to have completed your continuing education credits by the last day of May. You would have to take the test and receive a certificate dated by the end of the month before your birth month the year that your credits are due.
These credits can be completed at anytime during the biennium. Please not that, if you earn more Radiography CE credits than you need during one biennium, the remaining credits cannot carry over into the next biennium.
The Radiology Continuing Education course that you take must be approved by a Recognized Continuing Education Evaluation Mechanism (RCEEM) for ARRT®. Good luck on your test!
Benefits of Taking X-ray Continuing Education Courses
Did you know that x rays were discovered all the way back in 1895? Since then, they have been an integral part of providing premier medical care to people across the world. As you might guess, a tool this complicated requires continuing education credits in order to master.
Not everybody understands what they need to do regarding x-ray continuing education, though. Let’s explore key information about how you can benefit from these types of radiology courses.
Job Security
One of the greatest attributes of continuing education is having better job security. The more extensive your knowledge, the harder you will be to replace. With enough effort, you will become virtually irreplaceable wherever you choose to work.
As you become a more well-rounded professional, you will be more competitive as a potential job candidate. Not only will this make it easier to achieve promotions in the future, but you will also have a much easier time finding a different job, if you’re looking to transition to a different facility later on.
This is something that you should not neglect, as it can have a large impact on your life when it comes to your career.
Higher Salary Potential
One of the most attractive benefits of increased knowledge is an increase in potential salary.
As you gain in experience, your skill set will become much more valuable. This means that employers may be willing to pay higher wages for your services. The difference could potentially be thousands of dollars each year, depending on how much effort you decide to put into continuing education.
Having advanced knowledge allows you to negotiate better wages, if you should ever find yourself in that position. This can ensure that you are properly compensated for the work that you do.
Better Patient Care
Radiology continuing education goes a long way when it comes to providing the best patient care possible.
Continuing education or CE courses primarily focus on refining your technical skills so that you can improve your capabilities and minimize mistakes.
For example, a common dilemma in radiographic positioning is dealing with a patient who is unable to physically get into the correct position to safely and effectively use an x-ray machine. From previous experience to reviewing case studies in radiology CE courses, your expertise will be invaluable. Not only will your patients receive better care, but your performance as a professional will also flourish.
Understanding Current Trends
The medical industry is one of the most fast-paced when it comes to trends and advancements. Continuing education courses are a great way to stay aware of all of the opportunities that present themselves in this field.
For example, the industry is making more extensive use of artificial intelligence as time goes on. Learning about this topic and how it pertains to your work can help make your job easier in the future. As long as you prioritize continuing education, you can be sure to stay on top of trends and make the most of them.
This could easily set you apart from your competitors in a variety of situations.
Increased Professional Opportunities
The more skilled you are, the more opportunities you will encounter as a professional. As previously mentioned, you will have an easier time securing a new role or new position.
The information you learned through continuing education courses can also help you move laterally within the industry. These courses can help you transition to a different role within the radiology department. From there you can begin moving in a different direction in your career, if you wish.
Regardless, having a greater knowledge of your profession and advancements within your field will allow you to navigate more efficiently as your career progresses. In many cases, though, you won’t be able to reach your goals without the right CE credits.
How Do I Get Started?
As you might already know, the first step you need to take is determining what type of courses you need to complete.
There are a variety of continuing education courses for radiology available, and some may be more applicable to your situation than others. Other factors to consider include the total number of hours or credits that you require. This will vary from person to person.
Afterwards, you need to find a reputable course provider. This will assure you that the continuing education you take will count toward the credits that you need.
What Should I Look for in a Provider?
One of the most important details to consider for CE credits is the reputation of the x-ray continuing education provider. You can learn a lot by performing research online. Is the provider approved by your state? Does ARRT® accept the provider’s courses? Does the provider offer courses in your modality or whatever modality you would like to get into?
The radiology continuing education provider you work with should be easy to reach and fully transparent about the process. The provider should prioritize helping you meet your goals.
Don’t Overlook X Ray Continuing Education
X-ray continuing education is one of the most valuable resources you have at your disposal. It can take your career to new heights, make you aware of new technologies, or peak an interest to try something new.
As long as you keep the above information in mind, you’ll be sure to meet your needs. Looking for more information about what we can do? Get in touch with us today to see how we can help.
Mammography Continuing Education Requirements
Did you know that mammograms can successfully identify about 87 percent of women who have breast cancer?
With such a meaningful career, ensuring you have everything you need to succeed is essential. Not only does it help keep your job safe, but it helps keep your patients and their well-being safe. What kind of continuing education do you need to succeed?
Luckily, we’re here to help you get started. Read on to learn more about mammography continuing education.
Do You Need a Certification to Perform Exams?
You don’t necessarily need mammography certification to perform these exams, but you do need to meet a few guidelines. Remember, you’ll need to at least have a general certification in radiographic technology.
What other requirements do you need to meet, though?
Requirements to Work as a Mammography Technologist
The FDA’s mammography technologist employment regulations first came into effect on April 28, 1999. They outline what needs to be done to become a mammography technologist, and also to stay a mammography technologist. Here’s what you need to know.
License or Board Certification
You’ll either need a mammography certificate or a state license to perform any radiographic procedures. You can get certified by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists® (ARRT®).
Initial Training
You’ll need to complete at least 40 hours of initial training to qualify for mammography technologist work. Here are a few of the things this training will require:
- Breast anatomy and physiology
- Special techniques for imaging those with breast implants
- Breast positioning and compression
- Other techniques for quality assurance
You’ll also need to complete at least 25 supervised mammograms. The time you spend on these can count toward the overall 40-hour total you’ll need for certification. If you’re a technologist that happened to qualify for certification before the guidelines were put into place on April 28, 1999, these guidelines don’t apply to you.
Continuing Experience
Next, for continuing experience, you’ll need to have completed at least 200 mammograms over the 36 months preceding the facility’s annual MQSA inspection.
Another thing to note is that any credits you earned during the initial application training at your facility can be used for both MQSA and FDA requirements. That doesn’t mean they apply to your state and ARRT® requirements, though, so it’s important to pay attention. For example, you can only apply eight CE hours of initial training towards your certification per biennium.
Continuing Education
In order to meet the MQSA ongoing education requirements, you must earn 15 mammography credits every three years. Whether digital or analog, these credits will count toward your final requirements.
There is, however, an initial one-time digital requirement needed prior to performing digital mammography exams. You’ll need eight hours of training to meet this qualification.
How to Know When Your Credits Are Due
The best way to know when your CE credits are due is to check with your facility supervisor. They’ll know the date of your upcoming MQSA inspection, and they’ll be able to help plan what you need to pass.
Typically, MQSA inspectors will count your credits starting 36 months prior to the date of the annual inspection. Others, however, may use a quarterly reporting system. This can affect your timeframe, which is why it’s essential to speak with your facility supervisor in advance.
The earlier you can meet these requirements, the more peace of mind you can have when the inspection occurs.
Documentation You Will Need
At the time of your inspection date, there are a few documents you’ll need to be able to provide.
This will include your state license, board certification, certificates of completion for your 15 credit hours, and documentation of your initial training period. You’ll also need to have the documentation proving you’ve met the MQSA continuing experience requirement. This means proof that you’ve performed at least 200 mammograms in the 36 months prior to the inspection.
What Happens if You Fail to Meet Requirements?
There are a few different things which can cause you to fail to meet the requirements of, and it can affect your work life. To start, you’ll immediately have to stop completing unsupervised mammograms. Then it depends on the requirement you failed to meet.
Continuing Experience
To meet the MQSA’s continuing experience requirement, you’ll need to perform at least 25 supervised mammography exams under direct supervision. Once you’ve completed this with a qualified mammography technologist, you’ll be permitted to begin unsupervised exams again.
Continuing Education
To start, you’ll need to earn 15 credits to meet the requirement. Until this happens, you won’t be able to perform any mammography exams while unsupervised. ARRT® requires 24 continuing education credits every 2 years, or every biennium, to keep the certification in good standing.
Before the FDA’s final guidelines were put into place, technologists could continue performing exams for 90 more days while completing their required CE credits. Once the final regulations were put into place, however, this was no longer the case.
Don’t Delay Your Mammography Continuing Education
When it comes to mammography continuing education, it’s best not to delay. While the MQSA requirements can seem daunting, they’re essential for helping you help patients. ARRT®’s requirements will help with learning about new equipment, techniques and patient care.
Luckily, you don’t have to do it all alone. We can help you get started. Check out our courses today to learn more.
5 Benefits of Continuing Radiology Education
The healthcare industry is expected to create around 4 million jobs by the year 2026. Presently there are around 250,000 radiologic technologists working in the U.SA. One important thing for your job security as a radiologic technologist or other professional in medical imaging is continuing radiology education.
Radiology continuing education may be considered something that must be done to meet licensing requirements. This is important but may not provide a lot of motivation to become a life-long learner.
There are many other ways radiology CE can benefit you and others which is why you may consider going above and beyond simply meeting the minimum requirements to stay licensed.
Interested? Keep reading to learn about just five of the benefits you can gain by pursuing radiology continuing education courses.
1. Keep Up with Current Trends
The medical field is constantly changing. But if you aren’t actively seeking information about what’s new, you may miss a lot of chances to know what’s available.
Some new technological advances that all radiologic technologists should be aware of include:
Smart Algorithms
Artificial intelligence (AI) has gained a lot of momentum in the medical field, but still has a long way to go. There has been a lot of work done in creating smart algorithms to help with surgical techniques and track follow-up recommendations which helps patients and medical staff.
When you are up-to-date, you can help your clinic or hospital stay on the cutting edge of technology. This will provide benefits to the hospital as well as patients.
2. Have Job Security
The medical field continues to offer some of the best job security compared to other industries, and keeping up with your credentials will help ensure that you stay relevant, so you’ll always have a job.
Through continuing education. you may seek to fulfill requirements to be eligible to find a parallel position in medical imaging and learn about new modalities. That would make you a more valuable employee demonstrating flexibility. Opportunities are there. For example, check out CT, MRI, Nuclear Medicine, Mammography and more.
3. Increase Income
In addition to having security in your job, you may find yourself able to make even more money following the completion of certain continuing education courses.
This is because you can gain additional skills and knowledge which makes you more valuable to your employer. As you bring more to the table, an employer is willing to spend more money to prevent you from looking elsewhere for work.
You may also be able to take on different roles within your current place of work that are higher-paying. This could include stepping up into more management-based positions which typically pay more than basic radiology positions.
4. Create More Opportunities
While CE can create plenty of opportunities for you within your current workplace, it will also allow you to seek opportunities elsewhere, if that’s something you want to do.
When looking for another job having various continuing education courses listed on your resume may be a quick way to impress a potential new employer who may be looking for people who have a strong desire to keep learning. That alone may get you in for that interview.
5. Provide Better Patient Care
Medical personnel help patients in their most needy moments. Whether a radiology CE course focuses on improving your technical skills or patient care, you can use what you learn to provide the best possible care to every patient that comes in.
For example, proper patient positioning is an essential aspect of radiology. However, let’s say you have a patient with a unique situation that doesn’t allow them to get into the right position for the x-ray they need. If you’ve taken continuing education courses on patient positioning, you’ll be prepared with several other options for ensuring you get the angles you need to help diagnose a patient.
Ready to Get Started with Continuing Radiology Education?
Now you know five of the benefits you can gain by taking radiology continuing education courses.
By becoming a life-long learner, you will increase your chances of keeping or finding a well-paying and secure position. You can also improve patient care which could save lives.
If you’re ready to get started, check out our radiology courses. You can take them online which allows you to go at your own pace in your own place. Save money, too, by checking out courses that are currently on sale!
How to Maintain Your X-Ray License in California
Is Radiologic Technology the Right Job for You?
The healthcare industry is expected to create around 4 million jobs by the year 2026.
With so much growth in this industry, it’s a great field to look into for future job opportunities. Along with growth, this field has several opportunities for advancement, as well as many positions that offer great benefits.
If you’re interested in entering the medical field and aren’t sure which job is right for you, why not consider a job as an x-ray technologist.
X-ray technologists get to work with the imaging equipment while interacting with patients regularly.
Keep reading to learn more about what an x-ray technologist does, how to become one, and how to maintain your x-ray license!
How Many Hours Are Needed to Maintain Your X-Ray License?
After an x-ray technologist has earned their certification, they must continuously renew it throughout their professional career. It sounds like it’s hard, but it’s not and you have the opportunity to learn new technologies, new imaging techniques and possibly move on to a different modality within the radiology department.
To renew your license or certification you must satisfy biennial recertification requirements. The ARRT® requires the x-ray technologist to complete an additional 24 continuing education credits every two years. This recertification process ensures that the individual is up to date on their knowledge and have the information necessary to do their job well.
Continuing Education Requirements Specific to California
Most states require licensure to become an x-ray technologist before starting a job while others don’t.
The State of California has specific requirements for radiology continuing education. Below is the summary.
Radiography – 24 hours in two-year period, 4 of which shall be in digital radiography
Limited – 24 hours in two-year period, 4 of which shall be in digital radiography
Mammography – 24 hours in two-year period: 10 of which must be in mammography
Certified Supervisors and Operators – 10 hours in two-year period
Fluoroscopy — 4 hours in radiation safety in two-year period
Fluoroscopy Certified Supervisors and Operators – 10 hours in two-year period, 4 of which shall be in radiation safety
Radiology continuing education courses must be in subjects related to the application of x-ray to the human body and may include x-ray administration, x-ray management, x-ray pathology, x-ray diagnosis and x-ray quality control. Courses in Ultrasound, MRI, CPR and topics not related to the application of x-ray s to the human body cannot be accepted.
Visit the California Department of Health website to see the complete requirements. https://www.cdph.ca.gov/Programs/CEH/DRSEM/CDPH%20Document%20Library/RHB/Certification/RHB-CEC-Renewal.pdf
After the individual has completed the credits, they’re required to keep the records for at least four years.
These documents must be made available to the RHB (Radiologic Health Branch), if reqested. Random audits are performed by California.
Aside from providing the x-ray technologist with up-to-date information, recertification is also necessary for staying in compliance with the Code of Ethics. The Code of Ethics is endorsed by The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists®.
A Closer Look at Recertification
Certified Radiologic Technologists (CRTs) need to earn 24 Category A or A+ CE credits for recertification of which four credits must be in digital radiography. These should be taken in the two years immediately preceding the expiration date on their permit.
Fluoroscopy Radiation Safety Mandatory Courses
Fluoroscopy permit holders have ADDITIONAL requirements. • CRTs with a permit are required to earn 24 approved continuing education credits; four of which are required to be in fluoroscopy radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy. [17 CCR 30403(a)(2)]. • PA with a permit will need to earn 24 approved continuing education credits; four of which are required to be in fluoroscopy radiation safety for the clinical uses of fluoroscopy.
California has taken the lead in requiring fluoroscopy radiation safety. Fluoroscopy is a dynamic visualization of the patient’s body functions and is an excellent diagnostic tool, but it also increases the patient’s radiation dose. Staying informed about fluoroscopy radiation safety is key for patient and staff safety during fluoroscopic procedures.
The Department accepts ARRT® 24 Hr. CE credits, if the certificate was issued within the two years immediately preceding the expiration date of the certificate or permit. These can include, but are not limited to the following modalities:
• Mammography* • Computerized Tomography • Bone Densitometry • Vascular-interventional Radiography • Cardiac-interventional Radiography • Interventional Radiology *Radiologist Assistant • Radiation Therapy
The ARRT® requires CE credits to be earned during the biennium ending on the last day of the month before the individual’s birth month. Technologists who are already certified and registered in one discipline but choose to become certified and registered in another discipline will maintain the CE schedule from their original discipline.
Stay up to date with new research, technology, and availability of jobs. It’s important. As professionals, one of the best things we can do is continually grow. It’s time to start looking at courses to satisfy those CE credits, so contact us to get started!
Why is Radiographic Positioning Important to Radiography?
What Is Radiographic Positioning?
Standard anatomical positioning ensures a universally understood description when imaging the body. Imagine a person standing up straight with their arms outstretched and palms facing forward.
Posterior refers to the back half of the body. Anterior means that a structure is closer to the front half of the body. For example, the tip of your nose is anterior to the back of your head. Structures that are farther from the bottom of your toes are said to be superior anatomically. Inferior is defined as being lower in position. Lateral and distal structures stray from the midline. Medial and proximal ones stay central.
Radiographic Projection
The final image depends on the direction and angle that the x-ray passes through the body.
Anteroposterior (AP) projections enter the body through the front of the chest and leave through the back. Posteroanterior (PA) projections, logically, do the opposite. Projections going from side-to-side or diagonally are lateromedial and oblique, respectively.
Things to Consider Before Taking That X-ray
There are several factors to consider when deciding which is the best radiographic position and projection to use.
Before proceeding with the X-ray consider:
- Who is the patient?
- What is their presentation?
- What is the diagnostic differential?
- What is the patient’s history
- Are there any special factors? (disability, pregnancy, etc)
- What resources are available?
Chest X-rays
Chest x-rays are among the most common procedures in medicine. They can show evidence of pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD), lung cancer, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and many other disorders.
PA and lateral chest x-rays are often prescribed when lung or heart disease is suspected.
PA projection on film appears as if the patient is facing you. Their right side will correspond to your left. A lateral view is useful because two structures that are ‘behind’ one another may superimpose on a PA view and become indistinguishable.
Abdominal X-rays
PA and AP can be used to investigate intestinal obstruction independently or may be used in conjunction particularly with obese patients.
Shoulder X-ray Views
The shoulder joints consist of various bones, tendons, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, and other structures in a confined area. Shoulder x-rays are often ordered in conjunction with CT or MRI scans. This is useful in patients with suspected trauma, shoulder pain, arthritis, or restriction of movement.
The AP view has proven to be useful for visualizing the glenohumeral joint, clavicle, superior ribs, and proximal humerus. The lateral view best demonstrates any suspected shoulder dislocation. Other shoulder x-ray views are indicated for certain trauma patients. A common one in these patients is called the modified trauma axial projection.
The Garth projection is a modification of this view specifically when glenohumeral dislocations are suspected. Others include the Grashey (AKA the true AP view) view, the Neers view, the axillary view, and the Stryker view.
Radiation Protection
Whatever case you are working on and whatever positioning view you use, always keep radiation protection in mind. When you position properly, when you use the correct view, you are more likely to get the best image and not have to subject the patient to another x-ray and more radiation. Also, “child size” your x-rays for children. Image gently. They are not small adults. Their cells are reproducing at a rapid pace and they have their whole life ahead, so the least amount of radiation is important for their medical imaging.
Continuing Education in Radiology
The field of radiology, like the vast majority of medical specialties, is highly competitive and continuously evolving. Things that were taught 10 years may now be outdated.
The best way to stay competitive professionally and improve the care you provide for your patients is to seek to improve your knowledge and ability through continuing education. You can earn CE and CME credits through these courses and even take online courses and tests for X-ray, CT, MRI, and other imaging modalities.
Radiographic Positioning, Radiation Safety, Radiography Continuing Education
A common dilemma in radiographic positioning is dealing with a patient who is unable to physically get into the correct position to safely and effectively use an x-ray machine. From previous experience to reviewing case studies in radiology CE courses, your expertise will be invaluable. Not only will your patients receive better care, but your performance as a professional will also flourish.
There are always certain things to consider when choosing the most appropriate radiographic positioning for each patient. This will depend on the particular characteristics of your patient, such as age and body type, the current condition, the part of the body to be evaluated, and the availability of imaging modalities in your health center.
Radiographic positions will always be important to know. They could make the difference between making and/or missing a crucial diagnosis, or having to subject your patient to another x-ray and more radiation.
We invite you to contact us if you are interested in advancing in the radiology field or just wanting to comply with ARRT®’s continuing education requirements. We have many options and special deals for all levels.